HUB5000 User Guide: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 93: | Line 93: | ||
{{UGC-Addressing}} | {{UGC-Addressing}} | ||
{{UGC-DataInterval}} | {{UGC-DataInterval}} | ||
{{UGC-NonPhidgetSensor}} | |||
{{UGC-Entry|Updating the OS and VINT Hub Firmware| | {{UGC-Entry|Updating the OS and VINT Hub Firmware| | ||
| | | | ||
Revision as of 18:13, 20 July 2023
Part 1: Setup
Part 2: Using Your Phidget
About
The Wireless VINT Hub provides a stable wireless interface to connect your devices to your computer over your wi-fi network. The Wireless VINT Hub has 6 ports. Each port can either:
- Connect to a VINT Device
- Read a 0-5V Voltage or ratiometric sensor (connect to Analog Input sensors)
- Act as a digital output (control LEDs, relays, digital circuits, and other simple electronics)
- Act as a digital input (read the state of a switch)
Explore Your Phidget Channels Using the Control Panel
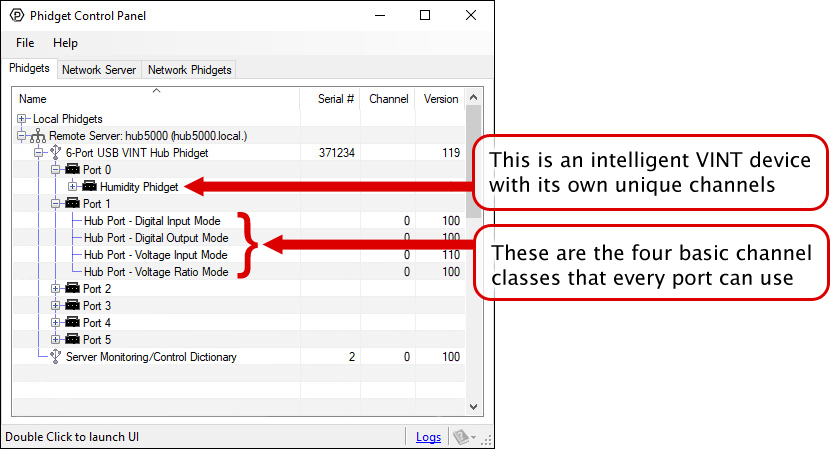
The Wireless VINT Hub is a connecting point between your computer and device allowing for simple communication. You can use your Control Panel to view your attached Phidgets. Explore the 5 types of connections bellow:
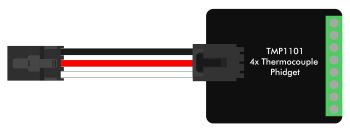
VINT Devices like the TMP1101 or DCC1003 are Phidgets that digitally communicate with the VINT Hub. Each device will have unique features, so it is recommended you visit the individual product page for more details.
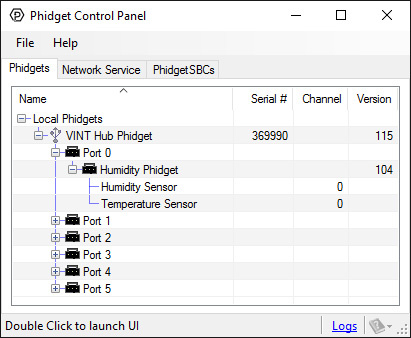
When attached correctly these Phidgets will appear by name in your Control Panel, with each channel listed below the name. For example, when the HUM1000 is attached you will see:
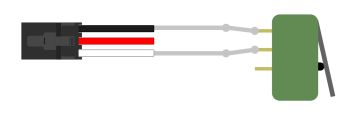
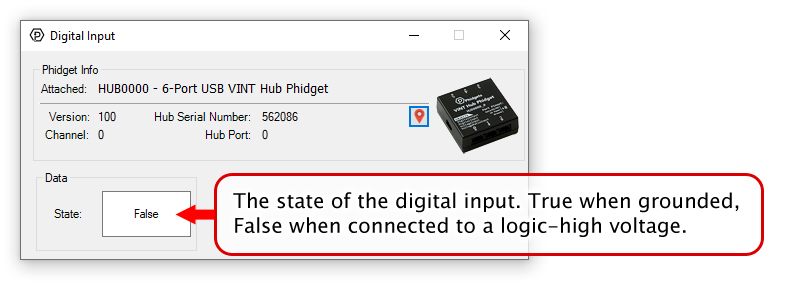
Digital Input is one of the VINT Hub’s built-in Channel Classes. Any of the these ports can act as an active-low digital input, making them useful for reading switches and buttons. The above image provides an example of how to wire a switch to be used with the VINT Hub.
