Analog Input Guide: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
* Phidget InterfaceKits such as the [{{SERVER}}/products.php?product_id=1018 1018 - PhidgetInterfaceKit 8/8/8] have multiple voltage inputs. | * Phidget InterfaceKits such as the [{{SERVER}}/products.php?product_id=1018 1018 - PhidgetInterfaceKit 8/8/8] have multiple voltage inputs. | ||
* The ports on a Phidget {{VINTHub}} can be used to read sensors like an analog input. See the page on [[ | * The ports on a Phidget {{VINTHub}} can be used to read sensors like an analog input. See the page on [[Phidgets Connectors]] for more information | ||
* Some VINT devices like the [{{SERVER}}/products.php?product_id=DAQ1000 DAQ1000] add analog inputs to your VINT Hub. | * Some VINT devices like the [{{SERVER}}/products.php?product_id=DAQ1000 DAQ1000] add analog inputs to your VINT Hub. | ||
Revision as of 20:00, 10 April 2017
Analog Inputs are used to interface many different types of sensors, such as temperature, humidity, position, or pressure sensors. There are three classes of Phidget products that can be used with these sensors:
- Phidget InterfaceKits such as the 1018 - PhidgetInterfaceKit 8/8/8 have multiple voltage inputs.
- The ports on a Phidget VINT Hub can be used to read sensors like an analog input. See the page on Phidgets Connectors for more information
- Some VINT devices like the DAQ1000 add analog inputs to your VINT Hub.
Each analog input provides power (Nominal +5VDC), ground, and an analog voltage return wire driven by the sensor to some voltage. The Interface Kit continuously measures this return voltage and reports it to the application.
Phidgets offers a wide variety of sensors that can be plugged directly into the board using the cable included with the sensor.
Mechanical Specifications

Each analog input uses a 3-pin, 0.100 inch pitch locking connector. Pictured here is a plug with the connections labeled.
The Phidget cables that are designed to plug into these inputs can be found here.
The connectors and pins they use are also commonly available (usually through digikey) - refer to the table below for manufacturer part numbers.
| Manufacturer | Part Number | Description |
| Molex | 50-57-9403 | 3 Position Cable Connector |
| Molex | 16-02-0102 | Wire Crimp Insert for Cable Connector |
| Molex | 70543-0002 | 3 Position Vertical PCB Connector |
| Molex | 70553-0002 | 3 Position Right-Angle PCB Connector (Gold) |
| Molex | 70553-0037 | 3 Position Right-Angle PCB Connector (Tin) |
| Molex | 15-91-2035 | 3 Position Right-Angle PCB Connector - Surface Mount |
Electrical Specifications
The maximum total current consumed by all analog inputs should be limited to 400mA. The voltage measurement is represented in the software through the Voltage property as a value between 0 and 5 volts. 5V corresponds to a high sensor value, and 0V corresponds to zero sensor activity.
The analog inputs on Phidgets InterfaceKits are designed for a maximum of 5V. More than this will cause unpredictable behaviour and could damage the board.
VoltageInput and VoltageRatioInput
Each analog input can be opened as either a VoltageInput object or a VoltageRatioInput in software.
If you are using a sensor whose output changes linearly with variations in the sensor’s supply voltage level, it is said to be ratiometric, and you should use the VoltageRatioInput object. Most of the sensors sold by Phidgets are ratiometric (you can find this in the specification table on the product page for your sensor). Opening the input as a VoltageRatioInput causes the reference to the internal Analog to Digital Converter to be set to the power supply voltage level. The VoltageRatio property ranges from 0.0 to 1.0, which denotes the ratio of the sensor voltage to the supply voltage. For example, if the supply is 5V and the sensor is outputting 2.5V, the VoltageRatio will be 0.5.
If you open the input using the VoltageInput object, the ADC reference is set to a 5.0V 0.5% stable voltage reference. This will allow you to correctly interface with sensors that output a set voltage range regardless of variations in the power you supply to it.
Trying to read a sensor using the wrong software object will result in incorrect readings.
Factors that can affect Accuracy
- High Output Impedance - Sensors that have a high output impedance will be distorted by the input impedance of the analog input.
If your output impedance is high, it is possible to correct for this distortion to some extent in your software application.
- Voltage Drop - Phidget cables have some resistance, which can cause voltage to drop across particularly long lengths of cable. For ratiometric sensors in particular, this can affect accuracy. Long cables also potentially expose the line to a greater amount of interference from surrounding electronics.
- Intrinsic Error In Sensors - For many sensors, the error is quite predictable by testing it alongside a more accurate sensor, and can be calibrated out in software.
