OUT1001 User Guide: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOINDEX__ | |||
__NOTOC__ | |||
<metadesc>Produce a voltage from -10 to +10 volts with the Isolated 12-Bit Voltage Output Phidget. Connects to a port on your VINT Hub.</metadesc> | |||
[[Category:UserGuide]] | [[Category:UserGuide]] | ||
== | ==Part 1: Setup== | ||
{{ | {{PT1 Deck Sequence}} | ||
== Part 2: Using Your Phidget == | |||
===About=== | |||
The OUT1001 can provide a DC voltage between -10V and +10V on the 10V terminal. The 5V terminal provides a voltage between 0V to 5V. This Phidget is ideal for analog voltage-controlled devices. | |||
[[Image:OUT1001_About.jpg|link=|center]] | |||
'''Note:''' The 10V terminal has a resolution of 4.9 mV DC. The 5V terminal has a resolution of 1.2 mV DC. | |||
===Explore Your Phidget Channels Using the Control Panel=== | |||
You can use your Control Panel to explore your Phidget's channels. | |||
===Current Sourcing and Sinking | '''1.''' Open your Control Panel, and you will find the '''Isolated 12-bit Volage Output Phidget''' channel: | ||
[[Image:OUT1001_Panel.jpg|link=|center]] | |||
'''2.''' Double click on the channel to open an example program. This channel belongs to the '''Voltage Output''' channel class: | |||
{{UGC-Start}} | |||
{{UGC-Entry|Isolated 12-bit Volage Output Phidget: |Produce a DC voltage for the connected circuit or device | |||
| | |||
In your Control Panel, double click on "Isolated 12-bit Volage Output Phidget": | |||
[[Image:OUT1001-VoltageOutput.jpg|center|link=]]}} | |||
{{UGC-End}} | |||
{{UG-Part3}} | |||
== Part 4: Advanced Topics and Troubleshooting == | |||
{{UGC-Start}} | |||
{{UGC-Addressing}} | |||
{{UGC-Firmware}} | |||
{{UGC-Entry|Current Sourcing and Sinking| | |||
| | |||
The OUT1001 should be subjected to a minimal current draw to ensure maximum voltage precision across the device's full range (less than 5mA in ±10V mode). 5V mode should only be used to set a voltage in high-impedance applications. | |||
However, in the event you plan to power a small load with this device, the OUT1001 will either be sourcing or sinking current when in use. | |||
The device will be a sourcing current when the device is connected to a circuit with a lower voltage potential than its voltage setting. In this situation, the current will be flowing out from the OUT1001 into the circuit. | |||
The device will be a sinking current when the device is connected to a circuit with a higher voltage potential than its voltage setting. In this situation, the current will flow from the circuit into the OUT1001. | |||
[[Image:sourcesink_diagram.jpg|link=|600px|center]] | [[Image:sourcesink_diagram.jpg|link=|600px|center]] | ||
The OUT1001 can source or sink up to 18mA of current depending on the selected output voltage and mode. | The OUT1001 can source or sink up to 18mA of current depending on the selected output voltage and mode. The chart below shows the maximum available voltage for a given expected current draw. | ||
[[Image:sourcesink1001_5v.jpg|link=|650px|center]] | [[Image:sourcesink1001_5v.jpg|link=|650px|center]] | ||
| Line 37: | Line 58: | ||
[[Image:sourcesink1001_10v.jpg|link=|650px|center]] | [[Image:sourcesink1001_10v.jpg|link=|650px|center]] | ||
For example, if the connected circuit is pulling 13mA of current, the OUT1001 will only be able to provide a maximum of 4V (in 0-5V mode), even if you try to set it to a higher value.}} | |||
{{UGC-Entry|I’m seeing strange readings when I start my program or when switching voltage range| | |||
| | |||
{{ | The OUT1001 may have an unpredictable output voltage for a very short time immediately after the device changes modes or is turned on. If this is a problem in your application, and you have no way to ignore it via software, we recommend using a [[Solid_State_Relay_Primer|solid-state relay]] to switch the output on once it has stabilized.}} | ||
{{UGC-End}} | |||
Latest revision as of 21:18, 17 January 2022
Part 1: Setup
Part 2: Using Your Phidget
About
The OUT1001 can provide a DC voltage between -10V and +10V on the 10V terminal. The 5V terminal provides a voltage between 0V to 5V. This Phidget is ideal for analog voltage-controlled devices.
