1024-1 User Guide: Difference between revisions
| Line 101: | Line 101: | ||
| | | | ||
If you are using multiple RFID readers, placing them too close together will cause interference when reading tags. You could work around this problem by rapidly "polling" each 1024 by turning the antenna on, checking for tags, and then turning it off in sequence. Of course, this will lengthen the amount of time it takes for your system to read a tag, since you may have to wait for the nearest reader to become active. | If you are using multiple RFID readers, placing them too close together will cause interference when reading tags. You could work around this problem by rapidly "polling" each 1024 by turning the antenna on, checking for tags, and then turning it off in sequence. Of course, this will lengthen the amount of time it takes for your system to read a tag, since you may have to wait for the nearest reader to become active. | ||
}} | |||
{{UGC-Entry|Object Speed| | |||
| | |||
When trying to read tags, you should allow the tag to remain within detection range for at least 50ms. Tags moving through the detection area faster than this may not register at all. | |||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 124: | Line 129: | ||
:This unit was tested with shielded cables on the peripheral devices. Shielded cables must be used with the unit to ensure compliance. | :This unit was tested with shielded cables on the peripheral devices. Shielded cables must be used with the unit to ensure compliance. | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{UGC-End}} | {{UGC-End}} | ||
Revision as of 20:21, 10 September 2024
Part 1: Setup
Part 2: Using Your Phidget
Phidget Control Panel
You can use the Phidget Control Panel to explore your device's functionality.
1. After opening the Phidget Control Panel you will find the following channels:
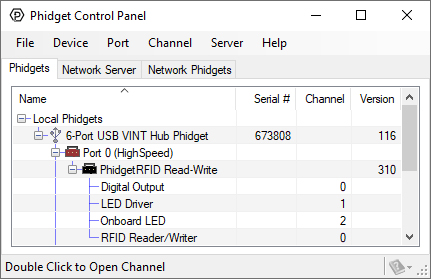
2. Double click on a channel to open an example program.
In your Control Panel, double click on "Digital Output":
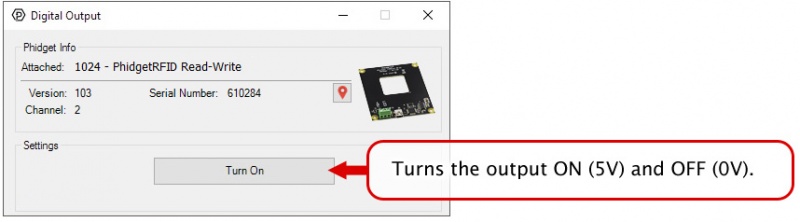
In your Control Panel, double click on "LED Driver":

In your Control Panel, double click on "Onboard LED":
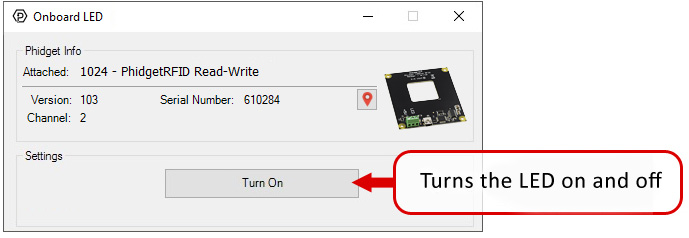
In your Control Panel, double click on "RFID Reader/Writer":
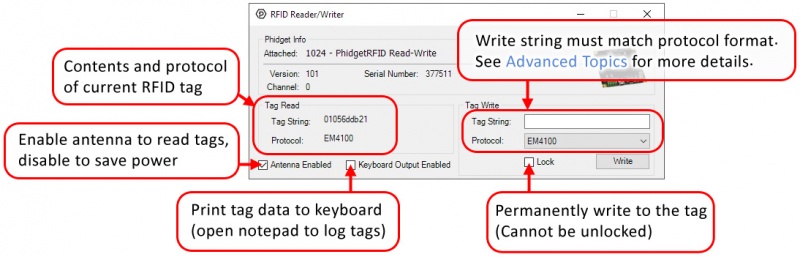
Part 3: Create your Program
Part 4: Advanced Topics and Troubleshooting
Firmware Upgrade
MacOS users can upgrade device firmware by double-clicking the device row in the Phidget Control Panel.
