Phidget Programming Basics: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
== Phidget Programming Outline == | |||
It is important to understand what a Phidget is, and how the hardware and software relate to one another before writing software using the {{Phidget22API}}. Please refer to [[What is a Phidget?]] for an introduction. | It is important to understand what a Phidget is, and how the hardware and software relate to one another before writing software using the {{Phidget22API}}. Please refer to [[What is a Phidget?]] for an introduction. | ||
| Line 50: | Line 51: | ||
A channel class will have properties and methods specific to the feature they belong to. For example, the <code>VoltageInput</code> class has a <code>Voltage</code> property that lets you access the current voltage measured by the device, the <code>Accelerometer</code> class has properties to set the sensitivity on each axis and the <code>RFID</code> has a method that writes to a writable RFID tag. | A channel class will have properties and methods specific to the feature they belong to. For example, the <code>VoltageInput</code> class has a <code>Voltage</code> property that lets you access the current voltage measured by the device, the <code>Accelerometer</code> class has properties to set the sensitivity on each axis and the <code>RFID</code> has a method that writes to a writable RFID tag. | ||
== | ==Addressing Phidgets== | ||
The following video summarizes the basics of how to address the proper channel in your code: | The following video summarizes the basics of how to address the proper channel in your code: | ||
| Line 87: | Line 57: | ||
<center>{{#ev:youtube|XKSenz9txKE}}</center> | <center>{{#ev:youtube|XKSenz9txKE}}</center> | ||
==== Opening a Channel on a USB Phidget ==== | ==== Opening a Channel on a USB Phidget ==== | ||
| Line 109: | Line 68: | ||
ch.setDeviceSerialNumber(324781); | ch.setDeviceSerialNumber(324781); | ||
ch.setChannel(3); | ch.setChannel(3); | ||
ch. | ch.openWaitForAttachment(5000); | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| Line 119: | Line 78: | ||
Phidget_setDeviceSerialNumber((PhidgetHandle)ch, 324781); | Phidget_setDeviceSerialNumber((PhidgetHandle)ch, 324781); | ||
Phidget_setChannel((PhidgetHandle)ch, 3); | Phidget_setChannel((PhidgetHandle)ch, 3); | ||
Phidget_openWaitForAttachment((PhidgetHandle)ch, 5000); | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| Line 128: | Line 87: | ||
ch.setDeviceSerialNumber(324781); | ch.setDeviceSerialNumber(324781); | ||
ch.setChannel(5); | ch.setChannel(5); | ||
ch. | ch.openWaitForAttachment(5000); | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| Line 138: | Line 97: | ||
Phidget_setDeviceSerialNumber((PhidgetHandle)ch, 324781); | Phidget_setDeviceSerialNumber((PhidgetHandle)ch, 324781); | ||
Phidget_setChannel((PhidgetHandle)ch, 5); | Phidget_setChannel((PhidgetHandle)ch, 5); | ||
Phidget_openWaitForAttachment((PhidgetHandle)ch, 5000); | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| Line 154: | Line 113: | ||
ch.setIsHubPortDevice(true); | ch.setIsHubPortDevice(true); | ||
ch.setHubPort(4); | ch.setHubPort(4); | ||
ch. | ch.openWaitForAttachment(5000); | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| Line 165: | Line 124: | ||
Phidget_setIsHubPortDevice((PhidgetHandle)ch, 1); | Phidget_setIsHubPortDevice((PhidgetHandle)ch, 1); | ||
Phidget_setHubPort((PhidgetHandle)ch, 4); | Phidget_setHubPort((PhidgetHandle)ch, 4); | ||
Phidget_openWaitForAttachment((PhidgetHandle)ch, 5000); | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| Line 187: | Line 146: | ||
ic.setChannel(4); | ic.setChannel(4); | ||
tc. | tc.openWaitForAttachment(5000); | ||
ic. | ic.openWaitForAttachment(5000); | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| Line 207: | Line 166: | ||
Phidget_setChannel((PhidgetHandle)ic, 4); | Phidget_setChannel((PhidgetHandle)ic, 4); | ||
Phidget_openWaitForAttachment((PhidgetHandle)ch, 5000); | |||
Phidget_openWaitForAttachment((PhidgetHandle)ch, 5000); | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| Line 223: | Line 182: | ||
ch.setDeviceSerialNumber(388624); | ch.setDeviceSerialNumber(388624); | ||
ch.setIsRemote(true); | ch.setIsRemote(true); | ||
ch. | ch.openWaitForAttachment(5000); | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| Line 235: | Line 194: | ||
Phidget_setIsRemote(ch, 1); | Phidget_setIsRemote(ch, 1); | ||
Phidget_openWaitForAttachment((PhidgetHandle)ch, 5000); | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
== Opening a Channel == | |||
After you have created a [[#Creating a Channel| channel instance]], you can call the <code>openWaitForAttachment()</code> method to begin the process of matching the channel to a Phidget device channel. | |||
For example, with the <code>Accelerometer</code> channel in Java: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang=java> | |||
accel.openWaitForAttachment(5000); | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
