1130 User Guide: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (26 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOINDEX__ | |||
<metadesc>The Phidgets pH/ORP Adapter connects to any of our pH or ORP probes to an Analog Input or VINT Hub port.</metadesc> | |||
[[Category:UserGuide]] | [[Category:UserGuide]] | ||
==Getting Started== | ==Getting Started== | ||
{{UgSensorIntro|1130|pH/ORP Adapter|Voltage Input port}} | |||
*{{CT|pHORPProbe|compatible pH/ORP probe}} | |||
Next, you will need to connect the pieces: | |||
[[Image:1130_0_Connecting_The_Hardware.jpg|500px|right|link=]] | |||
#Connect the | # Connect the 1130 to the HUB0000 with the Phidget cable. | ||
#Connect the | # Connect the pH/ORP probe to the 1130. | ||
#Use the DIP switch to select pH or ORP to correspond to the type of electrode you | # Use the DIP switch to select pH or ORP to correspond to the type of electrode you're using. | ||
#Connect the | # Connect the HUB0000 to your computer with the USB cable. | ||
= | <br clear="all"> | ||
{{UGIntroDone|1130}} | |||
{{ | ==Using the 1130== | ||
{{UGcontrolpanelSensor|1130|HUB0000}} | |||
{{UGSensorVoltageInput|1130|pH/ORP}} | |||
==Technical Details== | ==Technical Details== | ||
===Measuring the pH=== | ===Measuring the pH=== | ||
To determine the pH of a solution, make sure the DIP switch on the board is flipped to the pH side. Given the | {{UGSensorFormula|pH}} To determine the pH of a solution, make sure the DIP switch on the board is flipped to the pH side. Given the voltage from the sensor, the following formula can be applied: | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
\text{pH = | \text{pH} = 3.56 \times \text{Voltage} - 1.889 | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
This formula assumes that the solution is at | This formula (and the Phidget library ''Sensor Value'' formula) assumes that the solution is at 25°C. Depending on the temperature of the solution and on the actual pH level, the output voltage can change dramatically. To incorporate temperature (in °C) for added accuracy, the following formula can be used: | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
\text{pH = 7 }- \frac{2.5 - \ | \text{pH = 7 }- \frac{2.5 - \text{Voltage}}{0.257179 + 0.000941468 \times \text{Temperature}} | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
<br clear="all"> | |||
The following example is to give an idea of how the temperature affects the output voltage: | |||
{|class ="wikitable" style="text-align: center;width: 50%;margin:auto" | |||
|style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Temperature (°C)''' | |||
|style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''pH''' | |||
|style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Voltage (V)''' | |||
|- | |||
|0 | |||
|2 | |||
|1.21 | |||
|- | |||
|25 | |||
|2 | |||
|1.095 | |||
|- | |||
|100 | |||
|2 | |||
|0.74 | |||
|- | |||
|style="background:#f0f0f0;" colspan="3" | | |||
|- | |||
|0 | |||
|8 | |||
|2.76 | |||
|- | |||
|25 | |||
|8 | |||
|2.78 | |||
|- | |||
|100 | |||
|8 | |||
|2.85 | |||
|} | |||
As shown above, temperature has a greater impact on solutions that have a pH further away from the reference pH of 7. Temperature also affects the impedance of the glass electrode, and can result in increased errors if not properly calibrated. If you want to monitor the temperature of the solution, you can use a thermocouple. You'll need to add some sort of protective shielding to the thermocouple if you’re using acidic or basic solutions, though. Check out our {{CT|TCInterface|thermocouple interfaces}} for more information. | |||
===Measuring Oxidation/Reduction Potential (ORP)=== | ===Measuring Oxidation/Reduction Potential (ORP)=== | ||
To determine the ORP of a solution, make sure the DIP switch on the board is flipped to the ORP side. Given the | {{UGSensorFormula|ORP}} To determine the ORP of a solution, make sure the DIP switch on the board is flipped to the ORP side. Given the voltage from the sensor, the following formula can be applied: | ||
:<math> | :<math> | ||
\text{ORP (V)} = \frac{2.5 - | \text{ORP (V)} = \frac{2.5 - \text{Voltage}}{1.037} | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
