Control Panel Graphing: Difference between revisions
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
=== Low-Pass Filter === | === Low-Pass Filter === | ||
This filter | This filter reduces and removes high frequency components of the graphed data. It's generally used to smooth out your graph since most noise sources are high-frequency. Select "Low Pass Filter" from the drop down menu and move the slider to select the averaging window. The larger the averaging window, the smoother the line will be. | ||
[[Image:lowpass.jpg|link=]] | [[Image:lowpass.jpg|link=]] | ||
Revision as of 17:38, 23 February 2022
In the Phidget Control Panel, open the channel for your device and click on the ![]() icon next to the data type that you want to plot. This will open up a new window:
icon next to the data type that you want to plot. This will open up a new window:
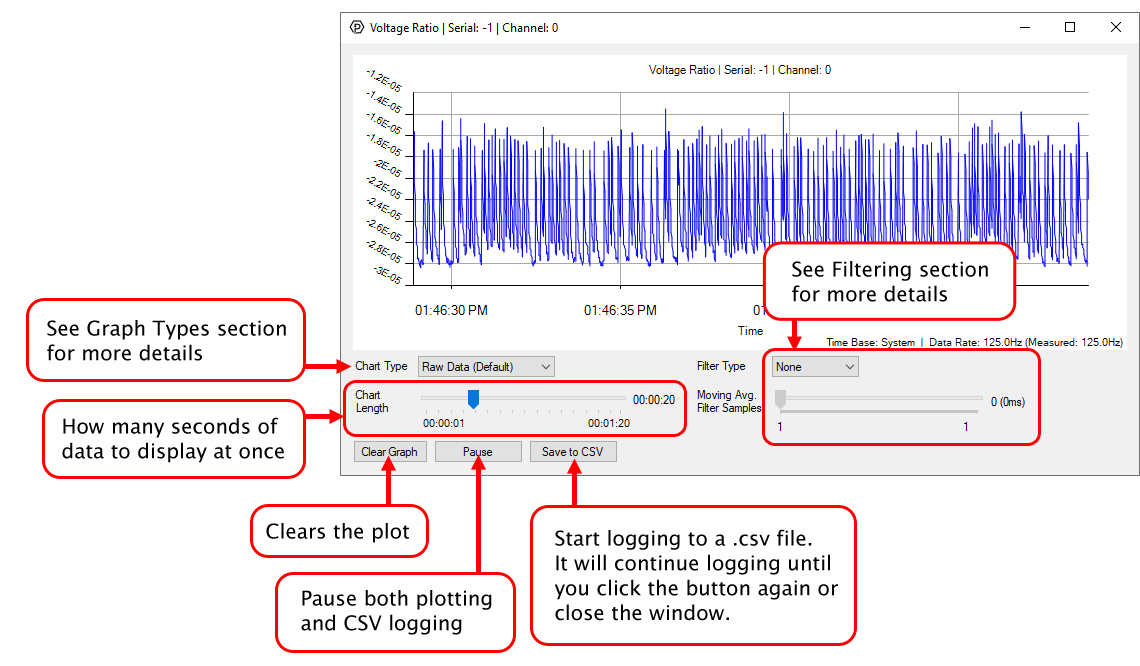
If you need more complex functionality such as logging multiple sensors to the same sheet or performing calculations on the data, you'll need to write your own program. Generally this will involve addressing the correct channel, opening it, and then creating an Event Handler and adding graphing/logging code to it.
The quickest way to get started is to download some sample code for your desired programming language and then search google for logging or plotting in that language (e.g. "how to log to csv in python") and add the code to the existing change handler.