Or in C: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang=c> | |||
Phidget_openWaitForAttachment((PhidgetHandle) accel, 5000); | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
To see how to use <code>openWaitForAttachment()</code> in other languages, please refer to the {{Phidget22API}}. | |||
There is also a non-blocking version of <code>openWaitForAttachment()</code> called <code>open()</code>. | |||
The <code>open()</code> and <code>openWaitForAttachment()</code> functions begin the process of matching the channel handle you created to a channel of a Phidget device, and do not actually ''open'' the Phidget itself. An open channel may match a new Phidget device when it is plugged in if that channel has not already found a Phidget device channel that meets its criteria. | |||
<code>open()</code> and <code>openWaitForAttachment()</code> can be used without specifying any addressing properties. In this case the system will match a channel with the first Phidget device channel that matches the channel class. The channel class itself is an implied addressing parameter. | |||
If there is more than one Phidget connected to the computer that supports the channel class, the <code>DeviceSerialNumber</code> property must be set determine which Phidget will match. | |||
If the Phidget connected to the computer has more than one channel of the same classes, the <code>Channel</code> property must be set to determine which Phidget device channel will match. | |||
If the Phidget Network Server is enabled on the computer, the <code>IsRemote</code> and <code>IsLocal</code> properties can be used to determine if the channel will match the Phidget device channel or the network channel. | |||
Please refer to the {{Phidget22API}}, and [[Best Phidgets Practices|Best Practices]] for more information on matching channels to Phidget device channels. | |||
===Details for Open()=== | |||
Because <code>open()</code> simply enables the process of matching a channel to a Phidget device channel, <code>open()</code> returns immediately and does not wait for the channel to attach to a Phidget device channel. The channel changes state to ''open'', but is not necessarily ''attached''. Until the channel actually becomes ''attached'' to a Phidget device channel, most of the channel class interface will not be available. | |||
As long as the channel is open (and not ''attached''), the system will continue to try to match it with a | |||
Phidget device channel that has not already been matched with a channel. The channel can only be matched once, and the Phidget device channel can only be matched once. For example, if you connected a single Phidget Accelerometer to a computer, and you created and opened two <code>Accelerometer</code> channels, only one of the channels would attach while the other would remain ''open'' but not ''attached''. If the ''attached'' channel were to be closed, the other channel would then attach to the Accelerometer. | |||
When the channel is matched with a Phidget device channel, the channel state is changed to ''attached'' and an event is fired. | |||
<code>openWaitForAttachment()</code> will perform the above matching, and hold the program either until the attach event has fired, or until it times out. | |||
'''Note:''' Once a Phidget device channel is matched to a channel, it will not be available to match another channel until the first channel is closed. The one exception is if the Phidget device channel is ''attached'' over the network through the [[Phidget Network Server]]. In that case, multiple channels are allowed to match and attach to the Phidget device channel. Some Phidgets, such as motor controllers will never match more than one channel at a time. | |||
== Attaching a Channel == | == Attaching a Channel == | ||
When a channel is open (and not ''attached''), the system will continue to try to match it with a | When a channel is open (and not ''attached''), the system will continue to try to match it with a | ||
Phidget device channel until either a match is found, or the channel is closed. When the | Phidget device channel until either a match is found, or the channel is closed. When the channel is matched with a Phidget device channel, the channel state is changed to ''attached'' and an event is fired. | ||
An event handler can be registered to catch the ''attach event'' through the channel's <code>Attach</code> event. Each channel also has | An event handler can be registered to catch the ''attach event'' through the channel's <code>Attach</code> event. Each channel also has an <code>Attached</code> property that can be read to determine if the class has | ||
been matched to a Phidget device channel. | been matched to a Phidget device channel. | ||
Revision as of 16:37, 6 June 2018
Phidget Programming Outline
It is important to understand what a Phidget is, and how the hardware and software relate to one another before writing software using the Phidget22 API. Please refer to What is a Phidget? for an introduction.
