Handling Out Of Range Errors
Your code should respond to Out of Range errors to provide uninterrupted data. This page will guide you through the different ways to handle these errors.


This revision of the TMP1200 differs from the _0 revision in the following ways:
The TMP1200 allows you to precisely measure temperature using RTDs, thermistors, and other resistance-based sensors. A resistance temperature detector (RTD) measures subtle temperature changes using a resistance of the element made of a pure metal (usually platinum). The resistance value will change in a precise and repeatable way. The RTD Phidget measures these subtle resistance changes, so you can get the most accurate temperature measurements. This Phidget connects to your computer through a VINT Hub.
This Phidget is a smart device that must be controlled by a VINT Hub. For more information about VINT, have a look at the VINT Overview page. You can use a Phidget Cable to simply and easily connect the two devices. Here's a list of all of the different VINT Hubs currently available:
| Product | Board Properties | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part Number | Price | Number of VINT Ports | VINT Communication Speed Max | Controlled By |
 VINT Hub Phidget
|
$40.00 | 6 | 1 Mbit/s | USB (Mini-USB) |
 1-Port VINT Hub Phidget
|
$24.00 | 1 | 1 Mbit/s | USB (USB-A) |
 VINT Hub Phidget
|
$35.00 | 6 | 1 Mbit/s | USB (Mini-USB) |
 VINT Hub Phidget
|
$30.00 | 6 | 100 kbit/s | USB (Mini-USB) |
 Wireless VINT Hub
|
$60.00 | 6 | 100 kbit/s | Local Network (Ethernet or Wi-Fi) |
 PhidgetSBC4
|
$120.00 | 6 | 100 kbit/s | — |
Here's a list of RTDs you can use with the TMP1200:
| Product | |
|---|---|
| Part Number | Price |
 PT1000 4-Wire RTD 11cm
|
$40.00 |
 PT1000 4-Wire RTD 20cm
|
$40.00 |
Use a Phidget cable to connect this device to the hub. You can solder multiple cables together in order to make even longer Phidget cables, but you should be aware of the effects of having long wires in your system.
| Product | Physical Properties | |
|---|---|---|
| Part Number | Price | Cable Length |
 Phidget Cable 10cm
|
$1.50 | 100 mm |
 Phidget Cable 30cm
|
$1.75 | 300 mm |
 Phidget Cable 60cm
|
$2.00 | 600 mm |
 Phidget Cable 60cm
|
$2.00 | 600 mm |
 Phidget Cable 90cm
|
$2.00 | 900 mm |
 Phidget Cable 120cm
|
$2.25 | 1.2 m |
 Phidget Cable 150cm
|
$2.50 | 1.5 m |
 Phidget Cable 180cm
|
$2.75 | 1.8 m |
 Phidget Cable 350cm
|
$3.00 | 3.5 m |
 Phidget Cable Kit
|
$10.00 | 80 mm |
 Phidget Cable Extension Wire 22AWG
|
$0.75/Meter | — |
The TMP1200 allows you to precisely measure temperature using RTDs, thermistors, and other resistance-based sensors. Measure temperature from your RTD in degrees Celsius by selecting the RTD type and the number of wires in the software. You can also read thermistors and other resistive sensors by using the resistance sensor object in your program. You'll receive the data in ohms and can convert to the desired unit by using the formula in your sensor's datasheet. You could even use it as a simple ohmmeter for resistances up to 19 kΩ.
You can use your Control Panel to explore your Phidget's channels.
