1014 User Guide: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (16 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOINDEX__ | |||
<metadesc>The Phidget InterfaceKit 0/0/4 connects to your computer via USB and has 4 SPDT mechanical relays rated at 210W for DC or 1750VA for AC. </metadesc> | |||
[[Category:UserGuide]] | [[Category:UserGuide]] | ||
==Getting Started== | ==Getting Started== | ||
{{UGIntro|1014}} | |||
*1014 Phidget InterfaceKit [{{SERVER}}/products.php?product_id=1014 1014 Phidget InterfaceKit] | |||
*USB cable and computer | |||
*something to use with the 1014 (e.g. power supply and load) | |||
{{ | Next, you will need to connect the pieces: | ||
[[Image:1014_2_Connecting_The_Hardware.jpg|600px|right|link=]] | |||
# Connect the load and power supply in series. | |||
# Connect one end to the 0C (Common) terminal, and the other to the NO (Normally open) terminal. | |||
# Connect the 1014 to your computer using the USB cable. | |||
<br clear="all"> | |||
{{UGIntroDone|1014}} | |||
== | ==Using the 1014== | ||
{{ | {{UGcontrolpanel|1014}} | ||
{{ | {{UgRelayOutput|1014}} | ||
}} | |||
{{ugAddressingInformation}} | |||
{{ | {{ugUsingYourOwnProgram|1014}} | ||
==Technical Details== | ==Technical Details== | ||
===Relays=== | ===Relays=== | ||
A relay is an electrically-controlled switch. Although many types of electrical switches exist, a relay’s mechanical nature gives it the advantage of reliability and current-switching capacity. The main disadvantage to using mechanical relays is their limited life-span, as opposed to solid state relays who do not suffer from this drawback. For more information, check the [[Mechanical Relay Guide]] and the [[Solid State Relay Guide]]. | |||
A relay is an electrically-controlled switch. | |||
===Using a Digital Output Relay=== | ===Using a Digital Output Relay=== | ||
[[File:1014_2_Relay_Diagram.jpg|right|300px|link=]] | [[File:1014_2_Relay_Diagram.jpg|right|300px|link=]] | ||
Relays have a connection scheme determined by the arrangement of contacts within the relay. | Relays have a connection scheme determined by the arrangement of contacts within the relay. Because relays are a type of switch, they are defined in the same way other electromechanical switches are defined. | ||
In switch schemes, the number of poles represents the number of common terminals a switch has, and the number of throws represents the number of switchable terminals that exist for each pole. | In switch schemes, the number of poles represents the number of common terminals a switch has, and the number of throws represents the number of switchable terminals that exist for each pole. The relays used in the InterfaceKit 0/0/4 are SPDT relays: single pole, double throw. The internal construction of this type of relay is depicted in the diagram above. Many other types of relays exist: SPST, DPDT, and DPST, to name a few. | ||
In an SPDT relay, one of the throw terminals is labelled | In an SPDT relay, one of the throw terminals is labelled ''normally closed'' (NC), and the other is labelled ''normally open'' (NO). As the name indicates, the normally closed terminal is the terminal connected to common when the relay coil is not powered. When the relay coil is energized by the relay control circuit, the electromagnetic field of the coil forces the switch element inside the relay to break its contact with the normally closed terminal and make contact with the normally open terminal. The switch element would then connect the normally open terminal and the common terminal. | ||
<br clear=all> | <br clear=all> | ||
===Using Relays as an H-Bridge for Motor Forward/Reverse=== | ===Using Relays as an H-Bridge for Motor Forward/Reverse=== | ||
[[File:1014_1_Bridge_Diagram.jpg|right|450px|link=]] | [[File:1014_1_Bridge_Diagram.jpg|right|450px|link=]] | ||
