OS - Linux: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
If you are already a pro, and just want the downloads: | If you are already a pro, and just want the downloads: | ||
*[{{SERVER}}/downloads/libraries/libphidget22.tar.gz Phidget Libraries for Linux] | *[{{SERVER}}/downloads/libraries/libphidget22.tar.gz Phidget Libraries for Linux] | ||
*[{{SERVER}}/downloads/libraries/ | *[{{SERVER}}/downloads/libraries/phidgetnetworkserver22.tar.gz Phidget Network Service for Linux] | ||
*[[Software License]] | *[[Software License]] | ||
Revision as of 22:00, 24 April 2017
On Linux, Phidgets can be either plugged directly into a USB Port or run over a network using the Network Service.
You need kernel version 2.6 (released in 2003) or later.
Quick Downloads
Linux has complete support for all Phidgets and their software APIs; the only thing it lacks when compared to Windows and OS X is a graphical user interface. We walk you through all steps for download, installation, checking, and starting to write code below.
If you are already a pro, and just want the downloads:
Getting Started with Linux
Installing
To install the libraries, follow these steps:
- Install libusb-1.0 development libraries -
libusb-1.0-0-dev.- Note that libusb-1.0 may be already on your system, but the development libraries probably aren't.
- Search for
libusb-1.0-0-devor similar in your distribution package directory viasudo apt-get install libusb-1.0-0-dev - Or install from source.
- Unpack and install the Phidget Libraries
- From the main unpacked libraries directory, run:
./configuremakesudo make install
- This will compile phidget22.h and place the library into your gcc path
- From the main unpacked libraries directory, run:
Note: Although these libraries are written in C, the additional libraries for Python, Java, and most other Phidget-supported languages depend on them so they must be installed no matter what else you want to do.
Checking
To confirm the libraries were installed and work correctly, you can check both the hardware and software sides of the interface. It is worth checking the software side first, because if it works then you know the hardware side is also okay.
Software
To confirm that the libraries were installed correctly and can be used in code, you can use the C examples.
The easiest way to confirm correct installation will be to compile and run the HelloWorld C example, included in the examples download. This does not involve writing any C code, but it does involve compiling the example and running it, which is a quick process as we show below. If you feel more comfortable running the HelloWorld example for your specific language, you can skip below and pick your language, but keep in mind that any problems could be with the C library installation and not necessarily with your language.
To compile and run the basic C example for checking your installation:
1. Unpack the Phidget Generic C Examples
2. Open a terminal (often Ctrl-Alt-T) and go to the directory where the examples are unpacked
3. Compile the HelloWorld.c example:
gcc HelloWorld.c -o HelloWorld -lphidget22
4. Run the HelloWorld example:
sudo ./HelloWorld
(The sudo is needed for USB access for now, see the Setting udev Rules section for how to change this)
The -lphidget22 will look in the standard library location for your Linux distribution (usually /usr/lib/) for the Phidget 22 library file. Generally, libraries to be linked on Linux through gcc have a naming convention. For example, -lphidget22 looks for the binary files libphidget22.a and libphidget22.so in the library location. These files are automatically put in the library location during the make install step of installing the libraries.
The HelloWorld program will simply print out basic information for any device you plug in, and print a message upon unplugging the device. For example, starting the program, plugging in an Interface Kit Phidget, unplugging the Interface Kit, and pressing Enter displays:
$ sudo ./HelloWorld
Opening...
Press Enter to end
Hello to Device Phidget InterfaceKit 8/8/8, Serial Number: 37299
Goodbye Device Phidget InterfaceKit 8/8/8, Serial Number: 37299
Closing...
Hardware
If the out-of-the-box examples do not work, make sure the Phidget is seen by your USB interface. To check this, you can use the kernel log reader dmesg. Pipe the output of dmesg into the utility tail to read the last ten lines of the log:
$> dmesg | tail
....(3 lines)....
[337.189132] usb 1-2: new full-speed USB device number 5 using ochi-pci
[337.464709] usb 1-2: New USB device found, idVendor=06c2 idProduct=0034
[337.464714] usb 1-2: New USB device strongs: Mfr=1, Product=2, SerialNumber=3
[337.464718] usb 1-2: Product: 1024_0
[337.464721] usb 1-2: Manufacturer: Phidgets Inc.