The Phidget software library matches a Phidget device channel with a software channel that is created by a user.
Software channels are each of a class, where that class defines a set of methods, properties, events and errors. Phidget devices are aware of the channel classes, and expose access to features of the device through the class interface.
To use a Phidget, you'll want to:
- Create an instance of the channel class that provides access to the device you want to control.
- Open the channel.
- Detect when the channel is attached to the Phidget.
- Use methods and properties of the attached channel.
- Close the channel.
Small code snippets are provided for each step in the sections below. Java and C were selected because Java is a high-level language and C is a low level language. The best reference to the features each channel class is the Phidget22 API for your specific language. This page is intended to be a high-level introduction.
Creating a Channel
A Phidget device exposes one or more device channels where each channel is an interface to a feature of the hardware. A channel class defines an interface to control and query a channel of the Phidget device. For example, a 1018 - Phidget InterfaceKit device includes support
for digital input and digital out, and therefore exports DigitalInput and DigitalOutput channels.
Phidget devices are controlled by creating an instance of a Phidget channel class. Each channel class has a function that allows you to create an instance, and a function to later delete the instance.
For example, in Java:
// Create a new Accelerometer channel
Accelerometer accel = new Accelerometer();
// Create a new RFID channel
RFID rfid = new RFID();
Or in C:
// Create a new Accelerometer channel
PhidgetAccelerometerHandle accel;
PhidgetAccelerometer_create(&accel);
// Create a new RFID channel
PhidgetRFIDHandle rfid;
PhidgetRFID_create(&rfid);
A channel class will have properties and methods specific to the feature they belong to. For example, the VoltageInput class has a Voltage property that lets you access the current voltage measured by the device, the Accelerometer class has properties to set the sensitivity on each axis and the RFID has a method that writes to a writable RFID tag.
Addressing Phidgets
The following video summarizes the basics of how to address the proper channel in your code:
Opening a Channel on a USB Phidget
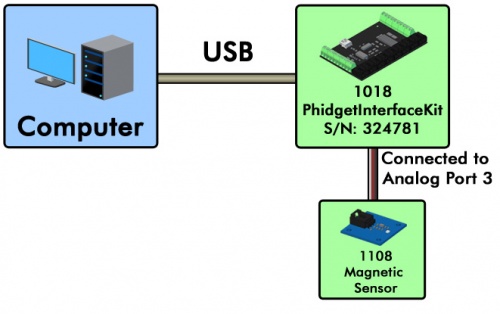
In this example, a 1018 PhidgetInterfaceKit 8/8/8 is connected to a computer. A 1108 Magnetic Sensor is connected to analog port 3 on the 1018. Here's how you would open the channel for the magnetic sensor in Java:
VoltageRatioInput ch = new VoltageRatioInput();
ch.setDeviceSerialNumber(324781);
ch.setChannel(3);
ch.openWaitForAttachment(5000);
Or in C:
PhidgetVoltageRatioInputHandle ch;
PhidgetVoltageRatioInput_create(&ch);
Phidget_setDeviceSerialNumber((PhidgetHandle)ch, 324781);
Phidget_setChannel((PhidgetHandle)ch, 3);
Phidget_openWaitForAttachment((PhidgetHandle)ch, 5000);
If you wanted to open digital input 5 in the same example, it would look like this in Java:
DigitalInput ch = new DigitalInput();
ch.setDeviceSerialNumber(324781);
ch.setChannel(5);
ch.openWaitForAttachment(5000);
Or in C:
PhidgetDigitalInputHandle ch;
PhidgetDigitalInput_create(&ch);
Phidget_setDeviceSerialNumber((PhidgetHandle)ch, 324781);
Phidget_setChannel((PhidgetHandle)ch, 5);
Phidget_openWaitForAttachment((PhidgetHandle)ch, 5000);
Opening a VINT Hub Port as a Channel
The ports on a VINT Hub can be opened as Digital Inputs, Digital Outputs, Voltage Inputs, or Voltage Ratio Inputs. Suppose you had a HUB0000 VINT Hub with a 1133 Sound Sensor connected to its fourth port.