Connect the load (typically a DC Motor) to the COM terminals of the relay. The | Connect the load (typically a DC Motor) to the COM terminals of the relay. The ''normally open'' (NO) terminals are connected to the power supply (VCC), and the ''normally closed'' (NC) terminals are connected to the ground (GND) of the power supply. You can toggle the corresponding output to switch the relays. | ||
Looking at the diagram, when LeftCtrl is enabled and RightCtrl is disabled, the current will flow from the NO terminal of relay K1 through the motor and into the NC terminal of relay K2. This will cause the motor to rotate in one direction. | Looking at the diagram, when LeftCtrl is enabled and RightCtrl is disabled, the current will flow from the NO terminal of relay K1 through the motor and into the NC terminal of relay K2. This will cause the motor to rotate in one direction. | ||
| Line 87: | Line 57: | ||
===Wetting Current=== | ===Wetting Current=== | ||
When a relay is in one switch position for a period of time, oxidation of the open contact(s) can occur. Depending upon the internal coating material of the contacts, oxide films of varying density will be displaced upon the surface of open contacts; this film acts as an insulator to current flow. When the relay is switched, a certain amount of current flowing through the contacts, known as the wetting current, is required to remove the film of oxides and ensure proper conduction. Because of this requirement, these relays are not reliable for signal switching. Check the specification table for your relay board to find out the Minimum Load Current or ''Wetting Current''. | |||
When a relay is in one switch position for a period of time, oxidation of the open contact(s) can occur. Depending upon the internal coating material of the contacts, oxide films of varying density will be displaced upon the surface of open contacts; this film acts as an insulator to current flow. When the relay is switched, a certain amount of current flowing through the contacts, known as the wetting current, is required to remove the film of oxides and ensure proper conduction. | |||
===Load Noise=== | ===Load Noise=== | ||
If highly inductive loads are used with the InterfaceKit, it is recommended that a noise limiting component be used to prevent damage to the device. An MOV, TVS diode, or kickback diode (for DC applications) shunted across the load will assist in dissipating voltage transients. | If highly inductive loads are used with the InterfaceKit, it is recommended that a noise limiting component be used to prevent damage to the device. An MOV, TVS diode, or kickback diode (for DC applications) shunted across the load will assist in dissipating voltage transients. | ||
{{UGnext|}} | |||
{{ | |||
Latest revision as of 19:49, 1 June 2023
Getting Started
Welcome to the 1014 user guide! In order to get started, make sure you have the following hardware on hand:
- 1014 Phidget InterfaceKit 1014 Phidget InterfaceKit
- USB cable and computer
- something to use with the 1014 (e.g. power supply and load)
Next, you will need to connect the pieces:
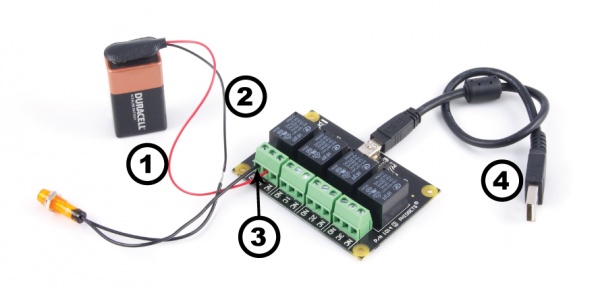
- Connect the load and power supply in series.
- Connect one end to the 0C (Common) terminal, and the other to the NO (Normally open) terminal.
- Connect the 1014 to your computer using the USB cable.
Now that you have everything together, let's start using the 1014!
Using the 1014
Phidget Control Panel
In order to demonstrate the functionality of the 1014, the Phidget Control Panel running on a Windows machine will be used.
The Phidget Control Panel is available for use on both macOS and Windows machines.
Windows
To open the Phidget Control Panel on Windows, find the ![]() icon in the taskbar. If it is not there, open up the start menu and search for Phidget Control Panel
icon in the taskbar. If it is not there, open up the start menu and search for Phidget Control Panel
macOS
To open the Phidget Control Panel on macOS, open Finder and navigate to the Phidget Control Panel in the Applications list. Double click on the ![]() icon to bring up the Phidget Control Panel.
icon to bring up the Phidget Control Panel.