[337.464724] usb 1-2: SerialNumber: 388624
[337.491426] usb 1-2: hid-generic 0003:06C2:0034.0004: hiddev0,hidraw1: USB HID v1.01 Device [Phidgets Inc. 1024_0] on usb-0000:00:06.0-2/input0
The number between the [ ] is the system time in seconds since the last boot up, so you can tell whether the event was recent or not. (This will also tell you the interrupt type of Phidget that is registered by the USB interface, see the common problems section below for more information on what this means.)
The Phidget should both connect and disconnect properly, so unplugging it should result in an additional line at the tail:
$> dmesg | tail
....(9 lines)....
[744.558055] usb 1-2: USB disconnect, device number 5
If you don't see similar lines to these at the tail of your kernel log, take a look at the troubleshooting section below, as well as the Communications section of our general troubleshooting page.
Troubleshooting
If the examples do not work but USB does work (i.e. your computer can consistently see the device in the hardware), take a moment to check the basics:
- No other programs, drivers, or processes are using that USB port in software
- You are running the example program as root (or your udev rules have been set properly)
- You are using libusb 1.0 (not the older 0.1 release)
- You have compiled versions of libphidget22.a and libphidget22.so in your system library location (usually
/usr/lib) - The Phidget libraries are the latest version (visit the quick downloads section to download them)
- Your Linux kernel version is 2.6 or later (type
uname -rin a terminal to get your kernel version) - Check the common problems section below, some specific combinations can cause problems
If your problem doesn't seem to be fixed by these steps, make sure that the Phidget is seen consistently by USB (if it is erratic, try our general troubleshooting guide). If you are still having problems after using the troubleshooting guide, please ask us!
Programming Languages
Now that you have the basic libraries installed, you can pick your language and begin programming!
If you are not using the network service (discussed below) to control a Phidget over a network, your next step will be to delve into the use of your specific language. Each page has its own set of specific libraries, code examples, and setup instructions.
On Linux, we recommend the following languages:
We also support these languages on Linux:
Phidget Network Service
The Phidget Network Service allows you to remotely control a Phidget over a network.
This section helps you install, check, and use the Network Service on Linux, but we also have an overview of the Phidget Network Service in general.
Installing the Network Service
To install the Network Service, you must first have the Phidget libraries installed. Then, follow these steps:
- Download avahi and its development libraries (mdnsresponder/bonjour is also an option, see the network service with mDNSResponder section)
- Try
apt-cache search avahiin a terminal to find current packages - Often, this is installed in a default system, you may already have it
- Try
- Unpack and install the Phidgets Network Service source code tarball for Linux
- From the unpacked Network Service source code directory, run:
./configuremakesudo make install
- This will compile the executable
phidget22networkserverand place it into/usr/bin/phidget22networkserver
- From the unpacked Network Service source code directory, run:
Network Service with mDNSResponder
To use mdnsresponder instead of avahi, change the configure script to be:
./configure --enable-zeroconf=bonjour
(To see all options, use ./configure --help like you would any configure script)
Setting Up the Network Service
To set up and use the Phidget Network Service, it helps to have set your udev rules. Otherwise, you must run it as root.
You can get command line help with phidget22networkserver by using the -h option:
$ phidget22networkserver -h
usage: phidget22networkserver [-D][-E][-c <cfg>][-l <logfile>][-v][-w]
-D run as daemon
-E log to stderr
-c <cfg> configuration file
-l <logfile> log to 'logfile'
-v enable verbose logging (may be specified more than once)
-p run phidget sever
-w run web server
You will see this help regardless of whether the network service was correctly hooked in to avahi. In fact, you will see it even if you explicitly disabled mDNS in the ./configure step at compile:
./configure --disable-zeroconf
Using the Network Service
To use a Phidget over the network service, you'll want to:
- Obtain code you can use to open a Phidget remotely
- Start the network service on the computer that directly connects to the Phidget
- Run your program on the remote computer that will control the Phidget over the network
The easiest way to test these steps on Linux is simply to set up the network service and run the Phidget program on the same computer, using the loopback interface. Later, you can replace one of the two ends with a different computer and/or operating system.