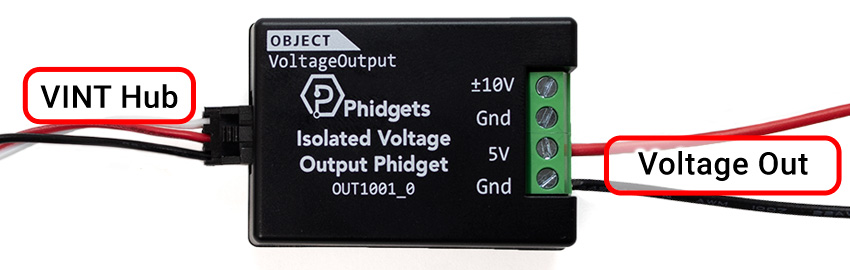
Note: The 10V terminal has a resolution of 4.9 mV DC. The 5V terminal has a resolution of 1.2 mV DC.
Explore Your Phidget Channels Using the Control Panel
You can use your Control Panel to explore your Phidget's channels.
1. Open your Control Panel, and you will find the Isolated 12-bit Volage Output Phidget channel:
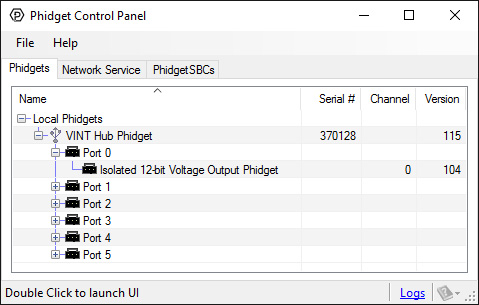
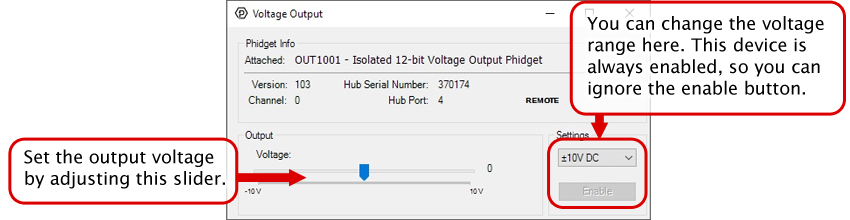
2. Double click on the channel to open an example program. This channel belongs to the Voltage Output channel class:
In your Control Panel, double click on "Isolated 12-bit Volage Output Phidget":
Part 3: Create your Program
Part 4: Advanced Topics and Troubleshooting
Before you open a Phidget channel in your program, you can set these properties to specify which channel to open. You can find this information through the Control Panel.
1. Open the Control Panel and double-click on the red map pin icon:
2. The Addressing Information window will open. Here you will find all the information you need to address your Phidget in your program.
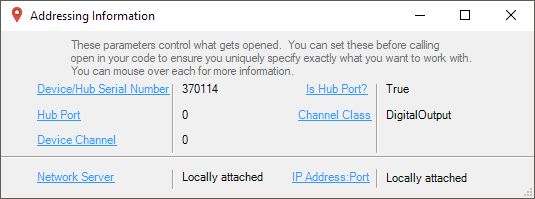
See the Phidget22 API for your language to determine exact syntax for each property.
Firmware Upgrade
MacOS users can upgrade device firmware by double-clicking the device row in the Phidget Control Panel.