For more information, take a look at the getting started guide for your operating system:
Linux users can follow the getting started with Linux guide and continue reading here for more information about the 1014.
First Look
After plugging the 1014 into your computer and opening the Phidget Control Panel, you will see something like this:
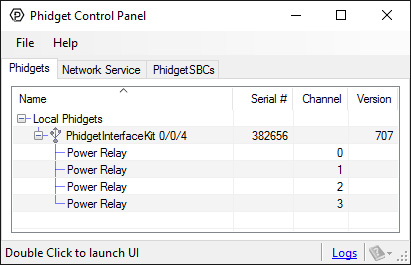
The Phidget Control Panel will list all connected Phidgets and associated objects, as well as the following information:
- Serial number: allows you to differentiate between similar Phidgets.
- Channel: allows you to differentiate between similar objects on a Phidget.
- Version number: corresponds to the firmware version your Phidget is running. If your Phidget is listed in red, your firmware is out of date. Update the firmware by double-clicking the entry.
The Phidget Control Panel can also be used to test your device. Double-clicking on an object will open an example.
Relay Output
Double-click on a Digital Output object labelled Power Relay in order to run the example:
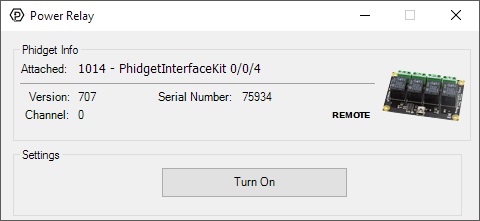
General information about the selected object will be displayed at the top of the window. You can also experiment with the following functionality:
- Toggle the state of the relay by pressing the button.
Finding The Addressing Information
Before you can access the device in your own code, and from our examples, you'll need to take note of the addressing parameters for your Phidget. These will indicate how the Phidget is physically connected to your application. For simplicity, these parameters can be found by clicking the button at the top of the Control Panel example for that Phidget.
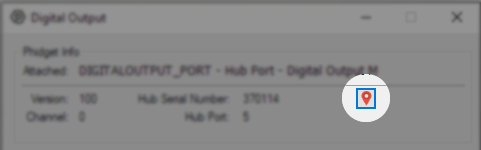
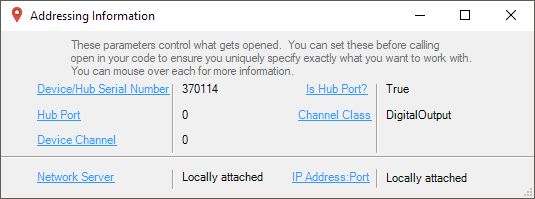
In the Addressing Information window, the section above the line displays information you will need to connect to your Phidget from any application. In particular, note the Channel Class field as this will be the API you will need to use with your Phidget, and the type of example you should use to get started with it. The section below the line provides information about the network the Phidget is connected on if it is attached remotely. Keep track of these parameters moving forward, as you will need them once you start running our examples or your own code.
Using Your Own Program
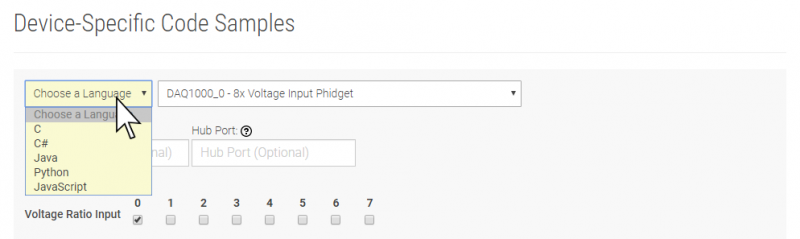
You are now ready to start writing your own code for the device. The best way to do that is to start from our Code Samples.
Select your programming language of choice from the drop-down list to get an example for your device. You can use the options provided to further customize the example to best suit your needs.
Once you have your example, you will need to follow the instructions on the page for your programming language to get it running. To find these instructions, select your programming language from the Programming Languages page.