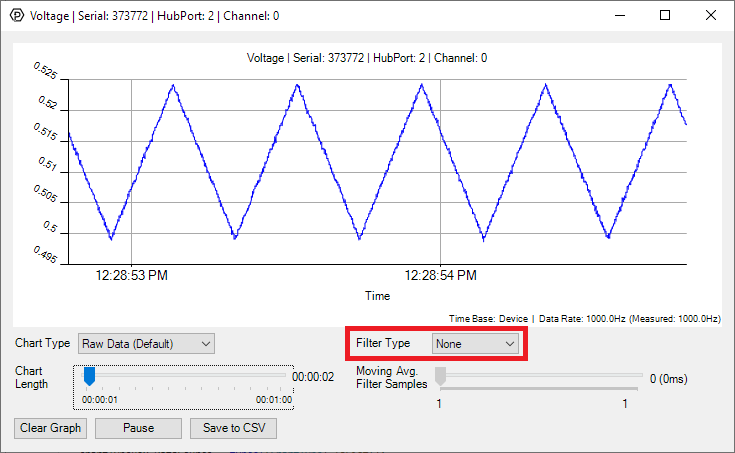
Filtering
You can perform filtering on the raw data in order to reduce noise in your graph.
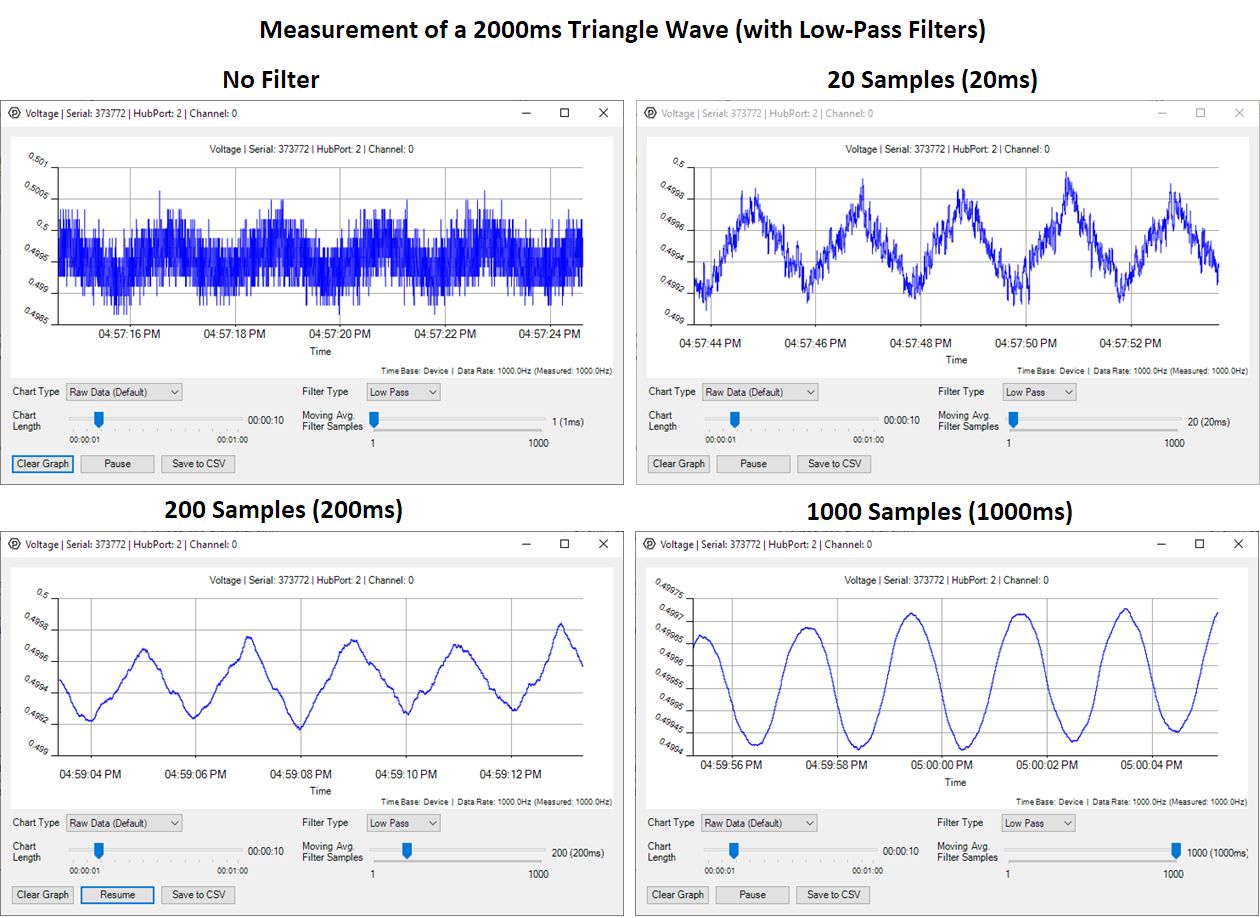
Low-Pass Filter
This filter reduces and removes high frequency components of the graphed data. It's generally used to smooth out your graph since most noise sources are high-frequency. Select "Low Pass Filter" from the drop down menu and move the slider to select the averaging window. The larger the averaging window, the smoother the line will be.