| Line 96: | Line 88: | ||
===Words of Caution=== | ===Words of Caution=== | ||
The 1130 should be used to measure solutions that are electrically quiet. Measuring pH in electrically noisy environments such as tanks with mixing pumps, and even other measuring devices is not recommended. | |||
Measuring pH in electrically noisy environments such as tanks with mixing pumps, and even other measuring devices is not recommended. | |||
===Choosing Electrodes=== | ===Choosing Electrodes=== | ||
Review the data sheet for the electrode you have selected for your application to ensure that it complies with the device specifications of the | Review the data sheet for the electrode you have selected for your application to ensure that it complies with the device specifications of the 1130. The important specification is the output voltage of the electrode. Many electrodes will work but it is important to verify compliance before connecting an electrode to the 1130. In fact, any type of sensor that uses a BNC connector and complies with the voltage range of the 1130 should work. We have reviewed the following electrodes, and found that they can be used with the 1130. This is by no means a comprehensive list, but can be used as a comparison with other electrodes if necessary. | ||
{| | {|class ="wikitable" style="text-align: center;margin:auto" | ||
|style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Manufacturer''' | |||
| | |style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Part Number''' | ||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | [https://www.omega.com Omega] || PHE13XX, PHE14XX, ORE1311, ORE1411 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | [https://www.coleparmer.com Cole-Parmer] || EW-59001, EW27003 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | [https://www.mt.com Mettler-Toledo] || InLab (BNC) Series | ||
|} | |} | ||
{{UGasens}} | {{UGasens}} | ||
== | ===Further Reading=== | ||
{{ | For more information on pH and ORP probes, check the [[PH/ORP Sensor Guide]]. | ||
{{UGnext|}} | |||
Latest revision as of 16:59, 1 June 2023
Getting Started
Welcome to the 1130 user guide! In order to get started, make sure you have the following hardware on hand:
- 1130 - pH/ORP Adapter
- Any Phidget with a Voltage Input port, here are some compatible products. We will be using the VINT Hub for this guide.
- USB cable and computer
- Phidget cable
- compatible pH/ORP probe
Next, you will need to connect the pieces:
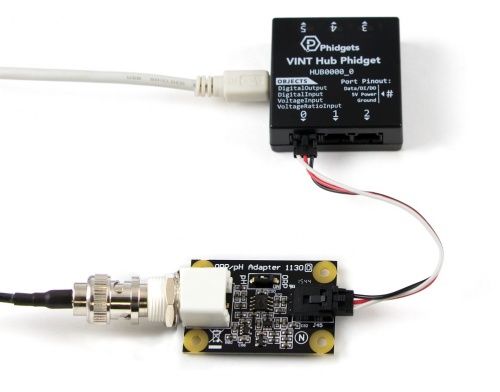
- Connect the 1130 to the HUB0000 with the Phidget cable.
- Connect the pH/ORP probe to the 1130.
- Use the DIP switch to select pH or ORP to correspond to the type of electrode you're using.
- Connect the HUB0000 to your computer with the USB cable.
Now that you have everything together, let's start using the 1130!
Using the 1130
Phidget Control Panel
In order to demonstrate the functionality of the 1130, we will connect it to the HUB0000, and then run an example using the Phidget Control Panel on a Windows machine.
The Phidget Control Panel is available for use on both macOS and Windows machines. If you would like to follow along, first take a look at the getting started guide for your operating system:
Linux users can follow the getting started with Linux guide and continue reading here for more information about the 1130.
First Look
After plugging in the 1130 into the HUB0000, and the HUB0000 into your computer, open the Phidget Control Panel. You will see something like this:
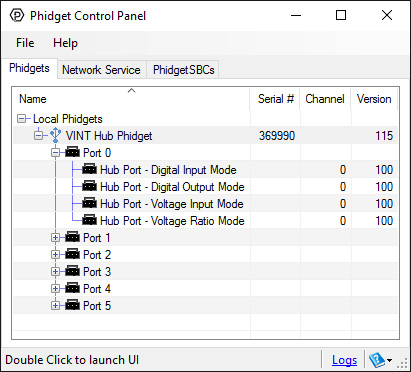
The Phidget Control Panel will list all connected Phidgets and associated objects, as well as the following information:
- Serial number: allows you to differentiate between similar Phidgets.
- Channel: allows you to differentiate between similar objects on a Phidget.
- Version number: corresponds to the firmware version your Phidget is running. If your Phidget is listed in red, your firmware is out of date. Update the firmware by double-clicking the entry.
The Phidget Control Panel can also be used to test your device. Double-clicking on an object will open an example.