1. Open your Control Panel, and you will find the following channels:
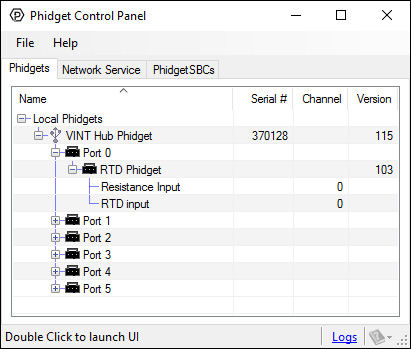
2. Double click on a channel to open an example program. Each channel belongs to a different channel class:
In your Control Panel, double click on "Resistance Input":
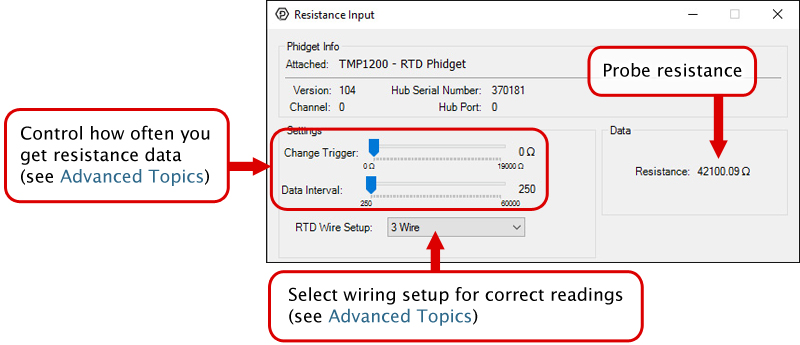
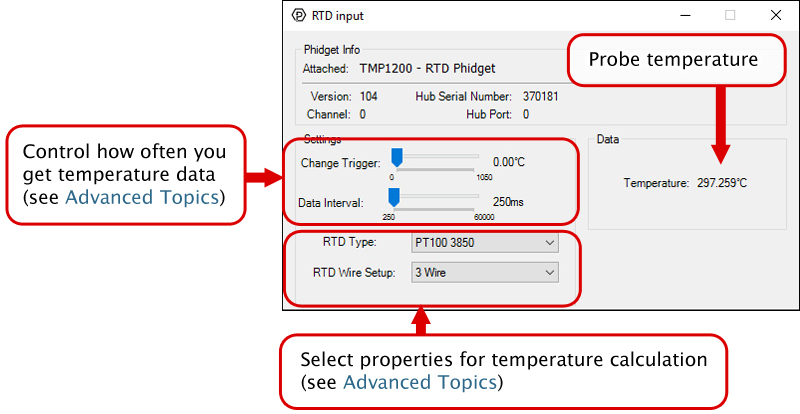
In your Control Panel, double click on "RTD Input":
Before you open a Phidget channel in your program, you can set these properties to specify which channel to open. You can find this information through the Control Panel.
1. Open the Control Panel and double-click on the red map pin icon:
2. The Addressing Information window will open. Here you will find all the information you need to address your Phidget in your program.
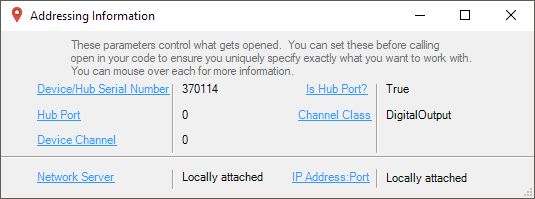
See the Phidget22 API for your language to determine exact syntax for each property.
The Change Trigger is the minimum change in the sensor data needed to trigger a new data event.
The Data Interval is the time (in ms) between data events sent out from your Phidget.
The Data Rate is the reciprocal of Data Interval (measured in Hz), and setting it will set the reciprocal value for Data Interval and vice-versa.
You can modify one or both of these values to achieve different data outputs. You can learn more about these properties here.
Note: Graphing and logging is currently only supported in the Windows version of the Phidget Control Panel.
In the Phidget Control Panel, open the channel for your device and click on the ![]() icon next to the data type that you want to plot. This will open up a new window:
icon next to the data type that you want to plot. This will open up a new window:
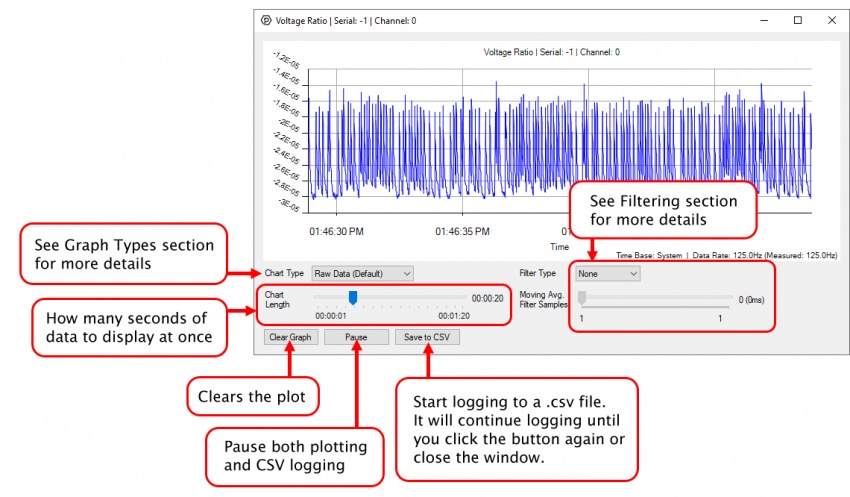
If you need more complex functionality such as logging multiple sensors to the same sheet or performing calculations on the data, you'll need to write your own program. Generally this will involve addressing the correct channel, opening it, and then creating an Event Handler and adding graphing/logging code to it.
The quickest way to get started is to download some sample code for your desired programming language and then search google for logging or plotting in that language (e.g. "how to log to csv in python") and add the code to the existing change handler.