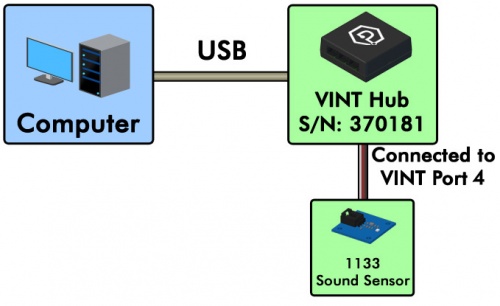
Here's how you would open it in Java:
VoltageInput ch = new VoltageInput();
ch.setDeviceSerialNumber(370181);
ch.setIsHubPortDevice(true);
ch.setHubPort(4);
ch.openWaitForAttachment(5000);
Or in C:
PhidgetVoltageInputHandle ch;
PhidgetVoltageInput_create(&ch);
Phidget_setDeviceSerialNumber((PhidgetHandle)ch, 370181);
Phidget_setIsHubPortDevice((PhidgetHandle)ch, 1);
Phidget_setHubPort((PhidgetHandle)ch, 4);
Phidget_openWaitForAttachment((PhidgetHandle)ch, 5000);
Opening a Channel on a VINT Device
In this example, we have a TMP1101 4x Thermocouple Phidget and a HUB0000 VINT Hub.
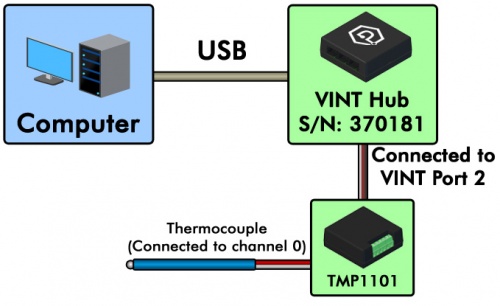
If we wanted to open both the thermocouple connected to port 0 and the integrated temperature sensor on the board, we first need to figure out which channels those are. Go to the product page for the TMP1101 and click on the API tab. From the table at the top of the tab, we can see that the integrated temperature sensor is TemperatureSensor channel 4. In Java, opening these channels would look like this:
TemperatureSensor tc = new TemperatureSensor(); // Handle for the thermocouple
TemperatureSensor ic = new TemperatureSensor(); // Handle for the integrated temperature chip
tc.setDeviceSerialNumber();
ic.setDeviceSerialNumber();
tc.setHubPort(2);
ic.setHubPort(2);
tc.setChannel(0);
ic.setChannel(4);
tc.openWaitForAttachment(5000);
ic.openWaitForAttachment(5000);
Or in C:
PhidgetTemperatureSensorHandle tc; // Handle for the thermocouple
PhidgetTemperatureSensorHandle ic; // Handle for the integrated temperature chip
PhidgetTemperatureSensor_create(&ch);
PhidgetTemperatureSensor_create(&ch);
Phidget_setDeviceSerialNumber(tc, 370181);
Phidget_setDeviceSerialNumber(ic, 370181);
Phidget_setHubPort((PhidgetHandle)tc, 2);
Phidget_setHubPort((PhidgetHandle)ic, 2);
Phidget_setChannel((PhidgetHandle)tc, 0);
Phidget_setChannel((PhidgetHandle)ic, 4);
Phidget_openWaitForAttachment((PhidgetHandle)ch, 5000);
Phidget_openWaitForAttachment((PhidgetHandle)ch, 5000);
Opening a Channel on a Remote Phidget
Suppose you wanted to open a locally connected Phidget remotely over the Network Service, so that you could have multiple programs connecting to it at the same time. In this example, we have a 1024 PhidgetRFID connected to a computer that has the Phidget Network Server enabled.