If you open Digital Input Mode in the Control Panel you will be able to see the state of your button/switch.
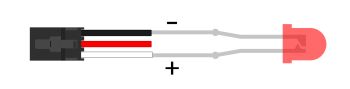
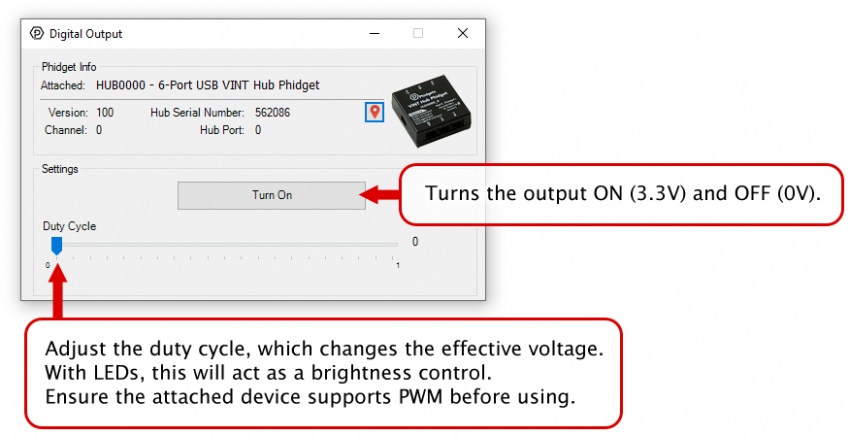
Digital Output is one of the VINT Hub’s built-in Channel Classes. Any of these ports can be used as a 3.3V digital output, making them useful for blinking LEDs. The above image demonstrates how to connect your LED to be used with the VINT Hub.
Open Digital Output Mode in the Control Panel to control the 3.3V output.
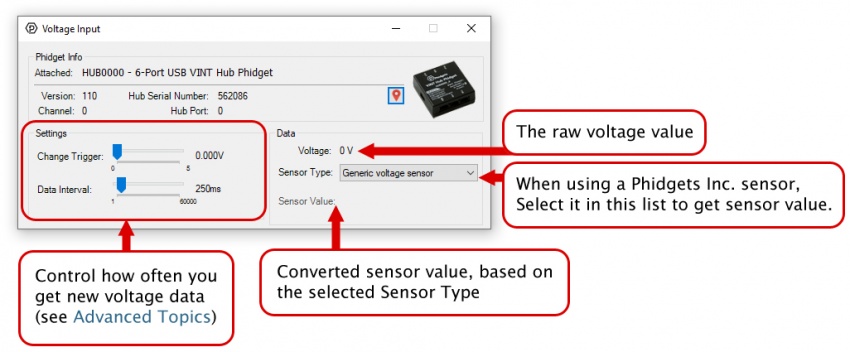
Voltage Input is one of the VINT Hub’s built-in Channel Classes. Any of these ports can be used to read voltage, making them great for reading non-ratiometric sensors and monitoring 5V digital circuits.
Open Voltage Input Mode in the Control Panel to view your device’s output voltage.
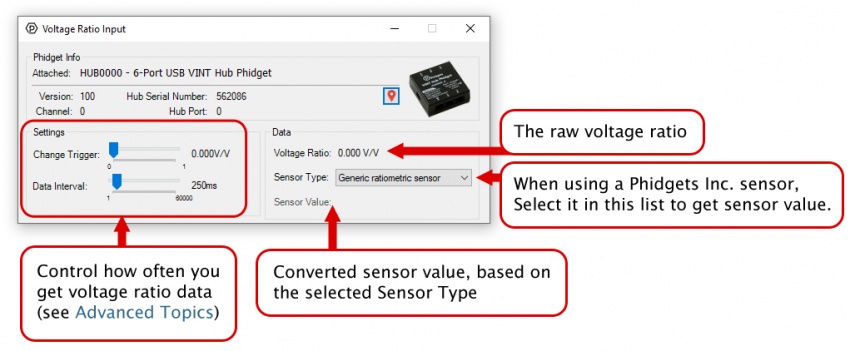
Voltage Ratio Input is one of the VINT Hub’s built-in Channel Classes. Any of these ports can act as a Voltage Ratio Input comparing the voltage provided to the voltage returned by the device, making it useful for connecting ratiometric sensors. The voltage ratio is reported in Volts per Volt. For example, if the Phidget is providing 5V and the sensor is sending back 2.5V, the ratio will be 0.5V/V.
