Language - C Windows CodeBlocks: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Language]] | [[Category:Language]]{{NoTitle}}{{Language_-_C_Dev_Environment_Table}} | ||
{{NoTitle}} | |||
{{Language_-_C_Dev_Environment_Table}} | |||
{| | {| | ||
|style="vertical-align:middle; width: 60%;"| | |style="vertical-align:middle; width: 60%;"| | ||
Revision as of 19:01, 22 May 2019
| C Development Environments | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Language - C Windows with Code::Blocks Welcome to using Phidgets with C! By using C, you will have access to the complete Phidget22 API, including events. Code::Blocks is a free, open source cross-platform IDE that can be used for C and C++. |
Install Phidget Drivers for Windows
Before getting started with the guides below, ensure you have the following components installed on your machine:
- You will need the Phidgets Windows Drivers
Use Our Examples
One of the best ways to start programming with Phidgets is to use our example code as a guide. In order to run the examples, you will need to download and install Code::Blocks.
Now that you have Code::Blocks installed, select an example that will work with your Phidget:
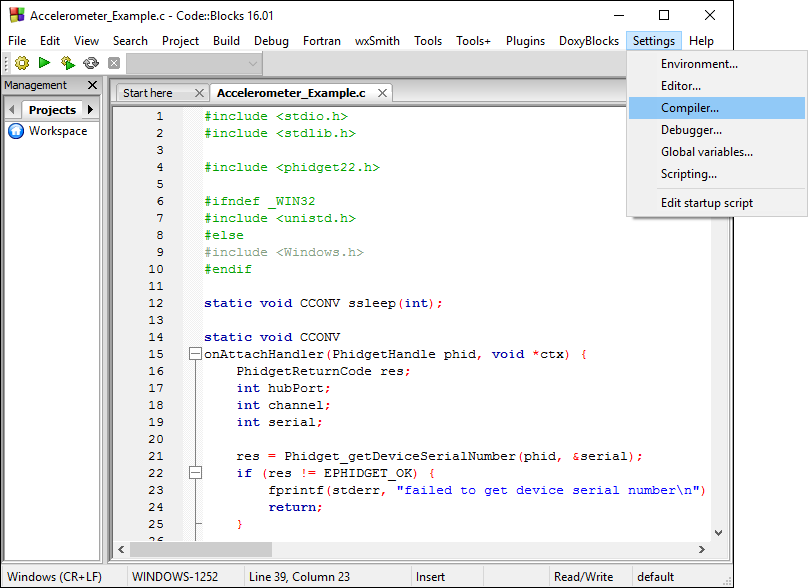
Next, open Code::Blocks, and navigate to Settings -> Compiler... as shown in the image below:
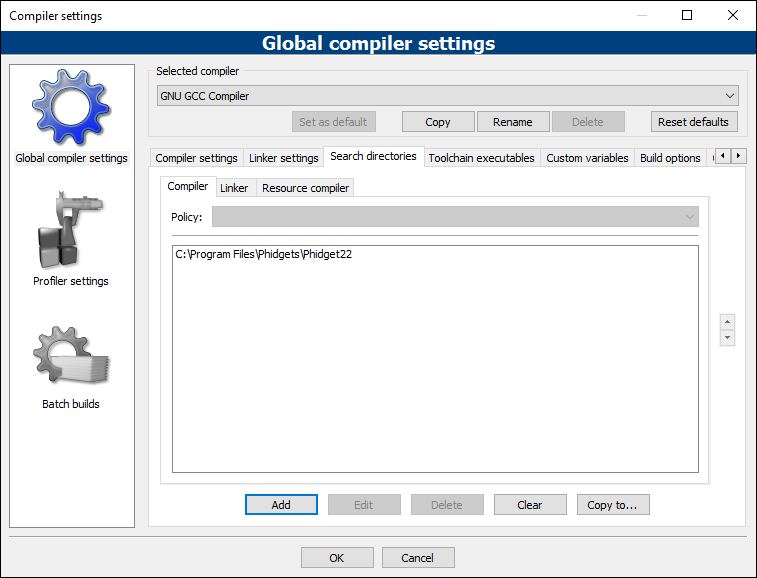
From the Global compiler settings screen, navigate to Search directories -> Compiler and add the following directory:
- C:\Program Files\Phidgets\Phidget22
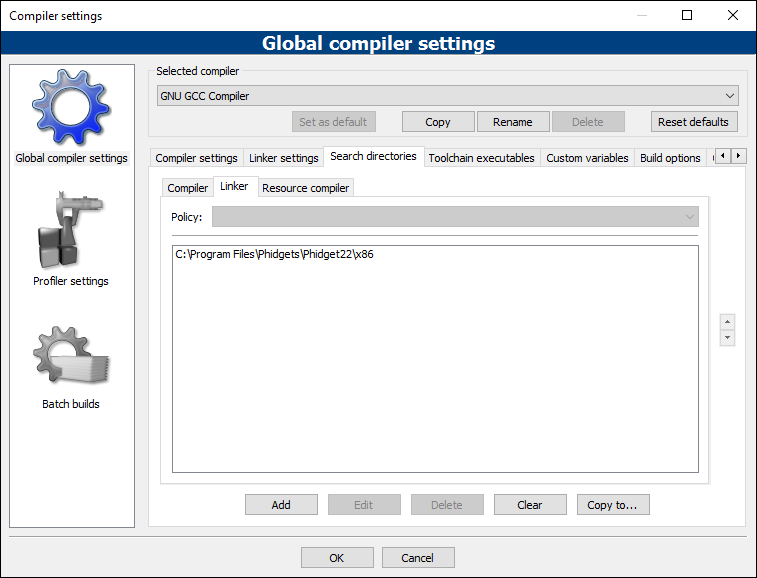
Next, select Search directories -> Linker and add the following directory:
- C:\Program Files\Phidgets\Phidget22\x86
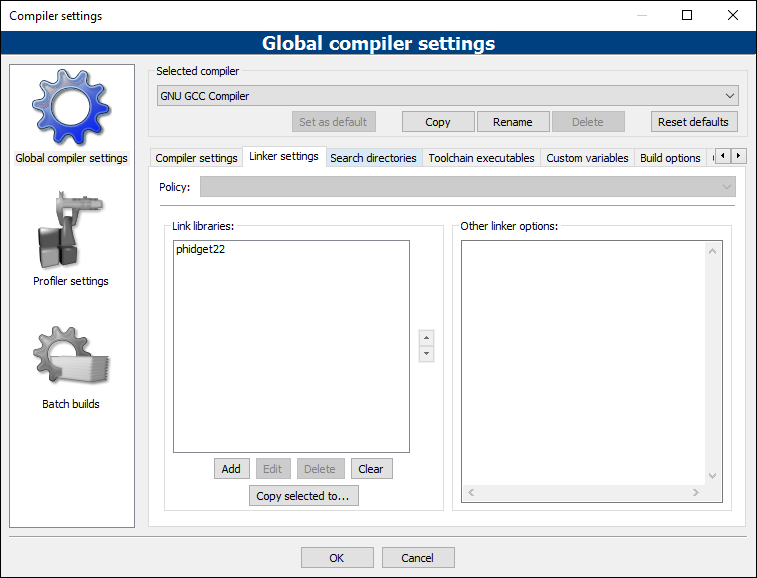
From the Global compiler settings screen, navigate to Linker settings and add the following line:
- phidget22
Next, create a new Console Application project, as follows:
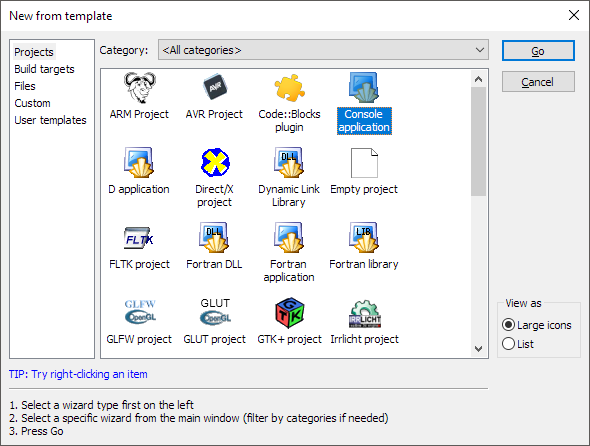
Name your project, and finish creating the project.