To quickly create code to run remotely, in our examples we include commented out lines with openRemote() function calls of different types. In the C example for your device, find the line that says:
CPhidget_open((CPhidgetHandle) device, -1)
and change it to be:
int serial_number = 37299
CPhidget_openRemoteIP ((CPhidgetHandle) device, serial_number, "127.0.0.1", 5001, NULL)
Except that you should replace 37299 with the serial number of your Phidget, which you can obtain from either the Phidget board itself, or from when you ran the HelloWorld example code. The IP address "127.0.0.1" simply loops back to the same computer, and 5001 is the default port as found from using phidget21networkservice -h in the Setting Up the Network Service section. The NULL is used to not specify a password.
Save the changed example under a different filename. In the walkthrough here, we are using the InterfaceKit.c example, and we rename it to be InterfaceKitRemote.c
Compile your new C file. In our InterfaceKitRemote.c case, this would be by:
gcc InterfaceKitRemote.c -o InterfaceKitRemote -lphidget21
1. Start two terminals to run this test, usually opened via Ctrl-Alt-T. Your udev rules need to be set up or you should use sudo for every command. First, start the network service in Terminal #1:
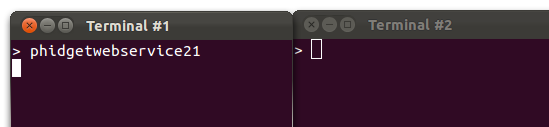
This will broadcast any Phidget events, and receive any Phidget requests, both over the network.
2. Start the InterfaceKitRemote program that you just compiled which will open the remote Phidget. In this case, it is InterfaceKitRemote:
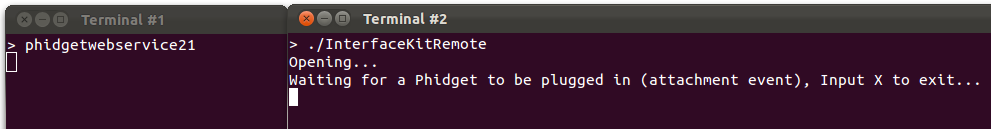
3. Now, plug in the Phidget! The phidget21networkservice program captures the attach and other events and sends them out over the network (in the background in Terminal #1) and the Phidget software objected opened with openRemote in Terminal #2 receives them:
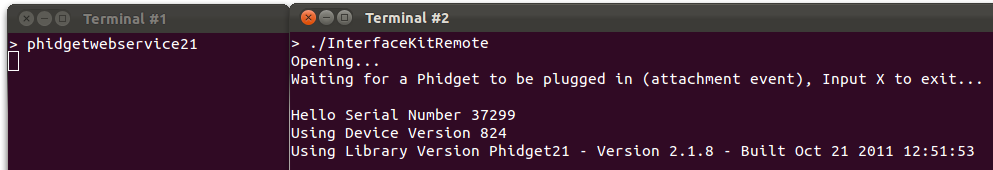
4. You can confirm that the network service was indeed behind this exchange by killing the network service process while still allowing the remote program to run:
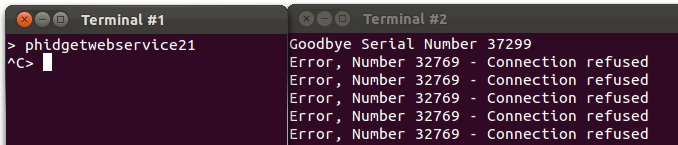
Debugging the Network Service
In addition to enabling logging in your Phidget code, you can get additional debugging information from the Network Service itself. You can enable logging by editing networkserver.cfg, which can be found in the build directory for the network service.
# Server log level
# verbose | debug | info | warn | err
loglevel: debug
# Server log file
logfile: "/home/<username>/Desktop/networkserver.log"
You can change the loglevel to change what kind of messages show up in the logfile. Each successive level contains the messages of the lower levels as well.
- err: The lowest logging level; Only messages from errors will be logged.
- warn: Adds warning messages which result from unexpected but not necessarily erroneous behaviour.