Voltage Input
Double-click on a Voltage Input object in order to run the example:
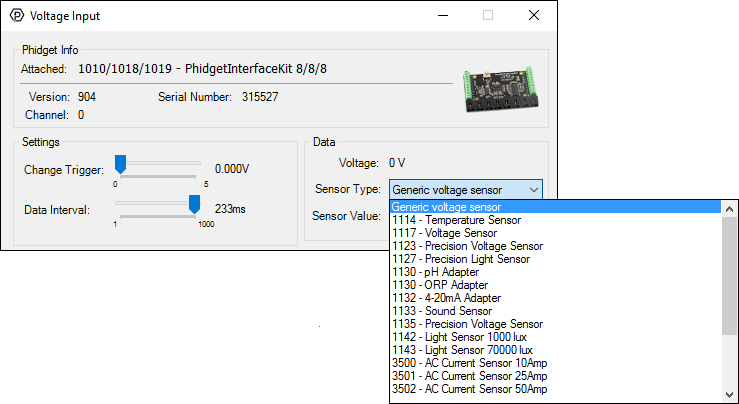
General information about the selected object will be displayed at the top of the window. You can also experiment with the following functionality:
- Modify the change trigger and/or data interval value by dragging the sliders. For more information on these settings, see the data interval/change trigger page.
- Select the 1130 from the Sensor Type drop-down menu. The example will now convert the voltage into pH/ORP automatically. Converting the voltage to pH/ORP is not specific to this example, it is handled by the Phidget libraries, with functions you have access to when you begin developing!
Technical Details
Measuring the pH
The Phidget libraries can automatically convert sensor voltage into pH by selecting the appropriate SensorType. See the Phidget22 API for more details. To determine the pH of a solution, make sure the DIP switch on the board is flipped to the pH side. Given the voltage from the sensor, the following formula can be applied:
This formula (and the Phidget library Sensor Value formula) assumes that the solution is at 25°C. Depending on the temperature of the solution and on the actual pH level, the output voltage can change dramatically. To incorporate temperature (in °C) for added accuracy, the following formula can be used:
The following example is to give an idea of how the temperature affects the output voltage:
| Temperature (°C) | pH | Voltage (V) |
| 0 | 2 | 1.21 |
| 25 | 2 | 1.095 |
| 100 | 2 | 0.74 |
| 0 | 8 | 2.76 |
| 25 | 8 | 2.78 |
| 100 | 8 | 2.85 |
As shown above, temperature has a greater impact on solutions that have a pH further away from the reference pH of 7. Temperature also affects the impedance of the glass electrode, and can result in increased errors if not properly calibrated. If you want to monitor the temperature of the solution, you can use a thermocouple. You'll need to add some sort of protective shielding to the thermocouple if you’re using acidic or basic solutions, though. Check out our thermocouple interfaces for more information.
Measuring Oxidation/Reduction Potential (ORP)
The Phidget libraries can automatically convert sensor voltage into ORP by selecting the appropriate SensorType. See the Phidget22 API for more details. To determine the ORP of a solution, make sure the DIP switch on the board is flipped to the ORP side. Given the voltage from the sensor, the following formula can be applied:
ORP electrodes give a typical range of -2V to 2V, where the positive values are for oxidizers and the negative values are for reducers.
Words of Caution
The 1130 should be used to measure solutions that are electrically quiet. Measuring pH in electrically noisy environments such as tanks with mixing pumps, and even other measuring devices is not recommended.
Choosing Electrodes
Review the data sheet for the electrode you have selected for your application to ensure that it complies with the device specifications of the 1130. The important specification is the output voltage of the electrode. Many electrodes will work but it is important to verify compliance before connecting an electrode to the 1130. In fact, any type of sensor that uses a BNC connector and complies with the voltage range of the 1130 should work. We have reviewed the following electrodes, and found that they can be used with the 1130. This is by no means a comprehensive list, but can be used as a comparison with other electrodes if necessary.
| Manufacturer | Part Number |
| Omega | PHE13XX, PHE14XX, ORE1311, ORE1411 |
| Cole-Parmer | EW-59001, EW27003 |
| Mettler-Toledo | InLab (BNC) Series |
Phidget Cable

The Phidget Cable is a 3-pin, 0.100 inch pitch locking connector. Pictured here is a plug with the connections labelled. The connectors are commonly available - refer to the Analog Input Primer for manufacturer part numbers.
Further Reading
For more information on pH and ORP probes, check the PH/ORP Sensor Guide.
What to do Next
- Programming Languages - Find your preferred programming language here and learn how to write your own code with Phidgets!
- Phidget Programming Basics - Once you have set up Phidgets to work with your programming environment, we recommend you read our page on to learn the fundamentals of programming with Phidgets.