- Voltage Reference - Voltage Reference error. The 5.0VDC voltage reference is accurate to 0.5%.
This can be a significant source of error in some applications, but can be easily measured and compensated for.
Changing the Data Interval
You can change the data interval for each VoltageInput or VoltageRatioInput object in software.
For analog inputs, 8 ms is the maximum transmission rate. This limit is set by the USB processor we use, so there isn't much you can do to get around it.
For values less than 8 ms, the data interval sets the sampling rate, not the transmission rate. If, for example, you set the data interval to 1ms, you will receive a packet containing 8 miliseconds worth of 1 ms samples every 8ms. Setting the data interval to 1, 2, or 4ms will not allow you to react to received sensor data any faster than every 8ms; You will simply get more data samples within the 8ms. This feature is useful if you need to log sensor data at less than 8 ms resolution but don't need to react to it in real-time.
Setting the data interval of the analog inputs is (in some ways) an alternative to setting the change trigger. For details on how these two properties interact with one another, have a look at the Data Interval/Change Trigger page.
There is also a limit as to how many channels can be set at a high sampling rate, since you will, at one point run out of bandwidth. We estimate that you can set up to 4 channels to 1ms or you could set all channels to 2ms. You can't turn channels off entirely to save bandwidth, you can only set them to a longer data interval. You will get an error when you exceed the available bandwidth, warning you of lost data samples.
Note that data interval is limited to at most 16ms when opening over the Phidget Webservice. Actual data interval will depend on network latency.
The method to change data interval is slightly different in each programming language; see the Phidget22 API for more information.
Changing the Change Trigger
You can change the change trigger of a sensor using the VoltageChangeTrigger or VoltageRatioChangeTrigger properties in software. You can think of change trigger as a minimum amount of change in voltage needed to register a change event in software. Whenever your sensor generates a new value, it will be compared to the change trigger. If the difference between the last triggered data point and the new data point is less than the change trigger value, no event will be generated.
Setting the change trigger of an analog input is an (in some ways) an alternative to setting the data interval. For details on how these two properties interact with one another, have a look at the Data Interval/Change Trigger page.
The method to change the change trigger is slightly different in each programming language; see the Phidget22 API for more information.
Connecting non-Phidget devices to the Analog Inputs
Here are some circuit diagrams that illustrate how to connect various non Phidgets devices to the analog inputs on your Phidget.
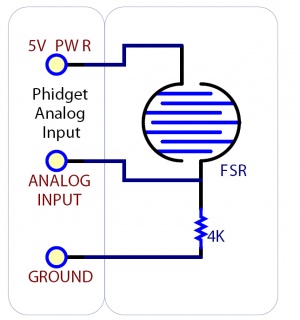
Sensing the Value of a Variable Resistance Sensor
In this diagram, an FSR (Force Sensitive Resistor) is shown.
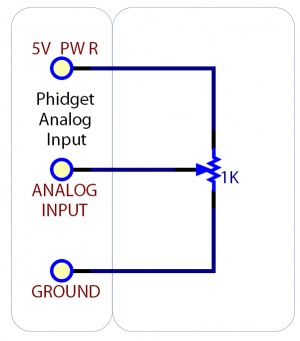
Sensing the Position of a Potentiometer
This diagram shows how to monitor the position of a potentiometer.
Interfacing to an Arbitrary Sensor
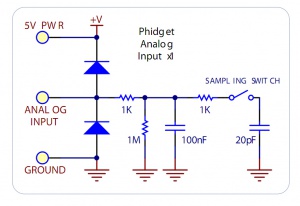
Normally, you can connect a sensor directly to the analog input as long as it has a 0-5V range (or smaller). However, if the sensor is not designed to send its signal across a long cable, you may need to add components as shown in the image.
Note the use of power supply decoupling and the RC Filter on the output. The RC filter also prevents VOUT from oscillating on many sensors.
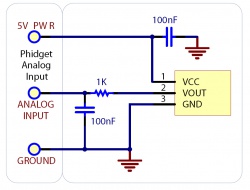
Interfacing 3.3V Sensors
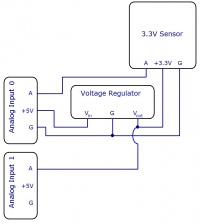
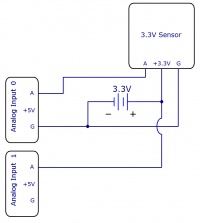
When using a 3.3V sensor with the analog input of a Phidget InterfaceKit, the main challenge is generating the 3.3V supply. You can either buy a 3.3V power supply, or you can buy a voltage regulator to convert the 5V line on the analog input to a 3.3V line, as illustrated in the diagrams. You can also use a second analog input to monitor the output of the 3.3V supply on the regulator.
