1051 User Guide: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "==Getting Started== ===Checking the Contents=== {{UGbox| '''You should have received:''' * A PhidgetTemperatureSensor 1-Input * A Mini-USB Cable | '''In order to test your ne...") |
No edit summary |
||
| (26 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOINDEX__ | |||
<metadesc>Connect a thermocouple to the PhidgetTemperatureSensor 1-Input to measure the temperature of an object or area. Plugs directly into a USB port. </metadesc> | |||
[[Category:UserGuide]] | |||
==Getting Started== | ==Getting Started== | ||
{{UGIntro|1051}} | |||
*[{{SERVER}}/products.php?product_id=1051 1051 Phidget TemperatureSensor 1-Input] | |||
*USB cable and computer | |||
*{{CT|TC|Thermocouple}} | |||
Next, you will need to connect the pieces: | |||
[[Image:1051_2_Connecting_The_Hardware.jpg|500px|right|link=]] | |||
# Connect the thermocouple to the | # Connect the thermocouple to the inputs on the Phidget TemperatureSensor. The datasheet or product page for the thermocouple should tell you which wire is positive and which is negative. | ||
# Connect the | # Connect the Phidget to your computer using the USB cable. | ||
= | <br clear="all"> | ||
{{UGIntroDone|1051}} | |||
{{ | ==Using the 1051== | ||
{{UGcontrolpanel|1051}} | |||
{{ugTemperatureSensorThermocouple|1051}} | |||
{{ | {{ugTemperatureSensorIC|1051|, labelled ''Temperature Sensor (IC)'', |(IC)}} | ||
{{ | {{ugVoltageInput|1051|}} | ||
}} | |||
{{ugAddressingInformation}} | |||
{{ | {{ugUsingYourOwnProgram|1051}} | ||
==Technical Details== | ==Technical Details== | ||
{{Coldjunctioncomp}} | |||
For more information on thermocouples, check out the [[Thermocouple | For more information on thermocouples, check out the [[Thermocouple Guide]]. | ||
{{UGnext|}} | |||
{{ | |||
Latest revision as of 19:56, 1 June 2023
Getting Started
Welcome to the 1051 user guide! In order to get started, make sure you have the following hardware on hand:
- 1051 Phidget TemperatureSensor 1-Input
- USB cable and computer
- Thermocouple
Next, you will need to connect the pieces:
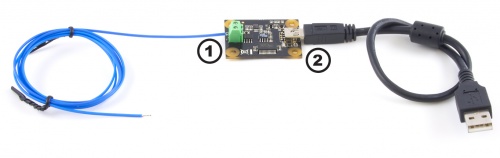
- Connect the thermocouple to the inputs on the Phidget TemperatureSensor. The datasheet or product page for the thermocouple should tell you which wire is positive and which is negative.
- Connect the Phidget to your computer using the USB cable.
Now that you have everything together, let's start using the 1051!
Using the 1051
Phidget Control Panel
In order to demonstrate the functionality of the 1051, the Phidget Control Panel running on a Windows machine will be used.
The Phidget Control Panel is available for use on both macOS and Windows machines.
Windows
To open the Phidget Control Panel on Windows, find the ![]() icon in the taskbar. If it is not there, open up the start menu and search for Phidget Control Panel
icon in the taskbar. If it is not there, open up the start menu and search for Phidget Control Panel
macOS
To open the Phidget Control Panel on macOS, open Finder and navigate to the Phidget Control Panel in the Applications list. Double click on the ![]() icon to bring up the Phidget Control Panel.
icon to bring up the Phidget Control Panel.
For more information, take a look at the getting started guide for your operating system:
Linux users can follow the getting started with Linux guide and continue reading here for more information about the 1051.
First Look
After plugging the 1051 into your computer and opening the Phidget Control Panel, you will see something like this:
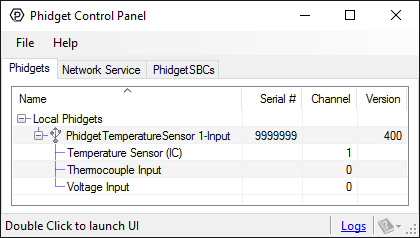
The Phidget Control Panel will list all connected Phidgets and associated objects, as well as the following information:
- Serial number: allows you to differentiate between similar Phidgets.
- Channel: allows you to differentiate between similar objects on a Phidget.
- Version number: corresponds to the firmware version your Phidget is running. If your Phidget is listed in red, your firmware is out of date. Update the firmware by double-clicking the entry.
The Phidget Control Panel can also be used to test your device. Double-clicking on an object will open an example.