- info: Adds informational messages that track important events in the network service.
- debug: For debugging the inner workings of the network service; not typically useful for end-users.
- verbose: The highest logging level; Even not-very-important events will be tracked, so it may be difficult to find the messages that matter.
The logfile path will lead you to the log file, or you can change the path to something else.
If you suspect multicast DNS (mDNS) may be the problem, you can:
- Try compiling the network service with mDNSResponder, as described in Installing the Network Service, or
- Try compiling the network service completely without mDNS, as described in Setting Up the Network Service
Advanced Uses
Setting udev Rules
If you don't want to be using sudo to run Phidget programs (including the Network Service) forever, you will want to create a udev rule to allow yourself access to the Phidget when you are not root.
Udev has an easy way to set the owner and permissions of the USB interface of the Phidget - it finds all devices that match a given set of rules, and applies new traits to them. But you need to give udev something to match in order to apply the new settings. Here, we will tell udev to match the vendor code for Phidgets, Inc.
We recommend that you use the rules file included in the library download you have already installed. Check the README file included in that download for information on how exactly to install it, or continue reading here.
The rules for udev are kept in files in /etc/udev/rules.d/ and are traditionally grouped into order of running (10 runs before 20, 30, etc) and device type (cd, network, etc). There should be one or more files in there already. Simply find the file named 99-libphidget22.rules included with our library files, and move it into /etc/udev/rules.d/.
Strictly speaking, the files run in lexical order (i.e. the order they're listed when you use ls). A device can match many rules, and all will apply (if possible). If conflicting rules are found, the first rule found is followed.
Starting the Network Service at Boot
If you are tired of starting the network service on the command line all the time, you can have the network service start when your system starts, every time.
User Space
If you are running a standard Linux machine with an X-server (Unity, KDE) the easiest way to do this is to have the Phidget Network Service start when your x server starts.
In this case, the network service will be running in user space, so your udev rules need to be set up for the your user permissions to be able to access the USB ports using libusb.
Within the X-windowing system, there is usually some sort of System → Settings/Preferences → Startup that you can choose to add programs that start when a user session starts. On Ubuntu you can use Unity to find programs listing "startup" in their names to accomplish the same thing. This will eventually lead you to a window like this one:
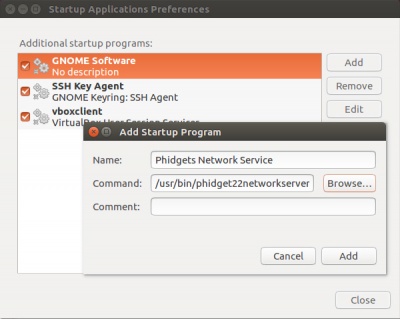
Simply add the /usr/bin/phidget22networkserver program to the list.
As A Service
You would want to set the boot start of phidgetnetworkservice21 to be a service if you are running a server, or a headless machine. It is handy any time you need the network service to be started as a booted, respawning service with a presence in different run levels and for all users.
A service is essentially a program that hangs out in the background, waiting to be used by some incoming task. When the service is needed, the service forks a program to handle that need. Most services that run on your Linux computer already have the ability to fork themselves.
The network service, however, is just a binary on Linux - phidgetnetworkservice21 - and so we need a program that handles the forking for us. For this, we use the start-stop-daemon program to spawn a standalone process for us, or kill it, based on our service-like start, stop, and restart commands.
To do this, we need:
- A script that tells the boot process how to start and handle the networkservice (i.e. by using
start-stop-daemon) - A link from that script to the boot list
- An initialization file for the script
First, the script. We will walk through Debian here, both because it is such a common distribution and because it is the distribution that our Single Board Computer runs. But init is surprisingly diverse on Linux, including everything from a different boot order, to different initialization programs and structure, and even different runlevels.
On Debian (including Ubuntu), the initialization script covers:
- Runlevels that the service should be present on
- Dependencies of the service
- Name of the service and other informative data
- The location of the PIDFILE, which stores the process ID (pid) for later dealing with a spawned instance
- Any configuration file locations
- What to do when the service is given instructions to start, stop, or reload.