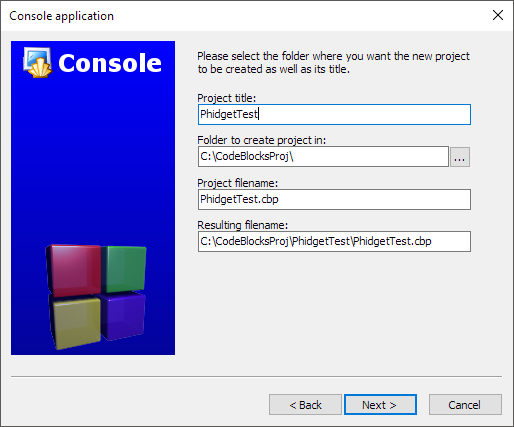
Next, remove main.c from the created project.
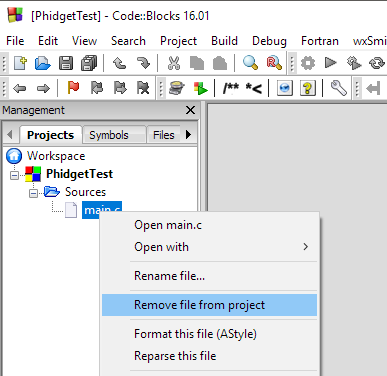
Copy the files from your downloaded example and paste them into the project directory.
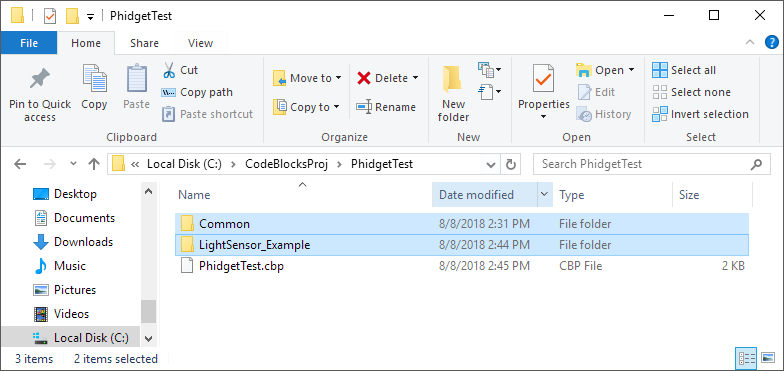
Add the example C file, and PhidgetHelperFunctions.c to the project.
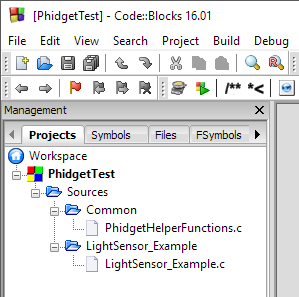
Lastly, you'll need to add the common directory to your project search directories. Right-click your project:
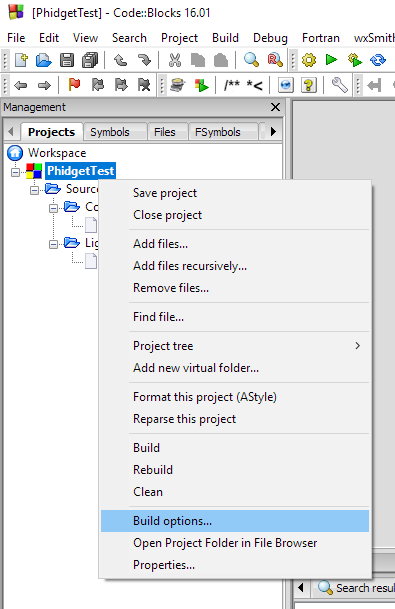
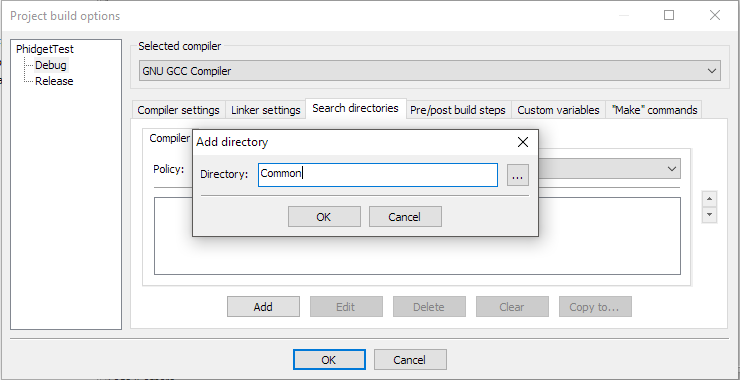
Then add the common directory under "Search directories":
You can now build and run the example:
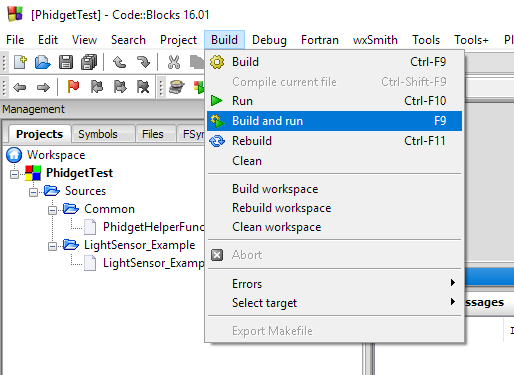
You should now have the example up and running for your device. Your next step is to look at the Editing the Examples section below for information about the example and important concepts for programming Phidgets. This would be a good time to play around with the device and experiment with some of its functionality.