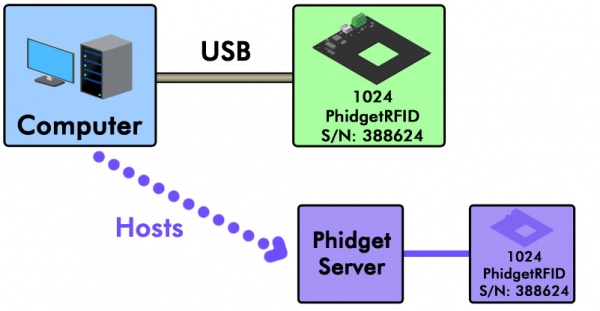
You could open the RFID reader channel remotely with the following code in Java:
RFID ch = new RFID();
ch.setDeviceSerialNumber(388624);
ch.setIsRemote(true);
ch.openWaitForAttachment(5000);
Or in C:
PhidgetRFIDHandle ch;
PhidgetRFID_create(&ch);
Phidget_setDeviceSerialNumber(ch, 388624);
Phidget_setIsRemote(ch, 1);
Phidget_openWaitForAttachment((PhidgetHandle)ch, 5000);
Opening a Channel
After you have created a channel instance, you can call the openWaitForAttachment() method to begin the process of matching the channel to a Phidget device channel.
For example, with the Accelerometer channel in Java:
accel.openWaitForAttachment(5000);
Or in C:
Phidget_openWaitForAttachment((PhidgetHandle) accel, 5000);
To see how to use openWaitForAttachment() in other languages, please refer to the Phidget22 API.
There is also a non-blocking version of openWaitForAttachment() called open().
The open() and openWaitForAttachment() functions begin the process of matching the channel handle you created to a channel of a Phidget device, and do not actually open the Phidget itself. An open channel may match a new Phidget device when it is plugged in if that channel has not already found a Phidget device channel that meets its criteria.
open() and openWaitForAttachment() can be used without specifying any addressing properties. In this case the system will match a channel with the first Phidget device channel that matches the channel class. The channel class itself is an implied addressing parameter.
If there is more than one Phidget connected to the computer that supports the channel class, the DeviceSerialNumber property must be set determine which Phidget will match.
If the Phidget connected to the computer has more than one channel of the same classes, the Channel property must be set to determine which Phidget device channel will match.
If the Phidget Network Server is enabled on the computer, the IsRemote and IsLocal properties can be used to determine if the channel will match the Phidget device channel or the network channel.
Please refer to the Phidget22 API, and Best Practices for more information on matching channels to Phidget device channels.
Details for Open()
Because open() simply enables the process of matching a channel to a Phidget device channel, open() returns immediately and does not wait for the channel to attach to a Phidget device channel. The channel changes state to open, but is not necessarily attached. Until the channel actually becomes attached to a Phidget device channel, most of the channel class interface will not be available.
As long as the channel is open (and not attached), the system will continue to try to match it with a
Phidget device channel that has not already been matched with a channel. The channel can only be matched once, and the Phidget device channel can only be matched once. For example, if you connected a single Phidget Accelerometer to a computer, and you created and opened two Accelerometer channels, only one of the channels would attach while the other would remain open but not attached. If the attached channel were to be closed, the other channel would then attach to the Accelerometer.
When the channel is matched with a Phidget device channel, the channel state is changed to attached and an event is fired.
openWaitForAttachment() will perform the above matching, and hold the program either until the attach event has fired, or until it times out.
Note: Once a Phidget device channel is matched to a channel, it will not be available to match another channel until the first channel is closed. The one exception is if the Phidget device channel is attached over the network through the Phidget Network Server. In that case, multiple channels are allowed to match and attach to the Phidget device channel. Some Phidgets, such as motor controllers will never match more than one channel at a time.
Attaching a Channel
When a channel is open (and not attached), the system will continue to try to match it with a Phidget device channel until either a match is found, or the channel is closed. When the channel is matched with a Phidget device channel, the channel state is changed to attached and an event is fired.
An event handler can be registered to catch the attach event through the channel's Attach event. Each channel also has an Attached property that can be read to determine if the class has
been matched to a Phidget device channel.