Linux users can upgrade via the phidget22admin tool (see included readme for instructions).
Windows users can upgrade the firmware for this device using the Phidget Control Panel as shown below.
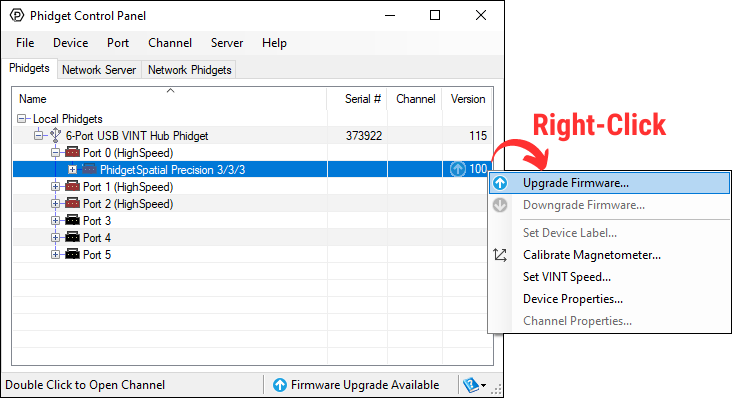
Firmware Downgrade
Firmware upgrades include important bug fixes and performance improvements, but there are some situations where you may want to revert to an old version of the firmware (for instance, when an application you're using is compiled using an older version of phidget22 that doesn't recognize the new firmware).
MacOS and Linux users can downgrade using the phidget22admin tool in the terminal (see included readme for instructions).
Windows users can downgrade directly from the Phidget Control Panel if they have driver version 1.9.20220112 or newer:
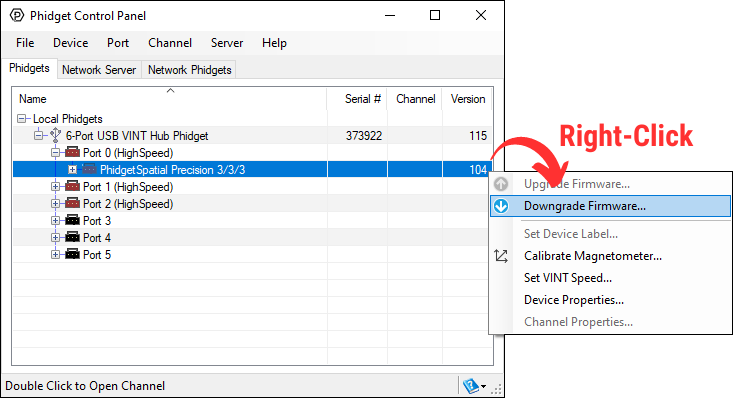
Firmware Version Numbering Schema
Phidgets device firmware is represented by a 3-digit number. For firmware patch notes, see the device history section on the Specifications tab on your device's product page.
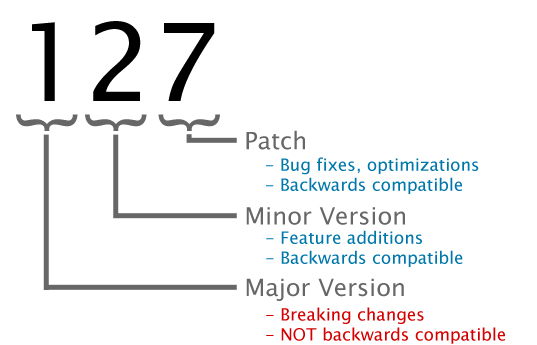
- If the digit in the 'ones' spot changes, it means there have been bug fixes or optimizations. Sometimes these changes can drastically improve the performance of the device, so you should still upgrade whenever possible. These upgrades are backwards compatible, meaning you can still use this Phidget on a computer that has Phidget22 drivers from before this firmware upgrade was released.