Open Voltage Ratio Input Mode in the Control Panel to view your device’s voltage ratio.
Part 3: Create your Program
Since you'll be accessing your Phidget devices over the network, you should read the Phidget Network Server page to learn how to connect to remote Phidgets in your code.
Part 4: Advanced Topics and Troubleshooting
Before you open a Phidget channel in your program, you can set these properties to specify which channel to open. You can find this information through the Control Panel.
1. Open the Control Panel and double-click on the red map pin icon:
2. The Addressing Information window will open. Here you will find all the information you need to address your Phidget in your program.
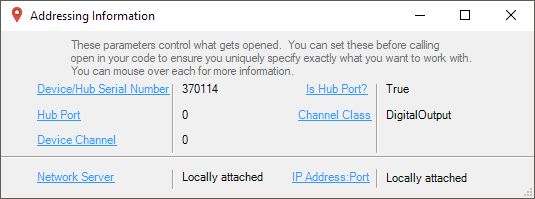
See the Phidget22 API for your language to determine exact syntax for each property.
The Change Trigger is the minimum change in the sensor data needed to trigger a new data event.
The Data Interval is the time (in ms) between data events sent out from your Phidget.
The Data Rate is the reciprocal of Data Interval (measured in Hz), and setting it will set the reciprocal value for Data Interval and vice-versa.
You can modify one or both of these values to achieve different data outputs. You can learn more about these properties here.

If the sensor requires 5V DC power and outputs a 0-5V signal, you can connect it directly to a VINT Port. The easiest way to connect it is to cut the end off of a Phidget Cable and solder the bare wires to the appropriate pins:
- Black: Ground
- Red: 5V Power
- White: 0-5V Analog Signal
You should check the sensor's datasheet to determine if it is Ratiometric or Non-Ratiometric. Ratiometric sensors output a voltage proportional to the voltage on the 5V power line, so they're more resilient against noise and power fluctuations. Non-Ratiometric sensors have their own 5V regulator, and always output a voltage relative to that 5V reference point. You need to use the appropriate channel class when opening the sensor (i.e. the VoltageRatioInput class or the VoltageInput class), or else your sensor readings will be inaccurate.
You can tell a sensor is ratiometric if the output in the datasheet is specified in units of volts-per-volt (V/V) or in terms of its supply voltage ("Vcc"):

This specification says the sensor outputs a voltage value of Vcc/512 for each inch of measurement, so it must be ratiometric.
If the sensor outputs a 0-5V signal, but requires 12-24V DC power, the VINT Hub cannot provide the correct voltage by itself. You can use a DAQ1400, and then connect that to one of the ports on your VINT Hub. See the DAQ1400 product page and User Guide for details.
An NPN sensor with a power requirement of 5V DC can be connected directly to a port on your VINT Hub:
- Black: Connect to sensor ground
- Red: Connect to sensor power
- White: Connect to sensor output
The easiest way to connect it is to snip the end off of a Phidget Cable and solder the wires to the sensor's wires.
A PNP sensor cannot be connected directly to a VINT Hub, because the digital inputs are active low. You'd need to use a pull-down resistor between the white and black wires of the Phidget cable that leads to the sensor in order for it to work.
Digital sensors that require 12V or 24V DC power can be used with the DAQ1400. See the DAQ1400 product page and User Guide for details.
Sensors with a 4-20mA output can also be interfaced with the DAQ1400. See the DAQ1400 product page and User Guide for details.
Sensors that use serial, I2C, or other digital communication protocols cannot easily be used with Phidgets. You should check the datasheet and pinout to see if they have an analog or 4-20mA output feature available.
To update the VINT Hub firmware, open the Phidget Control Panel and check if there is an upgrade icon beside the version number. If there is, right-click and select "Upgrade Firmware".
