Language - Python
![]() Python is an object oriented programming language developed by the Python Software Foundation, is powerful and easy to learn.
Python is an object oriented programming language developed by the Python Software Foundation, is powerful and easy to learn.
Introduction
Quick Downloads
Getting started with Python
If you are new to writing code for Phidgets, we recommend starting by running, then modifying existing examples. This will allow you to:
- Make sure your libraries are properly linked
- Go from source code to a test application as quickly as possible
- Ensure your Phidget is hooked up properly
Instructions are divided up by operating system. Choose:
- Windows 2000 / XP / Vista / 7
- OS X
- Linux (including PhidgetSBC)
Windows (2000/XP/Vista/7)
Description of Library
Python programs on Windows depend on the following. The installers in the Quick Downloads section put only the phidget21.dll into your system. You will need to manually put the Phidget Python Module into your system.
phidget21.dllcontains the actual Phidget library, which is used at run-time. By default, it is placed inC:\Windows\System32.Phidget Python Moduleis the Phidget library for Python.setup.pyis used to install the Phidget module into the standard location for third party Python modules. On typical Python environments, this setup will install the Phidget Python module in thesite-packagesdirectory.
If you do not want to use our installer, you can download the phidget21.dll.
The first thing you will have to do is to install the Phidget Python Module.
Afterwards, Running the examples and writing your own code can be fairly compiler-specific, so we include instructions for each environment below.
Installing the Phidget Python Module
Please start by downloading Phidget Python Module. After extracting the file, open up a command line terminal, traverse to the directory containing setup.py and enter the following to install the Phidget Python module into the Python environment.
python setup.py install
Command Line
Use Our Examples
Please ensure that the Phidget Python Module is installed onto your system.
Next, download the examples and unpack them into a folder. While these examples were written in Python 3.0, they are also compatible with Python 2.5(with a minor modification). If you aren't sure what the software example for your device is called, check the software object listed in the Getting Started guide for your device.
Now, open up a command line prompt and navigate to the directory of the example folder.
Next, enter the following to run the example:
python example.py
Once you have the Python examples running, we have a teaching section below to help you follow them.
Write Your Own Code
When you are building a project from scratch, or adding Phidget function calls to an existing project, you'll need to configure your environment to properly link the Phidgets Python libraries. Please see the Use Our Examples section for instructions.
Then, in your code, you will need to reference to the Phidget Python library.
from Phidgets.PhidgetException import *
from Phidgets.Events.Events import *
Then, you will also have to add a reference to your particular Phidget. For example, you would include the following line for a PhidgetInterfaceKit:
from Phidgets.Devices.InterfaceKit import *
Please see the examples on how to add a reference to your particular Phidget.
The project now has access to the Phidget function calls and you are ready to begin coding.
The same teaching section which describes the examples also has further resources for programming your Phidget.
IDLE
Use Our Examples
Please ensure that the Phidget Python Module is installed onto your system.
Next, download the examples and unpack them into a folder. While these examples were written in Python 3.0, they are also compatible with Python 2.5(with a minor modification). If you aren't sure what the software example for your device is called, check the software object listed in the Getting Started guide for your device. Now, open the example in the IDLE editor.
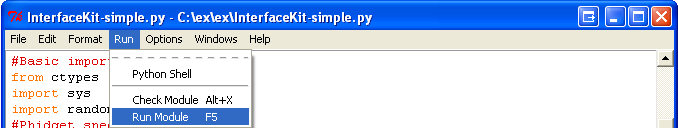
The only thing left to do is to run the examples! Click on Run → Run Module.
Once you have the Python examples running, we have a teaching section below to help you follow them.
Write Your Own Code
When you are building a project from scratch, or adding Phidget function calls to an existing project, you'll need to configure your environment to properly link the Phidget Python library. Please see the Use Our Examples section for instructions.
Then, in your code, you will need to reference to the Phidget Python library.
from Phidgets.PhidgetException import *
from Phidgets.Events.Events import *
Then, you will also have to add a reference to your particular Phidget. For example, you would include the following line for a PhidgetInterfaceKit:
from Phidgets.Devices.InterfaceKit import *
Please see the examples on how to add a reference to your particular Phidget.
The project now has access to the Phidget function calls and you are ready to begin coding.
The same teaching section which describes the examples also has further resources for programming your Phidget.