Technical Details
Relays
A relay is an electrically-controlled switch. Although many types of electrical switches exist, a relay’s mechanical nature gives it the advantage of reliability and current-switching capacity. The main disadvantage to using mechanical relays is their limited life-span, as opposed to solid state relays who do not suffer from this drawback. For more information, check the Mechanical Relay Guide and the Solid State Relay Guide.
Using a Digital Output Relay
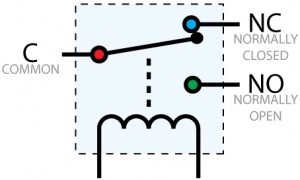
Relays have a connection scheme determined by the arrangement of contacts within the relay. Because relays are a type of switch, they are defined in the same way other electromechanical switches are defined.
In switch schemes, the number of poles represents the number of common terminals a switch has, and the number of throws represents the number of switchable terminals that exist for each pole. The relays used in the InterfaceKit 0/0/4 are SPDT relays: single pole, double throw. The internal construction of this type of relay is depicted in the diagram above. Many other types of relays exist: SPST, DPDT, and DPST, to name a few.
In an SPDT relay, one of the throw terminals is labelled normally closed (NC), and the other is labelled normally open (NO). As the name indicates, the normally closed terminal is the terminal connected to common when the relay coil is not powered. When the relay coil is energized by the relay control circuit, the electromagnetic field of the coil forces the switch element inside the relay to break its contact with the normally closed terminal and make contact with the normally open terminal. The switch element would then connect the normally open terminal and the common terminal.
Using Relays as an H-Bridge for Motor Forward/Reverse
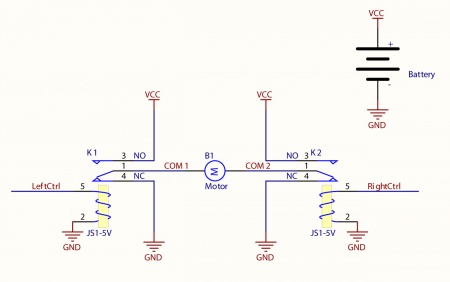
Connect the load (typically a DC Motor) to the COM terminals of the relay. The normally open (NO) terminals are connected to the power supply (VCC), and the normally closed (NC) terminals are connected to the ground (GND) of the power supply. You can toggle the corresponding output to switch the relays.
Looking at the diagram, when LeftCtrl is enabled and RightCtrl is disabled, the current will flow from the NO terminal of relay K1 through the motor and into the NC terminal of relay K2. This will cause the motor to rotate in one direction.
Similarily, if LeftCtrl is disabled and RightCtrl is enabled, the current will flow from the NO terminal of relay K2 through the motor and into the NC terminal of relay K1. This will cause the motor to rotate in the opposite direction.
When both LeftCtrl and RightCtrl are disabled, both ends of the motor will be shorted to ground and no current will flow. When both leftCtrl and RightCtrl are enabled, both ends of the motor will be shorted to VCC and again, no current will flow.
Wetting Current
When a relay is in one switch position for a period of time, oxidation of the open contact(s) can occur. Depending upon the internal coating material of the contacts, oxide films of varying density will be displaced upon the surface of open contacts; this film acts as an insulator to current flow. When the relay is switched, a certain amount of current flowing through the contacts, known as the wetting current, is required to remove the film of oxides and ensure proper conduction. Because of this requirement, these relays are not reliable for signal switching. Check the specification table for your relay board to find out the Minimum Load Current or Wetting Current.
Load Noise
If highly inductive loads are used with the InterfaceKit, it is recommended that a noise limiting component be used to prevent damage to the device. An MOV, TVS diode, or kickback diode (for DC applications) shunted across the load will assist in dissipating voltage transients.
What to do Next
- Programming Languages - Find your preferred programming language here and learn how to write your own code with Phidgets!
- Phidget Programming Basics - Once you have set up Phidgets to work with your programming environment, we recommend you read our page on to learn the fundamentals of programming with Phidgets.