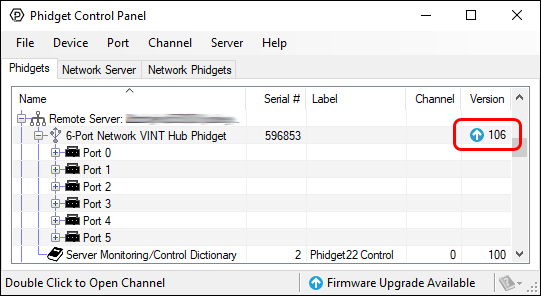
To update the OS firmware, go to the Network Phidgets tab in the control panel, find your HUB5000 and double-click on it. If the OS firmware is out of date, you'll see the following window pop up:
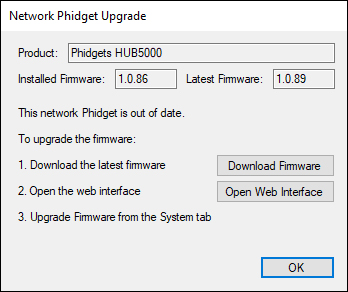
Follow the steps in the window above:
- Download the firmware (you can get it here if the button does not work)
- Open the web interface by clicking the button or entering the HUB5000's IP address in your web browser.
- Go to the System tab and scroll down to the Upgrade Firmware section. Select the file you just downloaded and click Upgrade and Restart. You'll be instructed to wait a few minutes before logging back into the web interface.
When you log in, you can confirm that the new version has successfully installed by checking to see if the firmware version listed in the "Status" section matches the first three numbers in the firmware file name that you downloaded. You can also check the version in the Network Phidgets tab on the Phidget Control Panel.
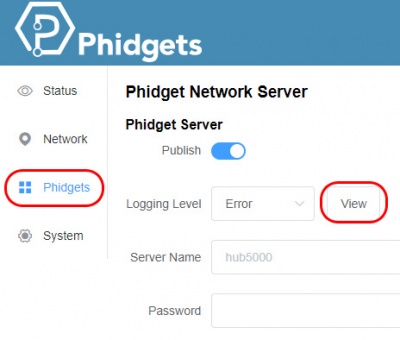
You can find the HUB5000's network server logs by opening the web configuration page as outlined in Part 1 of this User Guide. From there, click on "Phidgets" and then "View" beside the logging level selection.
For an ethernet connected HUB5000 to be completely CE compliant, you must put a ferrite bead on the ethernet cable. Ferrite beads are only necessary when building the HUB5000 into a larger system that needs to be CE compliant. You can find clamp-on ferrite beads at electronic parts stores such as Digikey.
For more information on the capabilities of the ports on the VINT Hub, see the VINT Guide.
To get to the HUB5000's configuration page, open the Phidget Control Panel and find it under the "Network Phidgets" tab as outlined in Part 1 of this User Guide.
If the HUB5000 is in access point mode, you can access the configuration page through your phone: Connect to the HUB5000 Wi-Fi signal and enter the password on the sticker. Once you're connected, go to your internet app and go to address 192.168.100.1 . This address will take you to the configuration login page.
- Status: This section lists the hardware and firmware version of the HUB5000, along with the network addresses.
- Network: This section allows you to change the network connection settings and switch between Access Point mode and Client mode.
- Phidgets: This section has the Phidget Server controls(including controls to change the log level and view the log file). This section also contains the Web Server controls.
- System: This section allows you to change the password, and has other advanced settings including firmware upgrade and system/kernel logs.

Pressing the reset button will reboot the HUB5000.
Holding the button down for 10 seconds before releasing will perform a reset. The reset will clear all settings, including the web configuration page password, and reset the Wi-Fi password to the one on the HUB5000's label.
As a last resort, you can perform a factory reset. Only perform a factory reset if the regular reset is not working, or there was an error during a firmware upgrade. Holding the button down before plugging in power, and keeping pressed for 15 seconds before releasing, will restore the original factory firmware. The red LED will start blinking after the button is released. Once the red LED turns solid, the restore is complete.
When opening channels with Phidgets, you can set several properties to make sure you are accessing the precise channel you want. The HUB5000 has a unique serial number that can be used to find its ports or any VINT devices connected to them. If you want something more customizable and human-readable, you can use the device label instead. You can customize the device label by using writeDeviceLabel on the Hub object after it has been opened.
With the device label, you can address any of the VINT Hub's channels, or any connected VINT device channels. The device label will remain after the VINT Hub is unplugged as it is stored in flash memory.