You can perform filtering on the raw data in order to reduce noise in your graph. For more information, see the Control Panel Graphing page.
You can perform a transform on the incoming data to get different graph types that may provide insights into your sensor data. For more information on how to use these graph types, see the Control Panel Graphing page.
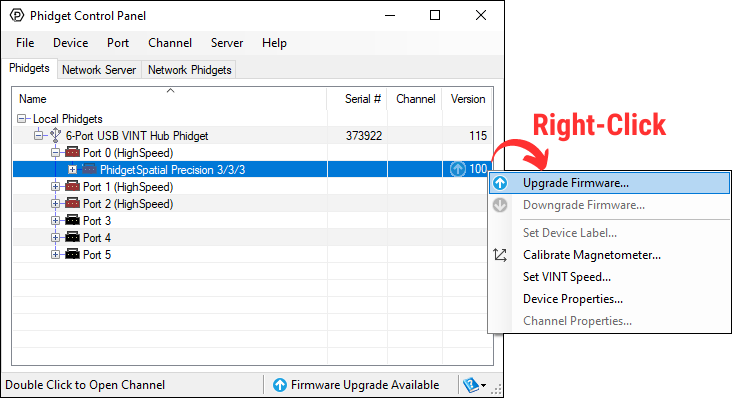
Firmware Upgrade
MacOS users can upgrade device firmware by double-clicking the device row in the Phidget Control Panel.
Linux users can upgrade via the phidget22admin tool (see included readme for instructions).
Windows users can upgrade the firmware for this device using the Phidget Control Panel as shown below.
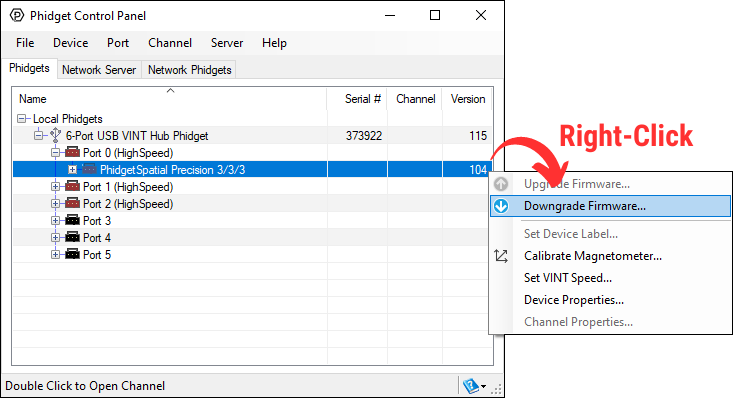
Firmware Downgrade
Firmware upgrades include important bug fixes and performance improvements, but there are some situations where you may want to revert to an old version of the firmware (for instance, when an application you're using is compiled using an older version of phidget22 that doesn't recognize the new firmware).
MacOS and Linux users can downgrade using the phidget22admin tool in the terminal (see included readme for instructions).
Windows users can downgrade directly from the Phidget Control Panel if they have driver version 1.9.20220112 or newer:
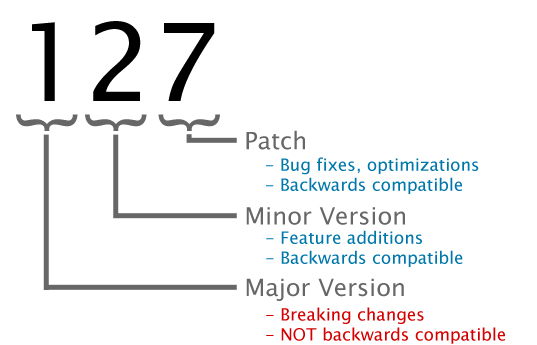
Firmware Version Numbering Schema
Phidgets device firmware is represented by a 3-digit number. For firmware patch notes, see the device history section on the Specifications tab on your device's product page.
If your device has a ![]() icon printed on the enclosure, it means that it has an improved filter on its VINT connection that upgrades performance when plugged into a port on a VINT Hub that also has the
icon printed on the enclosure, it means that it has an improved filter on its VINT connection that upgrades performance when plugged into a port on a VINT Hub that also has the ![]() icon:
icon:
For details on how the maximum cable length is impacted, see the specifications tab on the product page for this device.

This is the simplest wiring setup for an RTD, but also the least accurate because the resistance of the leads are not taken into account. To connect a 2-wire RTD to the RTD Phidget, connect one wire to the RTD+ terminal, and the other to the RTD- terminal. Then connect the EXC+ terminal to the RTD+ terminal and the EXC- to the RTD- terminal with two short wires.