Linux users can upgrade via the phidget22admin tool (see included readme for instructions).
Windows users can upgrade the firmware for this device using the Phidget Control Panel as shown below.
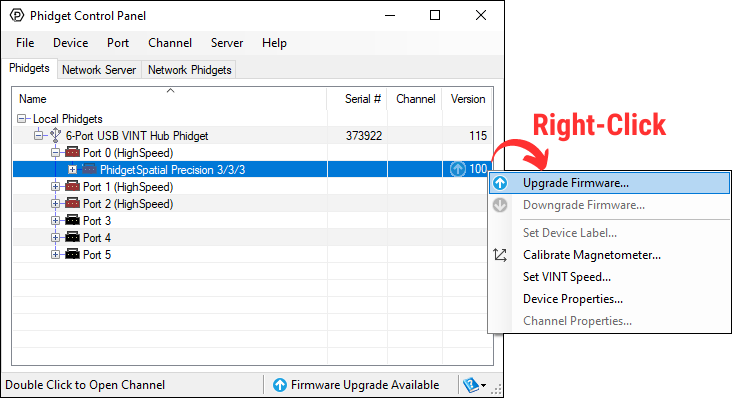
Firmware Downgrade
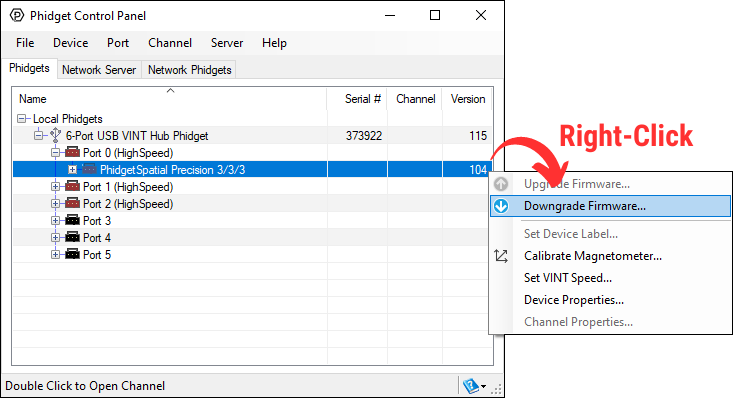
Firmware upgrades include important bug fixes and performance improvements, but there are some situations where you may want to revert to an old version of the firmware (for instance, when an application you're using is compiled using an older version of phidget22 that doesn't recognize the new firmware).
MacOS and Linux users can downgrade using the phidget22admin tool in the terminal (see included readme for instructions).
Windows users can downgrade directly from the Phidget Control Panel if they have driver version 1.9.20220112 or newer:
Firmware Version Numbering Schema
Phidgets device firmware is represented by a 3-digit number. For firmware patch notes, see the device history section on the Specifications tab on your device's product page.
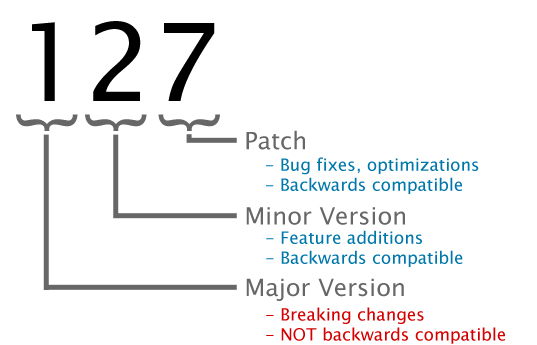
- If the digit in the 'ones' spot changes, it means there have been bug fixes or optimizations. Sometimes these changes can drastically improve the performance of the device, so you should still upgrade whenever possible. These upgrades are backwards compatible, meaning you can still use this Phidget on a computer that has Phidget22 drivers from before this firmware upgrade was released.
- If the digit in the 'tens' spot changes, it means some features were added (e.g. new API commands or events). These upgrades are also backwards compatible, in the sense that computers running old Phidget22 drivers will still be able to use the device, but they will not be able to use any of the new features this version added.
