1031 User Guide
Required Hardware
- A 1031 PhidgetLED-64
- LEDs and cables
- A power supply
- A USB Cable
- A computer
Connecting the Pieces
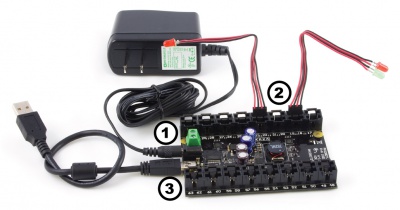
- Connect the power supply to the barrel jack. If your power supply does not have a jack, you can connect the wires to the power terminal beside it, making sure the polarity is correct.
- Connect LEDs to the PhidgetLED's outputs. You can slide the pins of an LED into the connector (short end to a black wire, and the long end to the red wire beside it), or you can cut the LED cable in half and solder the LED on.
- Connect the PhidgetLED to your computer using the USB cable.
Testing Using Windows
Phidget Control Panel
In order to demonstrate the functionality of the 1031, the Phidget Control Panel running on a Windows machine will be used.
The Phidget Control Panel is available for use on both macOS and Windows machines.
Windows
To open the Phidget Control Panel on Windows, find the ![]() icon in the taskbar. If it is not there, open up the start menu and search for Phidget Control Panel
icon in the taskbar. If it is not there, open up the start menu and search for Phidget Control Panel
macOS
To open the Phidget Control Panel on macOS, open Finder and navigate to the Phidget Control Panel in the Applications list. Double click on the ![]() icon to bring up the Phidget Control Panel.
icon to bring up the Phidget Control Panel.
For more information, take a look at the getting started guide for your operating system:
Linux users can follow the getting started with Linux guide and continue reading here for more information about the 1031.
First Look
After plugging the 1031 into your computer and opening the Phidget Control Panel, you will see something like this:
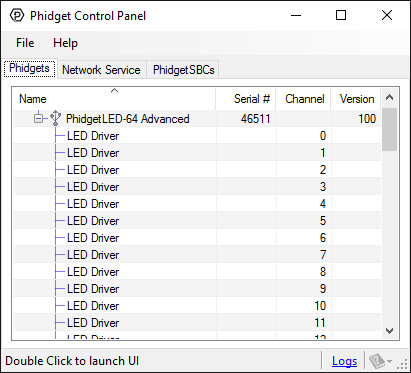
The Phidget Control Panel will list all connected Phidgets and associated objects, as well as the following information:
- Serial number: allows you to differentiate between similar Phidgets.
- Channel: allows you to differentiate between similar objects on a Phidget.
- Version number: corresponds to the firmware version your Phidget is running. If your Phidget is listed in red, your firmware is out of date. Update the firmware by double-clicking the entry.
The Phidget Control Panel can also be used to test your device. Double-clicking on an object will open an example.
Digital Output (LED)
Double-click on a Digital Output object, labelled LED Driver, in order to run the example: [[Image:{{{1}}}_DigitalOutputLED_Example.jpg|center|link=]]
General information about the selected object will be displayed at the top of the window. You can also experiment with the following functionality:
- From the Forward Voltage drop-down menu, select the appropriate voltage for your LED. It is recommended to set the forward voltage to the first setting above the maximum voltage specified by your LED's datasheet.
- Use the Current Limit slider to set an appropriate limit for your LED. The current limit will be specified in your LED's datasheet.
- Use the large button to toggle power to the LED.
- Use the Duty Cycle slider to precisely control the amount of power supplied to the LED.
Testing Using macOS
- Go to the Quick Downloads section on the macOS page.
- Download and run the Phidget macOS Installer
- Click on System Preferences >> Phidgets (under Other) to activate the Preference Pane
- Make sure your device is properly attached
- Double click on your device's objects in the listing to open them. The Preference Pane and examples will function very similarly to the ones described above in the Windows section.
Testing Using Linux
For a general step-by-step guide on getting Phidgets running on Linux, see the Linux page.
Using a Remote OS
We recommend testing your Phidget on a desktop OS before moving on to remote OS. Once you've tested your Phidget, you can go to the PhidgetSBC, or iOS pages to learn how to proceed.
Technical Details
The 1031 uses four controller chips that allow you to vary the current and voltage supplied to each channel. It does not use pulse-width modulation, another common control method for LEDs.
Multiple LEDs on a Single Channel
You can have multiple LEDs hooked up to a single channel on the 1031, (for example, a short string of LEDs) to reduce the amount of wiring, although keep in mind that you'll lose control of the individual lights, and can only toggle or dim the entire string. When using multiple LEDs on a single channel, you'll need to increase the voltage limit for that channel. If the LEDs are too dim at the maximum voltage, you should spread them out to other channels.
High-Current Considerations
If you're using high-current LEDs, you should spread your load evenly across the board to avoid having one of the controller chips overheat. There are four controller chips, each controlling the channels on a quarter of the board.
Controller 1: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31
Controller 2: 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23
Controller 3: 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 62, 63
Controller 4: 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55
Board Connector Diagram
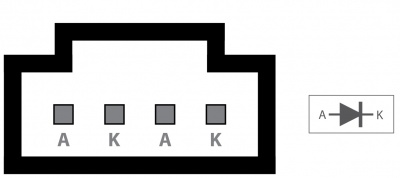
The connector used on the 1031 LED board is a Molex 70543-0003. The mating connector used on our LED cables is the Molex 50-57-9404.
Further Reading
For more information, take a look at the LED Primer.
What to do Next
- Programming Languages - Find your preferred programming language here and learn how to write your own code with Phidgets!
- Phidget Programming Basics - Once you have set up Phidgets to work with your programming environment, we recommend you read our page on to learn the fundamentals of programming with Phidgets.
Product History
Template:UGhist Template:UGrow Template:UGrow |- |style="background: #fff0f0" align=center| January 2013||style="background: #fff0f0" align=left colspan=3| Product Discontinued. Succeeded by the 1032 - PhidgetLED Advanced. The main improvement of the 1032 is the ability to set the current limit of each channel separately.