Eclipse with PyDev
Use Our Examples
1. Please ensure that the Phidget Python Module is installed onto your system.
2. Next, download the examples and unpack them into a folder. While these examples were written in Python 3.0, they are also compatible with Python 2.5(with a minor modification). If you aren't sure what the software example for your device is called, check the software object listed in the Getting Started guide for your device. You will need this example source code to be imported into your project later on.
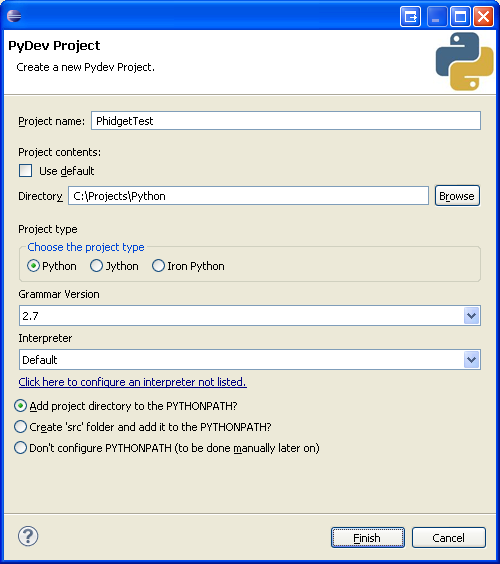
3. Next, a new project will need to be created. Generate a new PyDev project with a descriptive name such as PhidgetTest.
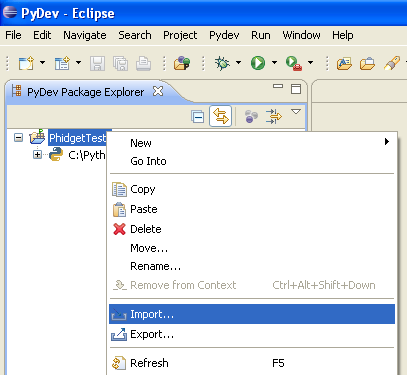
4. To import the example program into your project, right click the Project and select Import.
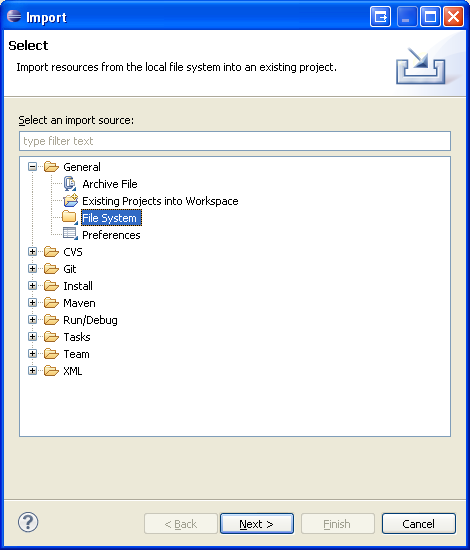
5. On the next screen, select File System and proceed to the next screen.
6. Browse to the directory where you extracted the examples into, and select the example you wish to open.
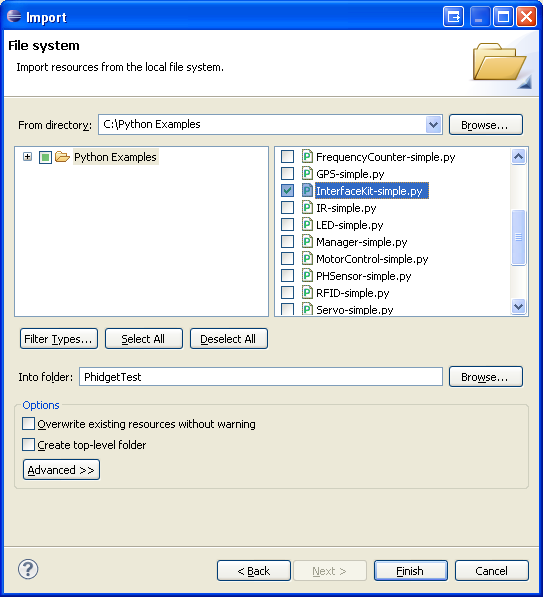
7. The only thing left to do is to run the examples! Click on Run → Run.
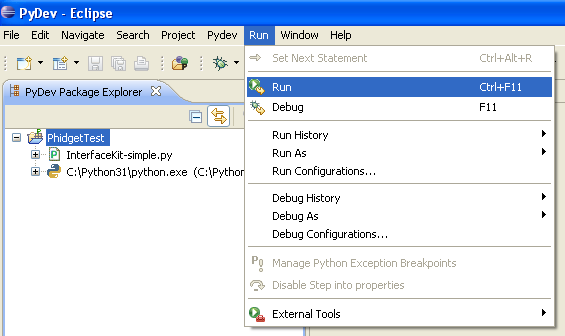
Once you have the Python examples running, we have a teaching section below to help you follow them.
