Logging Explained
Logging
Logging is a set of functionality designed to quietly track the operation of a software program to be stored for later examination. It is generally used for debugging purposes.
Getting Started
For basic use of the log class, the only functions you need to worry about are enable and log.
Simply enable logging with log level INFO, and use log to write your own messages to the log file.
Anatomy of a Log
To better understand the concepts in this guide, we will dissect a log entry to clarify its component parts.
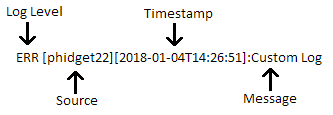
Source
Sources are a property of Phidgets Log messages that indicate where the log message originated. By default, the writing to the log using the log function of your language will write to the source named phidget22.
For more advanced applications, some log functions will allow you to specify custom sources to allow for specialized logging implementations.
Hidden Sources
In addition to the default phidget22 source, there are a number of background log sources that are hidden by default. This is to keep log files relatively clean and allow focus on messages that matter to the application.
These sources are:
| _phidget22bridge | Internal Use Phidget Bridge Logs (Not the physical device) |
| _phidget22channel | Internal Use Channel Information Logs |
| _phidget22disp | Internal Use Phidget Dispatch Logs |
| _phidget22match | Internal Use Channel Matching Logs |
| _phidget22netctl | Internal Use Network Control Logs |
| _phidget22usb | USB Processing Logs |
| phidget22net | Network Logs |
Log Level
Log levels are designed to sort messages in terms of importance, with lower log levels being generally the most important, and higher log levels carrying supplemental information.
Log levels are arranged as follows:
| Lowest Level | CRITICAL | Indicates something very important that should always be logged. |
| ERROR | Describes errors that occur during a program's operation. | |
| WARNING | Warnings about a program's behaviour. | |
| INFO | Supplemental information about a program's status. | |
| DEBUG | Extra information that is only useful for debugging purposes. | |
| Highest Level | VERBOSE | More information than is useful for most applications except intensive debugging. |
Setting the log level will filter log entries to only allow messages of that level and below to be added to the log. For example, if the log level was INFO, then logs of level DEBUG and VERBOSE will be ignored, while all other logs would be stored.
Log levels can be independently set for all sources using the variant of setSourceLevel for your language. This is useful for filtering out log messages from sources that would otherwise flood the log. It can also be used to show logs from sources that are hidden by default.
Timestamp
The time that the message was logged in local time, formatted as:
YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SS
Message
This is the message written to the log. It will contain the information intended to be logged.
Log Rotation
Log rotation is the automated process of archiving the current log file and starting a new one once the log becomes too large. Rotating log files is a method of keeping file size down while still keeping track of all the latest log information.
Log rotation is enabled by default in Phidget22, and will keep two files: the current log file and the latest archived log file. The maximum size and number of archived log files can be adjusted using the setRotating function in your language of choice.
Archived log files will have a timestamp of the time they were archived appended to the end of the log filename, as follows:
log.txt.2018-01-05T10_47_16