To get our example code to run in a custom application, simply remove the calls to AskForDeviceParameters and PrintEventDescriptions, and hard-code the addressing parameters for your application.
If you are unsure what values to use for the addressing parameters, check the Finding The Addressing Information page.
For instance:
AskForDeviceParameters(&channelInfo, (PhidgetHandle)ch);
prc = Phidget_setDeviceSerialNumber((PhidgetHandle)ch, channelInfo.deviceSerialNumber);
CheckError(prc, "Setting DeviceSerialNumber", &(PhidgetHandle)ch);
prc = Phidget_setHubPort((PhidgetHandle)ch, channelInfo.hubPort);
CheckError(prc, "Setting HubPort", &(PhidgetHandle)ch);
prc = Phidget_setIsHubPortDevice((PhidgetHandle)ch, channelInfo.isHubPortDevice);
CheckError(prc, "Setting IsHubPortDevice", &(PhidgetHandle)ch);
Phidget_setChannel((PhidgetHandle)ch, channelInfo.channel);
CheckError(prc, "Setting Channel", &(PhidgetHandle)ch);
if (channelInfo.netInfo.isRemote) {
prc = Phidget_setIsRemote((PhidgetHandle)ch, channelInfo.netInfo.isRemote);
CheckError(prc, "Setting IsRemote", &(PhidgetHandle)ch);
if (channelInfo.netInfo.serverDiscovery) {
prc = PhidgetNet_enableServerDiscovery(PHIDGETSERVER_DEVICEREMOTE);
CheckEnableServerDiscoveryError(prc, &(PhidgetHandle)ch);
} else {
prc = PhidgetNet_addServer("Server", channelInfo.netInfo.hostname,
channelInfo.netInfo.port, channelInfo.netInfo.password, 0);
CheckError(prc, "Adding Server", &(PhidgetHandle)ch);
}
}
Might become:
prc = Phidget_setDeviceSerialNumber((PhidgetHandle)ch, 370114);
CheckError(prc, "Setting DeviceSerialNumber", &(PhidgetHandle)ch);
prc = Phidget_setHubPort((PhidgetHandle)ch, 2);
CheckError(prc, "Setting HubPort", &(PhidgetHandle)ch);
prc = Phidget_setIsHubPortDevice((PhidgetHandle)ch, 1);
CheckError(prc, "Setting IsHubPortDevice", &(PhidgetHandle)ch);
Notice that you can leave out any parameter not relevant to your application for simplicity.
You can then manipulate the rest of the code as your application requires. A more in-depth description of programming with Phidgets can be found in our guide on Phidget Programming Basics.
Setting up a New Project
When you are building a project from scratch, or adding Phidget functionality to an existing project, you'll need to configure your development environment to properly link the Phidget C library.
To start, open Code::Blocks, and navigate to Settings -> Compiler... as shown in the image below:

From the Global compiler settings screen, navigate to Search directories -> Compiler and add the following directory:
- C:\Program Files\Phidgets\Phidget22

Next, select Search directories -> Linker and add the following directory:
- C:\Program Files\Phidgets\Phidget22\x86

From the Global compiler settings screen, navigate to Linker settings and add the following line:
- phidget22

Next, create a new Console Application project, as follows:

Name your project, and finish creating the project.

Now your project is created, and you can open the generated main.c to begin coding.
To include the Phidget C library, add the following line to your code:
#include <phidget22.h>
Your project now has access to the Phidget libraries.
What's Next?
Now that you have set up Phidgets to work with your programming environment, we recommend you read our guide on Phidget Programming Basics to learn the fundamentals of programming with Phidgets.![]()