The Debian script we use to start the network service on the Single Board Computer:
#!/bin/sh
### BEGIN INIT INFO
# Provides: phidgetnetworkservice
# Required-Start: $network $remote_fs
# Required-Stop: $network $remote_fs
# Should-Start: avahi
# Should-Stop: avahi
# Default-Start: 2 3 4 5
# Default-Stop: 0 1 6
# Short-Description: Phidget Network Service
# Description: Phidget Network Service for controlling Phidgets over the network.
### END INIT INFO
DESC="Phidget Network Service"
NAME=phidgetnetworkservice
BIN=phidgetnetworkservice21
DAEMON=/usr/bin/$BIN
PIDFILE=/var/run/$NAME.pid
CFG=/etc/default/$NAME
# Gracefully exit if the package has been removed.
test -x $DAEMON || exit 0
# load config
pws_port="5001"
pws_serverid=""
pws_password=""
[ -f $CFG ] && . $CFG
start() {
[ -z "$pws_port" ] || OPTIONS="-p $pws_port "
[ -z "$pws_password" ] || OPTIONS="$OPTIONS-P $pws_password "
if [ -z "$pws_serverid" ]; then
OPTIONS="$OPTIONS -n $( hostname )"
else
OPTIONS="$OPTIONS -n $pws_serverid"
fi
echo -n "Starting $DESC: "
start-stop-daemon -S -b -q -p $PIDFILE -m -x $DAEMON -- $OPTIONS && echo "OK" || echo "ALREADY RUNNING"
}
stop() {
echo -n "Stopping $DESC: "
start-stop-daemon -K -q -p $PIDFILE -x $DAEMON && echo "OK" || echo "NOT RUNNING"
}
case "$1" in
start)
start
;;
stop)
stop
;;
restart|force-reload)
stop
sleep 1
start
;;
*)
echo "Usage: $0 {start|stop|restart}"
esac
exit 0
Save the script into a file called phidgetnetworkservice, and use chmod 755 to make it executable.
Also on Debian, startup service scripts should go in /etc/init.d, and then put within the appropriate runlevel-numbered folder - by symbolic link. There is a handy tool to do this for you, called insserv:
sudo insserv -d phidgetnetworkservice
The insserv program is the program that makes use of the ### BEGIN INIT INFO...### END INIT INFO that appears at the top of the phidgetnetworkservice script. Use man insserv for more information. The insserv tool handles the mess of finding the right runlevel folders (i.e. the rc.d numbered folders) and making the appropriate links. You can see what links would be updated by running insserv with the -n option, for a dry run.
Note: When you run insserv, all of the dependencies for the boot order are re-written. This means that all of the initialization scripts in /etc/init.d are re-examined. So, you'll probably get a lot of output when you run the command.
Then, you can check that phidgetnetworkservice is on the service list with:
service --status-all
And you can start it right now without rebooting like this:
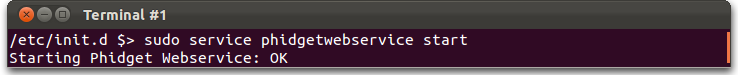
The service command has many options to start and stop services like the phidgetnetworkservice, try man service for more information.
At this point, you can follow the client instructions on using the network service to create a loopback test for the new network service that should now be running.
The final piece, for future configuration changes, is that the /etc/init.d script looks for the file /etc/default/phidgetnetwork service upon starting up. The file is expected to contain the port, server ID, and password for the server side of the network service. These are also set in the phidgetnetworkservice script in init.d, as you can see from reading the code above, but if you want to change them a lot, you can edit the configuration file rather than changing the phidgetnetworkservice script and re-installing by insserv every time. The configuration file in /etc/default/ should contain the same syntax as that used in the script source above:
pws_port="5001"
pws_serverid=""
pws_password=""
Cross-Compiling with a Custom Toolchain
This would allow you to have the Phidget libraries compiled to include in code for an embedded device. When developing for an embedded device, you will often write code for it on your 'normal' computer, and then build the code to binary with a different target than the processor in your computer. Many microcontrollers do not have the ability to run a full operating system, and hence cannot compile code natively.