Write Your Own Code
When you are building a project from scratch, or adding Phidget function calls to an existing project, you'll need to configure your environment to properly link the Phidget Python library. Please see the Use Our Examples section for instructions.
Then, in your code, you will need to include a reference to the Phidget Python library.
from Phidgets.PhidgetException import *
from Phidgets.Events.Events import *
You will also have to add a reference to your particular Phidget. For example, you would include the following line for a PhidgetInterfaceKit:
from Phidgets.Devices.InterfaceKit import *
Please see the examples on how to add a reference to your particular Phidget.
The project now has access to the Phidget function calls and you are ready to begin coding.
The same teaching section which describes the examples also has further resources for programming your Phidget.
OS X
Python has excellent support on OS X.
The first step in using Python on Mac is to install the Phidget libraries. Compile and install them as explained on the getting started guide for your device. Then, the OS - OS X page also describes the different Phidget files, their installed locations, and their roles....
Linux
Python has excellent support on Linux.
The first step in using Python on Linux is to install the Phidget libraries. These are the core Phidget libraries, written in C, which when compiled become part of the programming libraries available to your system. Download, compile, and install from the links and instructions on the main Linux page. That Linux page also describes the different Phidget files, their installed locations, and their roles.
The next step is to install the Phidget Python module. Download it here:
Then, unpack the module and enter the root of the newly unzipped directory. There will be a script in the base directory called setup.py. This is used the same way as most other distributed Python modules - from a command line type:
python setup.py install
This will build the module and install the built python module files into your site-packages directory.
Use Our Examples
First, download the examples:
Unpack them, and enter the root directory. You will find examples specific to each Phidget device, as well as a HelloWorld.py example. The HelloWorld.py code is probably the easiest example to run as it will work with any Phidget device. Or you can use the example specific to your Phidget. In that case, find the source file that is named the same as the software object for your device. If you are not sure what the software object for your device is, it can be found in the Software/API section on the Product Page for your device.
The Phidget examples were written in Python 3.0 and this tutorial assumes its use. However, they should still be compatible with Python 2.6. To run the examples using Python 2.5, you will need to modify the example code in the exception handling to read “except RuntimeError, e:”, instead of “except RuntimeError as e:”.
If needed, make those changes to the HelloWorld.py example or the one for your Phidget.
Then, if you have not set up your udev rules for USB access, you will need to run the Python example as root:
sudo python HelloWorld.py
Write Your Own Code
When writing your code from scratch, you start it as you would any Python code on Linux, such as within a text editor like Emacs, Vi, Gedit, or Kate. In your .py source code file, you must include a reference to the Phidget module:
from Phidgets.PhidgetException import *
from Phidgets.Events.Events import *
In addition, you should include the module functions for your specific device. In the case of the Interface Kit, this would be:
from Phidgets.Devices.InterfaceKit import *
For other devices, it would be the software object you found when running the examples above. Then, you would run your Python code the same way as the examples.
To learn how to write your own code for your Phidget, and to learn more about our API, we have a teaching section to help you follow the provided Python examples and which has resources such as the API reference.
Follow the Examples
By following the instructions for your operating system and compiler above, you probably now have a working example and want to understand it better so you can change it to do what you want. This teaching section has resources for you to learn from the examples and write your own.
Your main reference for writing Python code will be our Python API information, with syntax for all of our functions:
Template:UsingAPhidgetInCodeGeneral
Example Flow
Code Snippets
Specific calls in Python will differ in syntax from those on the General Phidget Programming page, but the concepts stay the same.
It may help to have the General Phidget Programming page and this section open at the same time, because they parallel each other and you can refer to the Python syntax. However, many additional concepts are covered on the General Phidget Programming page on a high level, such as using multiple Phidgets, handling errors, and different styles of programming.
