Template:SBC Running A Program Automatically
To quickly test whether a program can be run automatically, you can try starting it from the SBC Web Interface.
1. To start the program, navigate to Projects->ProjectName->Startup Settings in the SBC Web Interface.
2. Select your program in the drop-down menu labeled Executable/Class Name.

3. Click the Start button on the SBC web interface.
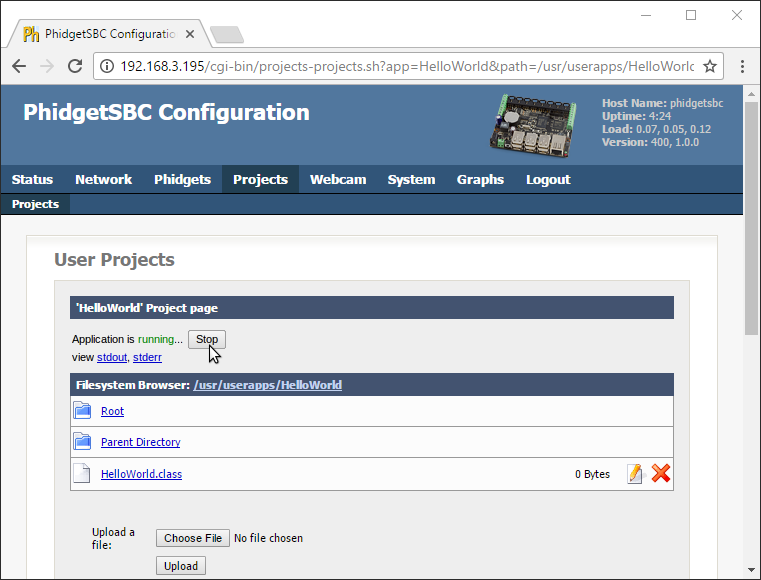
4. You'll note that as it runs, there are two links below the Stop button which can be used to view the program output:
- stdout: view the program output like you would in a terminal or command prompt
- stderr: view the program error output
Running on boot ensures that your program will never miss an event. As long as the SBC is running, your code will be running. This section assumes you have written and compiled your program on an external computer, and have uploaded it to the SBC Web Interface. If you are not using the SBC Web Interface, jump ahead to using a boot script.
To have your program run on boot, navigate to Projects->ProjectName->Startup Settings in the SBC Web Interface. After selecting your project, copy the settings from the image below:
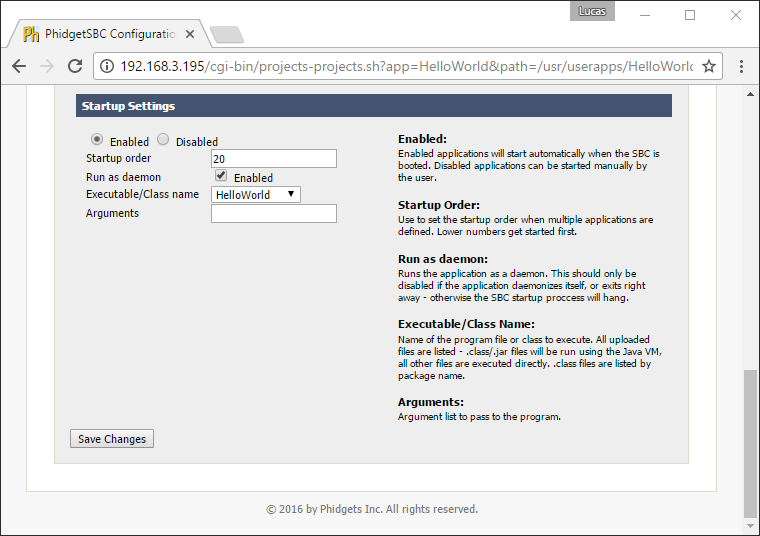
We will review some of the options that are shown in the image above:
- Startup Order: lower numbers boot first. Booting later means more programs are available for use, booting earlier means other programs can use your program.
- Run as a daemon: starts the program as a daemon. Unless you have explicitly written your program as a daemon, leave this checked, or else your SBC may hang on boot.
- Executable/Class name: your main Java class or C file.
- Arguments: any command line arguments the program needs.
After saving your changes, your program will run automatically whenever your SBC boots.
Running your program on a schedule allows you to perform your task once a week, or once a minute without worrying about memory management issues or instability problems that may arise. It executes, and then gets cleaned up. To run your program on a schedule, we recommend using Cron. Cron can automatically schedule programs (known as jobs, or cron jobs). Cron simply reads a crontab file and runs whatever programs are listed, with whatever timing they are listed with. Cron runs continuously in the background, but the cron jobs only run as long as they naturally would, and then they exit.
Let's set up your first cron job. We will use nano to edit the crontab file, but feel free to use whatever editor you prefer.
First, set your editor to nano:
export EDITOR=nano
Next, edit your crontab file:
crontab -e
Finally, schedule your cron job:
#cron job that will run at 5AM every week:
0 5 * * 1 /root/code/myprogram argument1
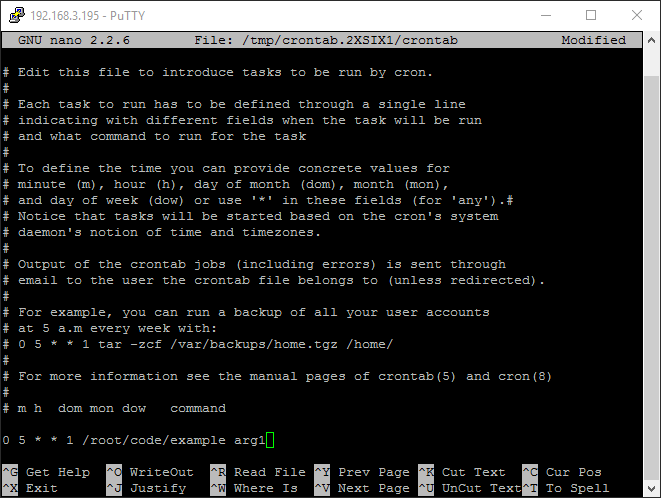
After entering your task, simply save and exit the file.