The collection of tools used to create binary code for a separate system is called a toolchain. Compiling the Phidget libraries specifically for an embedded system, and placing them into the path for writing code on top of the libraries is like adding another link in this chain.
You can use the typical ./configure setup for custom build targets:
./configure --prefix=toolchain_location --build=this_system --host=target_system
For the Phidget libraries, the ./configure tool works this way as well. You'd use this in the install the libraries section setup. For example, let's say you're building the libraries to develop code for the Single Board Computer as a target. Your system is a standard Linux system (i686-pc-linux-gnu) and the target system for the SBC is arm-linux-gnueabi. For this target, you'll need the base of the GNU embedded Debian chain:
sudo apt-get install gcc-arm-linux-gnueabi
Then, download the Phidget libraries above and unpack them into a folder phidget_libraries. If /usr/arm-linux-gnueabi is the location of your ARM toolchain (downloaded above in gcc-arm-linux-gnueabi), type:
~/phidget_libraries $> ./configure --prefix=/usr/arm-linux-gnueabi --build=i686-pc-linux-gnu --host=arm-linux-gnueabi
Linux on Non-Standard Systems
We occasionally get requests to use Phidgets on Linux systems other than a standard laptop or desktop. One example is the Raspberry Pi system. Often these systems include USB ports, so the combination makes sense.
Our libraries are installed by building from source, and their main dependency is the libusb-1.0-0-dev library, so if you can get gcc on your machine (or set up a cross compiler for it) and you can also install the libusb-1.0 development headers, you can probably get Phidgets to work. Of course, we don't offer much support for these systems, so - depending on your system - expect to spend some raw time getting it up and going.
If you're new to the embedded computer thing, keep in mind that for these super basic systems, once you've gotten a power supply, and storage, and put the kernel you want on it, and then spent a couple of days of time getting things working, and more time getting your drivers going, costs add up pretty quickly. If you want a compact system that works right out of the box (and which can use all of our analog sensors in addition to our USB Phidgets), check out our Single Board Computer. Our SBC3:
- Has many more USB ports than super-stripped devices, and also has digital and analog ports
- Includes a power supply and can run on batteries easily
- Has a nice amount of RAM, a decent embedded processor, and built-in onboard storage (we've run R, GRASS, and X11 on it)
- Includes installed Debian, working Phidget drivers, and networked Phidget drivers from the moment it ships
- Has access to the full Debian repository including Python, Mono .NET, Ruby, and gcc
- Has a kernel development kit with patch file and instructions for adding new drivers (bluetooth, wireless, and so on)
- Comes with very in-depth documentation and technical support by phone and email
- Etc, etc.
The networked support in particular allows it to work with your cell phone and more.
But if you really do want a raw hobbyist system to tinker with, go for it! We're all nerds here - we've been there too and we certainly understand!
Common Problems and Solutions
Low Speed Phidgets (Max of 8): Linux will only schedule one low-speed interrupt transfer per millisecond.
You can find out the type of your Phidget by attaching it and then running dmesg | tail, which will display the type of Phidget from your kernel logs, as described above in the hardware section. The practical consequence of this is if your system has many low speed Phidgets attached, they will each be throttled down. Low speed Phidgets require an interrupt transfer as often as every 8 milliseconds. A Linux system could only have up to 8 of these Phidgets attached.
Sample Overrun Error: The data read from a program, or the first packet on the Network Service, can give a sample overrun error (EEPHIDGET_OVERRUN).
Linux only polls data from the analog inputs on Phidgets when you ask it to. So there is some delay between when you open the device and when it actually attaches when data from those inputs are accumulating...and overrunning the buffer. This is simply in the nature of how Linux polls USB - we recommend catching (but ignoring) this one-time initial error.
Raspberry Pi USB Current: Your device doesn't seem to run as expected on a Raspberry Pi.
The USB ports on the standard Raspberry Pi are only capable of supplying around 100mA reliably. Since USB specification dictates 500mA of current maximum, many USB devices require several hundred mA to run smoothly. Since the Pi cannot supply this much current it is common to see buggy performance or complete failure to run at all. The get around this you should use a USB hub connected to the Pi that has it's own external power supply. This will allow the devices connected to have as much power as they require.