High-Pass Filter
Unlike the low-pass filter, this filter is used specifically to look at the high-frequency noise in your signal. Select "High Pass Filter" from the drop down menu to see the noise.
Graph Type
You can perform a transform on the incoming data to get different graph types that may provide insights into your sensor data.
Fast Fourier Transform (FFT)
The FFT graph type will transform your data into a frequency plot, which can sometimes reveal hidden information about your data. For example, if you look at this accelerometer raw data:
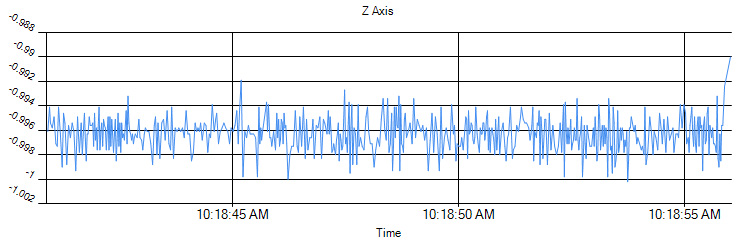
It's clear that there's around ±0.002g of noise in the signal, but just from looking at the raw data it may be unclear where the noise is coming from- is it the sensor itself, or something external? Switching to the FFT plot gives us a clue:
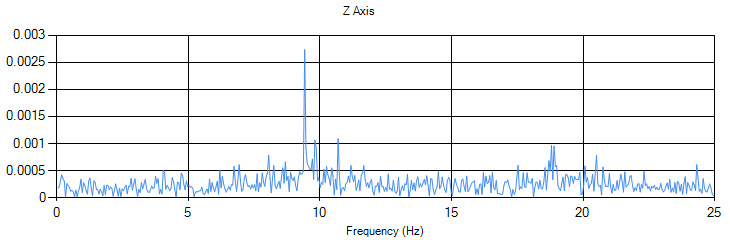
The FFT plot reveals that the noise is mostly coming from something vibrating at 9Hz- in this case, a nearby motor was running. You can increase the graph length to sharpen the frequency spikes, but it will also take longer for the graph to react to changes in the incoming data.
In general, the FFT plot is only useful for certain sensors and noise analysis when sources of a specific frequency come into play.
Allan Deviation
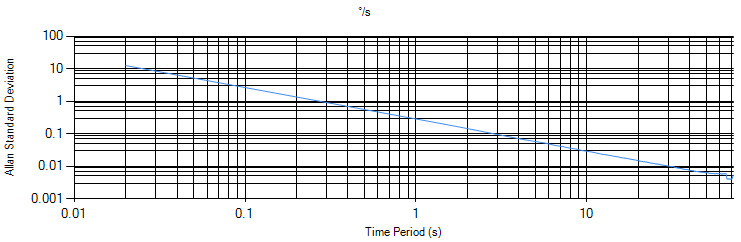
Allan Deviation is a very specialized type of graph used to compare noise characteristics between sensors. Interpreting the Allan Deviation plot is outside the scope of this guide, but in general your sensor should be stabilized (e.g. if it's a spatial, it should be stationary. If it's a temperature sensor, the ambient temperature should be kept at a static level).