Temperature Sensor (Thermocouple)
Double-click on the Temperature Sensor object, labelled Thermocouple Input, in order to run the example:
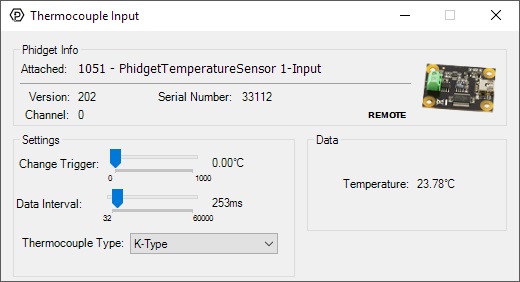
General information about the selected object will be displayed at the top of the window. You can also experiment with the following functionality:
- Modify the change trigger and/or data interval value by dragging the sliders. For more information on these settings, see the data interval/change trigger page.
- Select your thermocouple type from the Thermocouple Type drop-down menu.
- The measured temperature will be updated next to the Temperature label. Touch the thermocouple wire with your hands to see the temperature increase. If the temperature decreases when it should be increasing, you may have the wires plugged in incorrectly.
Temperature Sensor (IC)
Double-click on the Temperature Sensor object , labelled Temperature Sensor (IC), in order to run the example:
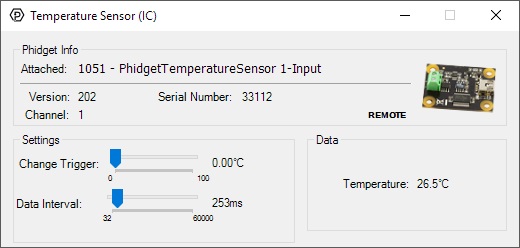
General information about the selected object will be displayed at the top of the window. You can also experiment with the following functionality:
- Modify the change trigger and/or data interval value by dragging the sliders. For more information on these settings, see the data interval/change trigger page.
- The measured temperature can be seen next to the Temperature label. Cover the board with your hands to see the temperature quickly rise.
Voltage Input
Double-click on the Voltage Input object in order to run the example:
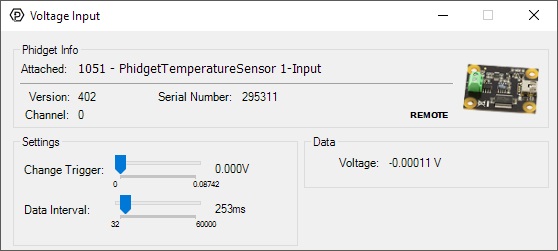
General information about the selected object will be displayed at the top of the window. You can also experiment with the following functionality:
- Modify the change trigger and/or data interval value by dragging the sliders. For more information on these settings, see the data interval/change trigger page.
Finding The Addressing Information
Before you can access the device in your own code, and from our examples, you'll need to take note of the addressing parameters for your Phidget. These will indicate how the Phidget is physically connected to your application. For simplicity, these parameters can be found by clicking the button at the top of the Control Panel example for that Phidget.
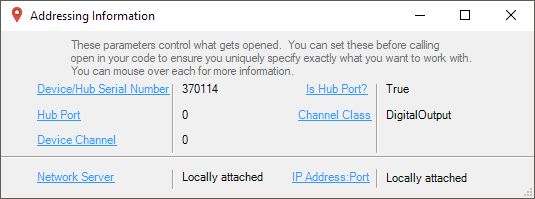
In the Addressing Information window, the section above the line displays information you will need to connect to your Phidget from any application. In particular, note the Channel Class field as this will be the API you will need to use with your Phidget, and the type of example you should use to get started with it. The section below the line provides information about the network the Phidget is connected on if it is attached remotely. Keep track of these parameters moving forward, as you will need them once you start running our examples or your own code.
Using Your Own Program
You are now ready to start writing your own code for the device. The best way to do that is to start from our Code Samples.
Select your programming language of choice from the drop-down list to get an example for your device. You can use the options provided to further customize the example to best suit your needs.
Once you have your example, you will need to follow the instructions on the page for your programming language to get it running. To find these instructions, select your programming language from the Programming Languages page.
Technical Details
Cold Junction Compensation and Self-heating
Thermocouples consist of two junctions, one where the thermocouple meets the Phidget and one where the two wires are welded together at the sensing end of the device. In simplified terms, a thermocouple works by detecting the temperature difference between these two junctions. As such, in order to measure the temperature at the sensing end we need to know the temperature where the thermocouple connects to the Phidget. To do so, there is an ambient temperature sensor on the board.
An important thing to note is that the ambient temperature sensor measures the temperature of the board and the air around it, though not specifically at the junction. Generally you can assume they are nearly the same temperature, however as the electronics heat up by being powered on there can be some small error introduced. This is exacerbated by having the board in an enclosed space where normal airflow is restricted thereby increasing the effect of self-heating. As a result we recommend that the board be left in as open and well ventilated/cooled a place as possible to minimize this error source.
For more information on thermocouples, check out the Thermocouple Guide.
What to do Next
- Programming Languages - Find your preferred programming language here and learn how to write your own code with Phidgets!
- Phidget Programming Basics - Once you have set up Phidgets to work with your programming environment, we recommend you read our page on to learn the fundamentals of programming with Phidgets.