- If the digit in the 'tens' spot changes, it means some features were added (e.g. new API commands or events). These upgrades are also backwards compatible, in the sense that computers running old Phidget22 drivers will still be able to use the device, but they will not be able to use any of the new features this version added.
- If the digit in the 'hundreds' spot changes, it means a major change has occurred (e.g. a complete rewrite of the firmware or moving to a new architecture). These changes are not backwards compatible, so if you try to use the upgraded board on a computer with old Phidget22 drivers, it will show up as unsupported in the Control Panel and any applications build using the old libraries won't recognize it either. Sometimes, when a Phidget has a new hardware revision (e.g. 1018_2 -> 1018_3), the firmware version's hundreds digit will change because entirely new firmware was needed (usually because a change in the processor). In this case, older hardware revisions won't be able to be upgraded to the higher version number and instead continue to get bug fixes within the same major revision.
The OUT1001 should be subjected to a minimal current draw to ensure maximum voltage precision across the device's full range (less than 5mA in ±10V mode). 5V mode should only be used to set a voltage in high-impedance applications.
However, in the event you plan to power a small load with this device, the OUT1001 will either be sourcing or sinking current when in use.
The device will be a sourcing current when the device is connected to a circuit with a lower voltage potential than its voltage setting. In this situation, the current will be flowing out from the OUT1001 into the circuit.
The device will be a sinking current when the device is connected to a circuit with a higher voltage potential than its voltage setting. In this situation, the current will flow from the circuit into the OUT1001.
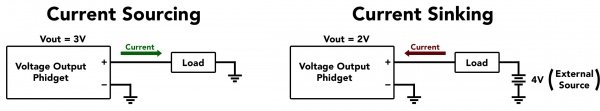
The OUT1001 can source or sink up to 18mA of current depending on the selected output voltage and mode. The chart below shows the maximum available voltage for a given expected current draw.
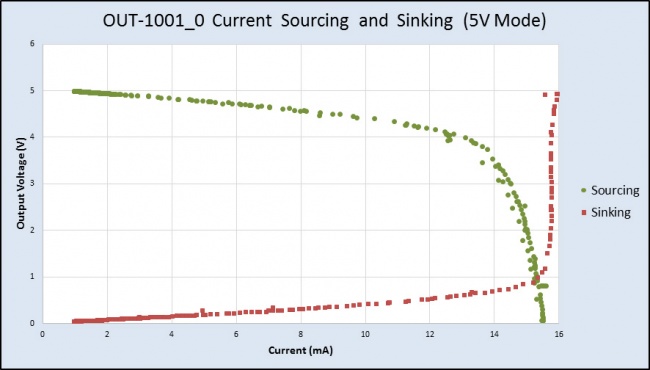
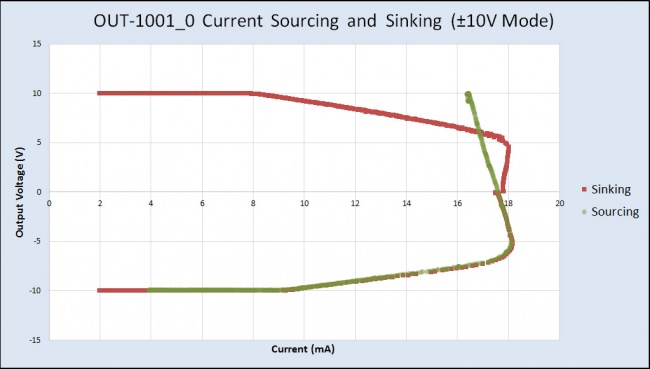
For example, if the connected circuit is pulling 13mA of current, the OUT1001 will only be able to provide a maximum of 4V (in 0-5V mode), even if you try to set it to a higher value.
The OUT1001 may have an unpredictable output voltage for a very short time immediately after the device changes modes or is turned on. If this is a problem in your application, and you have no way to ignore it via software, we recommend using a solid-state relay to switch the output on once it has stabilized.