In your program, set RTDWireSetup to 2-wire mode. In the Phidget22 API select the TMP1200 and your programming language of choice to see exact naming conventions.

In a three-wire RTD, the extra wire is added to measure the resistance of one of the leads. This calculation assumes that both leads have the same resistance. Your RTD should have two wires that share a color; connect one of these wires to the RTD- terminal and the other to the EXC- terminal. The differently colored wire connects to the RTD+ terminal. Then connect the EXC+ terminal to the RTD+ terminal with a short wire.
In your program, set RTDWireSetup to 3-wire mode. In the Phidget22 API select the TMP1200 and your programming language of choice to see exact naming conventions.

A four-wire RTD is normally used in precision measurement, when the assumption that both leads have the same resistance is not accurate enough. Unfortunately the RTD Phidget does not support this particular feature of four-wire RTDs. It does support the use of four-wire RTDs using the same assumption as three-wire mode. To connect a four-wire RTD, simply connect one pair of same-colored wires to the RTD+ and EXC+ terminals, and the other pair to the RTD- and EXC- terminals.
In your program, set RTDWireSetup to 4-wire mode. In the Phidget22 API select the TMP1200 and your programming language of choice to see exact naming conventions.
In three and four wire modes, this device will measure the line resistance every 5 minutes. This measurement will cause a delay in measurement for data intervals of less than 500ms. To force the line resistance to be recalculated, you must close and re-open the device.
| Board Properties | |
|---|---|
| Controlled By | VINT |
| VINT Communication Speed Max | 1 Mbit/s |
| Resistance Input | |
| Maximum Measurable Resistance | 5 kΩ |
| Resistance Noise (PT100 Mode) | 17 mΩ |
| Resistance Noise (PT1000 Mode) | 47 mΩ |
| Resistance Resolution | 1 mΩ |
| RTD Input | |
| Temperature Error Max | * 0.2 °C |
| Sampling Interval Min | 333 ms/sample |
| Sampling Interval Max | 60 s/sample |
| Electrical Properties | |
| Current Consumption Max | 3 mA |
| Physical Properties | |
| Recommended Wire Size | 16 - 26 AWG |
| Operating Temperature Min | -30 °C |
| Operating Temperature Max | 85 °C |
| Customs Information | |
| Canadian HS Export Code | 8471.80.00 |
| American HTS Import Code | 8471.80.40.00 |
| Country of Origin | CN (China) |
* - The maximum temperature error varies depending on the RTDType and temperature. See the table below:
| RTDType | Below 300ºC | Above 300ºC |
|---|---|---|
| PT100 | 0.1 ºC | 0.2 ºC |
| PT1000 | 0.02 ºC | 0.2 ºC |
| Date | Board Revision | Device Version | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| August 2017 | 0 | 104 | Product Release |
| January 2018 | 0 | 105 | Increased maximum change trigger |
| January 2018 | 0 | 106 | Library bug fixes |
| March 2020 | 0 | 107 | Fixed bug where wire resistance could be NaN |
| April 2020 | 0 | 108 | Fixed equations. Added internal calibration (only for new TMP1200) |
| December 2021 | 0 | 109 | Fixed bug that blocked sensor data at higher data intervals |
| December 2021 | 0 | 110 | Fixed bug that caused unusual readings when device is rapidly unplugged and replugged |
| April 2022 | 0 | 111 | Fixed calculation error for 3 and 4-wire mode |
| January 2022 | 1 | 300 | Hardware changes; Improved accuracy, minimum data interval increased to 333ms, , added |
| May 2023 | 1 | 301 | Added support for auto-setSpeed |
| January 2024 | 1 | 302 | DataInterval now consistent even when RTD is disconnected |
| Channel Name | API | Channel |
|---|---|---|
| RTD input | TemperatureSensor | 0 |
| Resistance Input | ResistanceInput | 0 |
| API | Detail | Language | OS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TemperatureSensor | Visual Studio GUI | C# | Windows | Download |
| TemperatureSensor | JavaScript | Browser | Download | |
| TemperatureSensor | Objective-C | macOS | Download | |
| TemperatureSensor | Swift | macOS | Download | |
| TemperatureSensor | Swift | iOS | Download | |
| TemperatureSensor | Visual Basic | Windows | Download | |
| TemperatureSensor | Max | Multiple | Download | |
| ResistanceInput | Visual Studio GUI | C# | Windows | Download |
| ResistanceInput | JavaScript | Browser | Download | |
| ResistanceInput | Objective-C | macOS | Download | |
| ResistanceInput | Swift | macOS | Download | |
| ResistanceInput | Swift | iOS | Download | |
| ResistanceInput | Visual Basic | Windows | Download | |
| ResistanceInput | Max | Multiple | Download |