To set an event handler to detect the attach in Java:
//create a Phidget accelerometer channel:
Accelerometer accel = new Accelerometer();
accel.addAttachListener((AttachEvent ae) -> {
Accelerometer accel = (Accelerometer) ae.getSource();
// Do things after attachment (i.e. read data, control the device)
}
});
Or in C:
// Define the attach handler function
void CCONV
onAttachedEventHandler(PhidgetHandle channel, void *userPtr) {
printf("A channel has been attached\n");
// Do things after attachment (i.e. read data, control the device)
}
int
main(int argc, char **argv) {
// .....Then, in the main code create the channel and set the attach handler:
PhidgetAccelerometerHandle accel;
PhidgetAccelerometer_create(&accel);
Phidget_setOnAttachHandler((PhidgetHandle)accel, onAttachedEventHandler, NULL);
// other stuff in main
}
The attach event handler should be set before the channel is opened; otherwise, the attach event could occur before the handler is set.
Do Things with a Channel
After a channel has been opened and attached, software can control the Phidget device via the channel class interface.
Like setting an event handler that executes when the channels is attached, handlers can be set to receive events when a state change occurs, or sensor data is received.
A Voltage Input channel for example, like one supported by the 1018 Phidget Interface Kit, can set an event handler that gets called as the voltage is processed.
In Java, this would look like:
// After creating and opening a VoltageInput channel called "sensorIn"
sensorIn.addVoltageChangeListener((VoltageInputVoltageChangeEvent de) -> {
System.out.println("Voltage: " + de.getVoltage());
});
Or in C:
void CCONV
onVoltageChangeHandler(PhidgetVoltageInputHandle voltageInput, void *ctx, double voltage) {
printf("Voltage: %lf V\n", voltage);
}
// .....Then, in the main code:
// After creating and opening a VoltageInput channel called "sensorIn"
PhidgetVoltageInput_setOnVoltageChangeHandler(sensorIn, onVoltageChangeHandler, NULL);
The voltage value delivered in the above snippets could also be accessed via the Voltage property of the channel. Properties that have related events are automatically updated each time the event is received by the channel, and calls between events always return the value set by the last event.
double val = sensorIn.getVoltage();
Or, in C:
double val;
PhidgetVoltageInput_getVoltage(sensorIn, &val);
Sensors, Input, and Output
Often, your Phidget will support more than one channel class. For example a 1018 Phidget Interface Kit has voltage inputs (black sensor ports), digital inputs and digital outputs (green terminal blocks). You can determine the channel classes supported by your Phidget from the product page and the Phidget22 API.
For InterfaceKits like the 1018:
- To the voltage inputs, you can attach various sensors (temperature, humidity, light, sound)
- To the digital inputs, you can attach various input devices (switches)
- To the digital outputs, you can attach simple indicators (LEDs, buzzers, relays)
The features and channels supported by each Phidget are many and varied, and we only include general concepts on this page. You can view the complete list of channels supported by a Phidget in the Phidget22 API. Select a device at the top of the screen, select your preferred programming language, and then select which channel class you want to view the documentation for.
Close a Channel
When you are finished with a channel, you should close and (in some languages) delete it. Once closed, the Phidget device channel the channel was matched to will be released and made available for another channel to match.
For example, in Java:
device.close();
device = null;
Or, in C:
Phidget_close((PhidgetHandle)channel);
Phidget_release((PhidgetHandle *)&channel); // will NULL the pointer
When you close a channel, it will reset all of the properties of that channel. For example, a digital output will revert back to FALSE when it is closed. If you want to have persistent properties, you can keep the channel open in another process over the Network Server and open it remotely with your main program. As long as the channel is opened in at least one program or process, its properties will persist.
Further Reading
Data Interval/Change Trigger - Learn about these two properties that control how much data comes in from your sensors.
Using Multiple Phidgets - How to know you are attaching to the Phidget you want.
Polling vs. Events - Your program can gather data in either a polling-driven or event-driven manner. Learn the difference to determine which is best for your application.
Logging, Exceptions, and Errors - Learn about all the tools you can use to debug your program.
Phidget Network Server - Phidgets can be controlled and communicated with over your network- either wirelessly or over ethernet.
Best Phidgets Practices - Good programming habits that will save you from common problems when writing code for your Phidgets.
