OS - Android: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (78 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<metadesc>Communicate over USB with sensors, controllers and relays with Phidgets! Program in Android using Android Java.</metadesc> | |||
[[Category:OS]] | [[Category:OS]] | ||
{| | |||
|style="vertical-align:middle; width: 60%;"| | |||
==Getting Started with Android== | |||
Welcome to using Phidgets with Android! | |||
[[ | If this is your first Phidget, we highly recommend working through the Getting Started guide for your specific Phidget device, which may be found in its [[:Category:UserGuide|user guide]]. If you are ready to go, the first step to creating an Android application with Phidgets is downloading the Phidget libraries on your development machine! | ||
|{{TOC limit|2}} | |||
|} | |||
==Download== | |||
The Phidget libraries for Android development are available here: | |||
*[https://cdn.phidgets.com/downloads/phidget22/libraries/android/phidget22-android.zip Android Java Libraries] | |||
Download and unpack the libraries. You will need to reference these files from your project in order to use Phidgets. This step is covered in detail in the [[Language - Android Java | Android Java page]]. If you need to access older versions of the libraries, [https://www.phidgets.com/downloads/phidget22/libraries/android/ click here]. | |||
==Direct USB Connection== | |||
For directly controlling a Phidget with your Android device (i.e. plugging a Phidget directly into your device), you will need to ensure the device is capable of being a USB host. Just having a port that the USB cable can fit into does not necessarily indicate that the port can host a USB device. On the other hand, some phones can use an OTG (on-the-go) cable to allow plugging USB devices into their charging port. Some tablets (like the Samsung Galaxy Tab, for example) have the large 30-pin connectors that can be changed into a USB host using an adapter. | |||
The best way to know before getting your hands on a device is to check its specifications for whether it can serve as a USB host. Alternately, a quick way to figure out if your device can serve as a USB host is to try plugging other devices (such as a mouse, or USB memory stick) into your Android device. | |||
== | ==Network Server== | ||
In applications where you aren't plugging Phidgets into your Android device directly, you must have a host computer that is running the Phidget Network Server. | |||
= | [[Image:android-connection.jpg|link=|center]] | ||
*Host computer: the computer that is physically connected to the Phidgets via USB and is running the Phidget Network Server. | |||
*Client computer: a computer running a Phidgets application that accesses Phidgets connected to the host computer. When developing for Android, your Android device acts as the client. | |||
In this case, you will need to install the Phidget libraries on your host computer, and get the Phidget Network Server up and running. Follow the ''Getting Started'' guide, and continue with the ''Network Server'' guide for your operating system. When you are done, come back and finish this guide! | |||
*[[OS - Windows| Windows]] | |||
*[[OS - macOS| macOS]] | |||
*[[OS - Linux| Linux]] | |||
*[[OS - Phidget SBC| Phidget Single Board Computer]] | |||
[ | |||
==Programming Languages== | ==Programming Languages== | ||
Now that you have the basics set up, check out the [[Language - Android Java|Android Java]] page for information on how to write code for Phidgets to run on your Android device. | |||
Note that Android Java is NOT the same as mainstream Java. Any Java programs you have will probably need significant modification before they run on Android, including our [[Language - Java|mainstream Java]] Phidget Examples. | |||
==Software License== | |||
By downloading the Android library you agree to adhere to the terms of the [{{SERVER}}/documentation/Licenses/Phidgets_EULA.pdf Phidgets End User License Agreement]. The C API section of Phidget22 is covered by the [https://opensource.org/licenses/BSD-3-Clause The 3-Clause BSD License]. The source code of C API can be found [{{SERVER}}/downloads/phidget22/libraries/linux/libphidget22.tar.gz here]. | |||
Latest revision as of 21:22, 19 December 2024
Getting Started with AndroidWelcome to using Phidgets with Android! If this is your first Phidget, we highly recommend working through the Getting Started guide for your specific Phidget device, which may be found in its user guide. If you are ready to go, the first step to creating an Android application with Phidgets is downloading the Phidget libraries on your development machine! |
Download
The Phidget libraries for Android development are available here:
Download and unpack the libraries. You will need to reference these files from your project in order to use Phidgets. This step is covered in detail in the Android Java page. If you need to access older versions of the libraries, click here.
Direct USB Connection
For directly controlling a Phidget with your Android device (i.e. plugging a Phidget directly into your device), you will need to ensure the device is capable of being a USB host. Just having a port that the USB cable can fit into does not necessarily indicate that the port can host a USB device. On the other hand, some phones can use an OTG (on-the-go) cable to allow plugging USB devices into their charging port. Some tablets (like the Samsung Galaxy Tab, for example) have the large 30-pin connectors that can be changed into a USB host using an adapter.
The best way to know before getting your hands on a device is to check its specifications for whether it can serve as a USB host. Alternately, a quick way to figure out if your device can serve as a USB host is to try plugging other devices (such as a mouse, or USB memory stick) into your Android device.
Network Server
In applications where you aren't plugging Phidgets into your Android device directly, you must have a host computer that is running the Phidget Network Server.
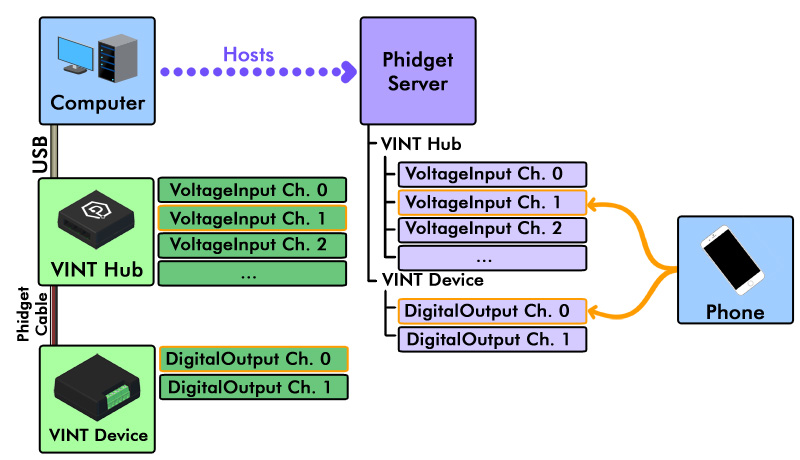
- Host computer: the computer that is physically connected to the Phidgets via USB and is running the Phidget Network Server.
- Client computer: a computer running a Phidgets application that accesses Phidgets connected to the host computer. When developing for Android, your Android device acts as the client.
In this case, you will need to install the Phidget libraries on your host computer, and get the Phidget Network Server up and running. Follow the Getting Started guide, and continue with the Network Server guide for your operating system. When you are done, come back and finish this guide!
Programming Languages
Now that you have the basics set up, check out the Android Java page for information on how to write code for Phidgets to run on your Android device.
Note that Android Java is NOT the same as mainstream Java. Any Java programs you have will probably need significant modification before they run on Android, including our mainstream Java Phidget Examples.
Software License
By downloading the Android library you agree to adhere to the terms of the Phidgets End User License Agreement. The C API section of Phidget22 is covered by the The 3-Clause BSD License. The source code of C API can be found here.