Interfacing 4-20mA Sensors
You can use the 1132 - 4-20mA Sensor Interface to read a 4-20mA sensor with an analog input. For more information on 4-20mA sensors, see the 4-20mA Sensor Interface Primer.
List of Devices with an Analog Input
| Product # | Name | # of Analog Inputs | Additional Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1010 | PhidgetInterfaceKit 8/8/8 Mini-Format | 8 | DIP-36 Package for compact and OEM applications, 8 Digital Inputs, 8 Digital Outputs |
| 1011 | PhidgetInterfaceKit 2/2/2 | 2 | Compact USB Dongle Size, 2 Digital Inputs, 2 Digital Outputs |
| 1018 | PhidgetInterfaceKit 8/8/8 | 8 | 8 Digital Inputs, 8 Digital Outputs |
| 1019 | PhidgetInterfaceKit 8/8/8 w/6 Port Hub | 8 | 8 Digital Inputs, 8 Digital Outputs, 6-port USB Hub |
| 1065 | PhidgetMotorControl 1-Motor | 2 | 1 DC Motor control, 2 Digital Inputs, 1 Encoder Input |
| 1073 | PhidgetSBC3 | 8 | Single Board Computer, 8 Digital Inputs, 8 Digital Output, 6-port USB Hub |
| 1203 | PhidgetTextLCD | 8 | LCD Character Screen, 8 Digital Inputs, 8 Digital Outputs |
| DAQ1000 | 8x Voltage Input Phidget | 8 | Connects to a VINT Hub |
Phidget Cables
| Product # | Name |
|---|---|
| 3002 | Phidget Cable 60cm |
| 3003 | Phidget Cable 10cm |
| 3004 | Phidget Cable 350cm |
| 3034 | Phidget Cable 15cm |
| 3038 | Phidget Cable 120cm |
| 3039 | Phidget Cable 180cm |
Connector Details

Each analog input uses a 3-pin, 0.100 inch pitch locking connector. Pictured here is a plug with the connections labeled.
The Phidget cables that are designed to plug into these inputs can be found here.
The connectors and pins they use are also commonly available (usually through digikey) - refer to the table below for manufacturer part numbers.
| Manufacturer | Part Number | Description |
| Molex | 50-57-9403 | 3 Position Cable Connector |
| Molex | 16-02-0102 | Wire Crimp Insert for Cable Connector |
| Molex | 70543-0002 | 3 Position Vertical PCB Connector |
| Molex | 70553-0002 | 3 Position Right-Angle PCB Connector (Gold) |
| Molex | 70553-0037 | 3 Position Right-Angle PCB Connector (Tin) |
| Molex | 15-91-2035 | 3 Position Right-Angle PCB Connector - Surface Mount |
Non Phidgets 0-5V Sensors
In addition to Phidgets sensors, any sensor that returns a signal between 0 and 5 volts can be easily interfaced. Here is a list of interesting sensors that can be used with the PhidgetInterfaceKit 8/8/8. Note: these sensors are not “plug & play” like the sensors manufactured by Phidgets.
| Manufacturer | Part Number | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MSI Sensors | FC21/FC22 | Load cells - measure up to 100lbs of force |
| Humirel | HTM2500VB | Humidity sensors |
| Measurement Specialties | MSP-300 | Pressure sensors - ranges up to 10,000 PSI |
| Freescale Semiconductor | MPXA/MPXH | Gas Pressure Sensors |
| Allegro | ACS7 series | Current Sensors - ranges up to 200 Amps |
| Allegro | A1300 series | Linear Hall Effect Sensors - to detect magnetic fields |
| Analog | TMP35 TMP36 TMP37 | Temperature Sensor |
| Panasonic | AMN series | Motion Sensors |
| Honeywell | FS01, FS03 | Small, accurate Piezo-resistive load cells |
| AllSensors-Europe | BARO-A-4V | Barometric Pressure Sensor - 600 to 1,100 mbar |
Note: Most of the above components can be bought at www.digikey.com
0-5V sensors often have their precision measured in mV/Unit. This value represents how many millivolts the sensor will output given a certain measured value. For example, a temperature sensor might output 1 mV per degree Celsius. You can use this value to build a formula so your program can convert it to the measured quantity. Some sensors can have their mV/Unit output changed, which allows you to tweak the sensor's full scale of measurement. Read your sensor's data sheet for conversion formulae and calibration information.