- If the digit in the 'hundreds' spot changes, it means a major change has occurred (e.g. a complete rewrite of the firmware or moving to a new architecture). These changes are not backwards compatible, so if you try to use the upgraded board on a computer with old Phidget22 drivers, it will show up as unsupported in the Control Panel and any applications build using the old libraries won't recognize it either. Sometimes, when a Phidget has a new hardware revision (e.g. 1018_2 -> 1018_3), the firmware version's hundreds digit will change because entirely new firmware was needed (usually because a change in the processor). In this case, older hardware revisions won't be able to be upgraded to the higher version number and instead continue to get bug fixes within the same major revision.
A protocol is a way of encoding data on an RFID tag. We support three reading and writing protocols with the 1024:
EM4100
EM4100 is a commonly used protocol that all previous PhidgetRFID readers have supported. This protocol encodes 40 bits of arbitrary data.
Phidgets represents this protocol as a 10-digit hex string, include leading 0's (e.g. 0087f3bc91).
ISO11785 FDX-B
ISO11785 defines tags used for animal IDs. If you have a pet cat or dog, chances are high that they have one of these tags implanted. FDX-B refers to the way that the ISO11785 data is encoded on the RFID tag, and is the industry-standard encoding scheme.
This tag consists of a 10-bit country code and a 38-bit unique ID.
The country code is ISO 3166. The '999' code is set aside for testing.
The unique ID is 38-bit unsigned, so that's a range of 0 - 274,877,906,943.
Phidgets represents this protocol as a 15-digit decimal number – with the 3-digit country code leading a 12-digit id. For example, 999000000000123 would represent the testing country code and an id of 123. Please note that the 12-digit id part cannot exceed the 38-bit maximum integer value of 274,877,906,943.
Animal tag strings with a valid country code are supposed to be uniquely assigned if actually deployed in the wild.
HID H10301 (HID 26-bit/Wiegand)
Note: This protocol is only supported with firmware version 310 or higher
The most common type of HID tag, the H10301 is commonly used for access control.
Phidgets represents this protocol as an eight-digit number - with a three-digit facility code and a five-digit card number. The card number is often printed on the card, while the facility code is not.
The facility code is 8-bits, and can support numbers up to 255, and the card number is 16 bits, and supports values up to 65535.
HID Generic
Note: This protocol is only supported with firmware version 310 or higher
HID provides a number of cards using proprietary protocols, from which the raw bits can be read and written, but not intelligently interpreted using the Phidget 1024_1. When an HID tag does not match the H10301 format, your Phidget will read the tag as an HID generic tag, and will present the 44 raw bits of tag data as an 11-digit hexadecimal string.
This means the 1024_1 can read and copy such tags, but cannot provide any insight on the protocol that would allow you to write new valid tags of the same kind.
PhidgetTAG
The PhidgetTAG protocol is unique to the PhidgetRFID 1024, added for users that want plain-text alphanumeric tag strings.
This protocol allows storing an ASCII string, up to 24 characters (e.g. I am a Phidgets Tag!)
This protocol supports 7-bit ASCII, and as such will support all standard text and control codes, but not extended ASCII codes.
If you are using multiple RFID readers, placing them too close together will cause interference when reading tags. You could work around this problem by rapidly "polling" each 1024 by turning the antenna on, checking for tags, and then turning it off in sequence. Of course, this will lengthen the amount of time it takes for your system to read a tag, since you may have to wait for the nearest reader to become active.
When trying to read tags, you should allow the tag to remain within detection range for at least 50ms. Tags moving through the detection area faster than this may not register at all.

|
Phidgets Inc |
| 1024_1 | |
| FCC ID: SUT1024-1 |
- This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
- (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and
- (2) This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
- Note: The manufacturer is not responsible for any radio or TV interference caused by unauthorized modifications to this equipment. Such modifications could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
- The user is cautioned that any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
- This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
- • Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
- • Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
- • Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
- • Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
- This unit was tested with shielded cables on the peripheral devices. Shielded cables must be used with the unit to ensure compliance.
