1017 User Guide

| |
| Go to this device's product page |
Getting Started
Checking the Contents
|
You should have received:
|
In order to test your new Phidget you will also need:
| |
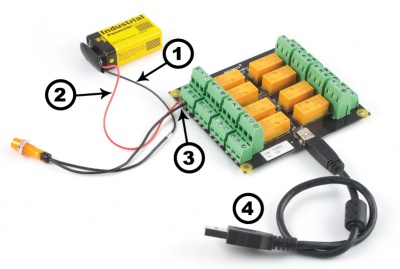
Connecting the Pieces
|
| |
Testing Using Windows 2000 / XP / Vista / 7
Make sure you have the current version of the Phidget library installed on your PC. If you don't, follow these steps:
- Go to the Quick Downloads section on the Windows page
- Download and run the Phidget21 Installer (32-bit, or 64-bit, depending on your system)
- You should see the
 icon on the right hand corner of the Task Bar.
icon on the right hand corner of the Task Bar.
Running Phidgets Sample Program
Double clicking on the ![]() icon loads the Phidget Control Panel; we will use this program to ensure that your new Phidget works properly.
icon loads the Phidget Control Panel; we will use this program to ensure that your new Phidget works properly.
The source code for the InterfaceKit-full sample program can be found in the quick downloads section on the C# Language Page. If you'd like to see examples in other languages, you can visit our Languages page.
Updating Device Firmware
If an entry in this list is red, it means the firmware for that device is out of date. Double click on the entry to be given the option of updating the firmware. If you choose not to update the firmware, you can still run the example for that device after refusing.
|
Double Click on the |
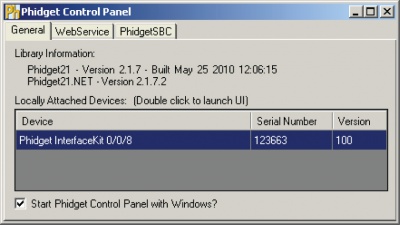
| |
|
File:1017 1 InterfaceKit Screen.jpg |
Testing Using Mac OS X
- Go to the Quick Downloads section on the macOS page
- Download and run the Phidget macOS Installer
- Click on System Preferences >> Phidgets (under Other) to activate the Preference Pane
- Make sure that the Phidget InterfaceKit 0/0/8 is properly attached.
- Double Click on Phidget InterfaceKit 0/0/8 in the Phidget Preference Pane to bring up the InterfaceKit-full Sample program. This program will function in a similar way as the Windows version.
Using Linux
For a step-by-step guide on getting Phidgets running on Linux, check the Linux page.
Using Windows Mobile / CE 5.0 / CE 6.0
Technical Details
Relays
A relay is an electrically-controlled switch. Although many types of electrical switches exist, a relay’s mechanical nature gives it the advantage of reliability and current-switching capacity. The main disadvantage to using mechanical relays is their limited life-span, as opposed to solid state relays who do not suffer from this drawback. For more information, check the Mechanical Relay Primer and the Solid State Relay Primer.
Using a Digital Output Relay
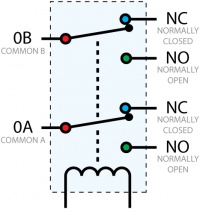
Relays have a connection scheme determined by the arrangement of contacts within the relay. Because relays are a type of switch, they are defined in the same way other electromechanical switches are defined.
In switch schemes, the number of poles represents the number of common terminals a switch has, and the number of throws represents the number of switchable terminals that exist for each pole. The relays used in the InterfaceKit 0/0/8 are DPDT relays: double pole, double throw. The internal construction of this type of relay is depicted in the diagram above. Many other types of relays exist: SPST, DPDT, and DPST, to name a few.
In a relay, one of the throw terminals is labelled Normally Closed (NC), and the other is labelled Normally Open (NO). As the name indicates, the normally closed terminal is the terminal connected to common when the relay coil is not powered. When the relay coil is energized by the relay control circuit, the electromagnetic field of the coil forces the switch element inside the relay to break its contact with the normally closed terminal and make contact with the normally open terminal. The switch element would then connect the normally open terminal and the common terminal.
Rated Current/Voltage/Power
These relays cannot be switched at maximum current and maximum voltage at the same time. Ensure that the total power of the load does not exceed the switching power of the relay. For example, you can switch these relays at 200V DC and 0.3 A (60W), or 30V DC and 2A (60W), but not 200V DC and 2A (400W).
Wetting Current
When a relay is in one switch position for a period of time, oxidation of the open contact(s) can occur. Depending upon the internal coating material of the contacts, oxide films of varying density will be displaced upon the surface of open contacts; this film acts as an insulator to current flow. When the relay is switched, a certain amount of current flowing through the contacts, known as the wetting current, is required to remove the film of oxides and ensure proper conduction. The wetting current required to operate this relay is low enough for use in signal switching applications. Check the specification table for your relay board to find out the Minimum Load Current ("Wetting Current").
Load Noise
If highly inductive loads are used with this InterfaceKit, it is recommended that a noise limiting component be used to prevent damage to the device. An MOV, TVS diode, or kickback diode (for DC applications) shunted across the load will assist in dissipating voltage transients.