For example, if we were using a Phidget Interface Kit as our device, the general calls would look like this:
Step One: Initialize and Open
# Create
try:
device = InterfaceKit()
except RuntimeError as e:
print("Runtime Error: %s" % e.message)
# Open
try:
device.openPhidget()
except PhidgetException as e:
print (“Phidget Exception %i: %s” % (e.code, e.detail))
exit(1)
The variable device is now a handle for the Phidget. This example is specific to the Interface Kit because the call InterfaceKit() is used. For another device, use the correspondingly named call in the Python API.
The handle device is then used for all the Python function calls using the Phidget for its device-specific functions - in this case, Interface Kit specific functions. Every type of Phidget also inherits functionality from the Phidget base class.
Note that open() opens the software object, but not hardware. So, it is not a guarantee you can use the Phidget immediately. The different types of open can be used with parameters to try and get the first device it can find, open based on its serial number, or even open across the network. The API manual lists all of the available modes that open provides.
Also note that you can catch exceptions thrown by the Phidget library as we did above when using the openPhidget() call. In other words, this should probably be present around most of your Phidget calls, especially when you are learning how to use the Phidget and debugging your code:
try:
# Your code goes here
except PhidgetException as e:
print (“Phidget Exception %i: %s” % (e.code, e.detail))
exit(1)
Step Two: Wait for Attachment (plugging in) of the Phidget
To use the Phidget, it must be plugged in (attached). We can handle this simply by calling waitForAttachment. This function works for any Phidget. WaitForAttachment will block indefinitely until a connection is made to the Phidget, or an optional timeout is exceeded:
device.waitForAttach(10000)
print ("%d attached!" % (device.getSerialNum()))
Sometimes, it makes more sense to handle the attachment via an event. This would be in instances where the Phidget is being plugged and unplugged, and you want to handle these incidents. Or, when you want to use event-driven programming because you have a GUI-driven program. In these cases,
def AttachHandler(event):
attachedDevice = event.device
serialNumber = attachedDevice.getSerialNum()
deviceName = attachedDevice.getDeviceName()
print("Hello to Device " + str(deviceName) + ", Serial Number: " + str(serialNumber))
- Insert code for -creating- device here....
try:
device.setOnAttachHandler(AttachHandler)
except PhidgetException as e:
# Insert code for handling any exceptions # A common exception will occur if you do not create the device properly above
- Insert code for -opening- device here....
Step Three: Do Things with the Phidget
MATLAB does not support event handling, so all data must be read and sent directly.
The most common thing you might want to do is read data from sensors. For example, in the code below, we might want to read data from a sensor on the Phidget Interface Kit.
Simply use the C API functions such as CPhidgetInterfaceKit_getSensorValue() or CPhidgetInterfaceKit_setOutState() for Interface Kits. The following reads and displays data from a sensor ten times as quickly as the while loop can execute:
while n<10
dataPointer = libpointer('int32Ptr',0);
calllib('phidget21', 'CPhidgetInterfaceKit_getSensorValue', device, 0, dataPointer)
disp(get(dataPointer, 'Value'));
n=n+1;
end
Step Four: Close and Delete
calllib('phidget21', 'CPhidget_close', ikhandle);
calllib('phidget21', 'CPhidget_delete', ikhandle);
At the end of your program, don’t forget to call close to free any locks on the Phidget that the open() call put in place!
The complete set of functions you have available for all Phidgets can be found in the C/C++ API. Note, however, MATLAB does not make use of the event functions in the C/C++ API. You can also find more description on any device-specific function either in the Device API page for calls available only on your specific Phidget.
Common Problems and Solutions/Workarounds
OS X: My application hangs when using multiple devices in a single Python application.
A call to open may hang indefinitely if multiple devices are being programmed in a single Python application. To circumvent this, allow the application to delay a short period between open calls. For most environments, a 1.25 millisecond delay is enough. For example:
import time
...
interface_kit.openPhidget(94695)
time.sleep(0.00125)
rfid.openPhidget(33502)
All Operating Systems: The examples produces an error while running in a Python 2.5 environment.
Running the examples produces an error similar to the following:
InterfaceKit-simple.py:33: Warning: 'as' will become a reserved keyword in Python 2.6
File "InterfaceKit-simple.py", line 33
except RuntimeError as e:
SyntaxError: invalid syntax
To run the example code in Python 2.5, all the lines containing:
except RuntimeError as e:
will need to be replaced with:
except Runtime, e:
