HUB5000 User Guide
Getting Started
Before you get started with plugging in and setting up your Wireless VINT Hub, we recommend downloading our libraries from here.
First Look
To begin, connect the power supply to the barrel jack on the HUB5000 and connect it to a modem or network switch using an ethernet cable.

After plugging the HUB5000 in, open the Phidget Control Panel and go to the "Network Phidgets" tab. You will see something like this:
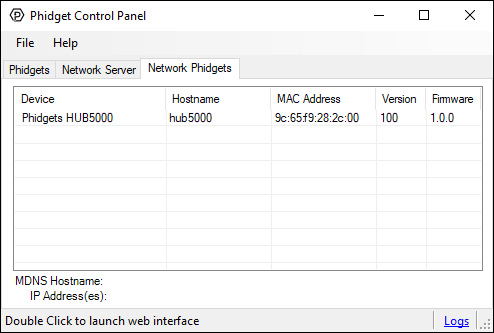
Double click on the HUB5000's row and you'll be brought to a webpage. Select a password and click "submit". You can use this password in the future to access this configuration page.

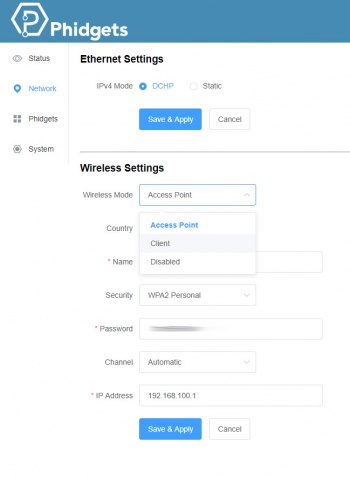
From here, click on the "Network" tab and change the mode from "Access Point" to "Client". You'll have to choose a name and password before saving. If you want to use the HUB5000 wirelessly, you should also enter your Wi-Fi network details here. The HUB5000 should now be accessible from the "Phidgets" tab of the Control Panel.
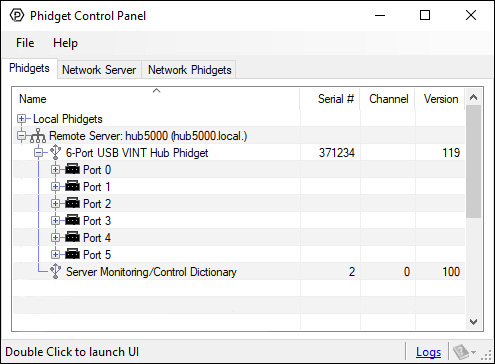
The Phidget Control Panel will list all connected Phidgets and associated objects, as well as the following information:
- Serial number: allows you to differentiate between similar Phidgets.
- Channel: allows you to differentiate between similar objects on a Phidget.
- Version number: corresponds to the firmware version your Phidget is running. If your Phidget is listed in red, your firmware is out of date. Update the firmware by double-clicking the entry.
If you haven't already, now would be a good time to upgrade the firmware of the HUB5000. Once you're done with that, use the Phidget Control Panel to test your device. Double-clicking on an object will open an example.
Using the HUB5000
This table will help you decide where to look next to get your devices plugged in and running:
|
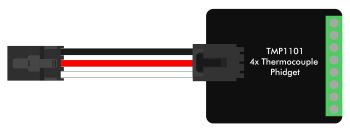
This mode is for connecting to a VINT device. These devices differ from analog sensors because instead of just reporting 0 to 5 volts, they communicate with the VINT Hub. The communication is digital, therefore it is immune to electrical interference between the hub and the device. | |
|
In digital input mode, the VINT Hub port can act as an active-low digital input. This mode is great for reading the state of buttons and switches. |
In voltage ratio input mode, the VINT Hub port will read the voltage on the white wire and compare it to the voltage being supplied on the red wire. This mode will let you read any ratiometric Phidgets sensor. |
|
In voltage input mode, the VINT Hub port will read the voltage on the white wire. This can be used to interface a non-ratiometric sensor, or to measure the voltage in a 5V digital circuit. |
In digital output mode, a VINT Hub port can behave like a 3.3V digital output. You could use this mode to blink an LED or switch on a MOSFET. And don't worry if you still need a 5V digital output; there are VINT modules available that provide multiple 5V digital outputs on a single VINT port. |
Now that you have everything together, let's start using the HUB5000!
VINT Device A VINT Device is any Phidget that must be controlled by a VINT Hub instead of plugging directly into your computer via USB. You can find a complete list of VINT devices here. When you double click on an VINT Device in the control panel, a window will open with controls and readouts for that specific class of Phidget. For instructions on how to use this example, find the user guide for that Phidget.
|
Digital InputUsing the Digital InputsWiring a switch to a Digital Input Connect the switch between the white and black wires of a Phidget cable, and plug the cable into a VINT port. Wiring the switch this way will make the input TRUE when the switch is closed, and FALSE when the switch is open.
Using the Control PanelDouble-click on a Digital Input object in order to run the example: 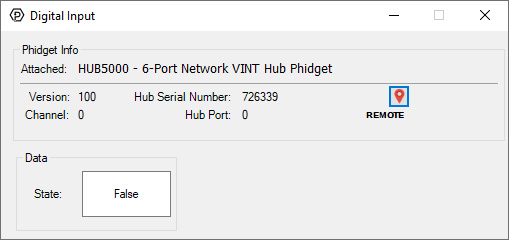
For more information about Digital Inputs, take a look at the Digital Input Primer |
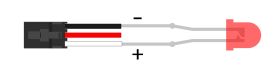
Digital OutputUsing the Digital OutputsHere are some diagrams that illustrate how to connect various devices to the digital outputs on your Phidget. Driving an LED Connecting an LED to a digital output is simple. Wire the anode (long side) to the white wire on the Phidget cable, and the cathode to the black wire of the Phidget cable. If you wire it backwards, the LED will not light but no harm will come to the system. You do not need to have a resistor in series with the LED to limit current, because this is handled by the internal circuitry of the VINT port.
Using the Control PannelDouble-click on a Digital Output object in order to run the example: 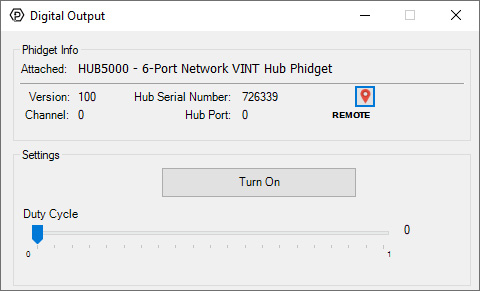 General information about the selected object will be displayed at the top of the window. You can also experiment with the following functionality:
For more information about Digital Outputs, check out the Digital Output Primer. |
Voltage InputUsing the Voltage InputsHere are some examples of how you can connect various devices to the voltage inputs on your Phidget:  Connect a SensorConnecting to a Phidget sensor is as simple as plugging it into the VINT Port with a Phidget cable.
Using the Control PannelDouble-click on a Voltage Input object in order to run the example: 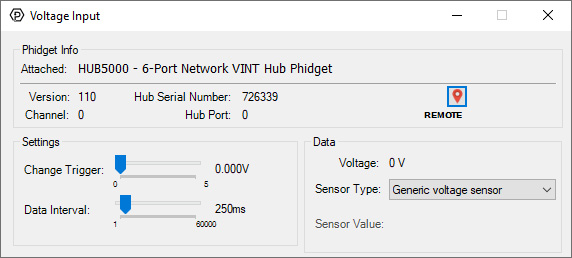
For more information about Voltage Inputs, check out the Voltage Input Primer. |
Voltage Ratio InputUsing the Voltage Ratio InputsHere are some examples of how you can connect various devices to the voltage ratio inputs on your Phidget: 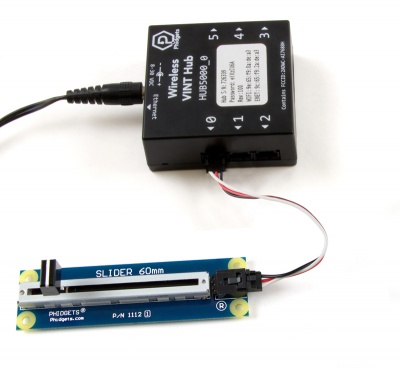 Connect a SensorConnecting to a ratiometric sensor is as simple as plugging it into the VINT Port with a Phidget cable.
Using the Control PannelDouble-click on a Voltage Ratio Input object in order to run the example: 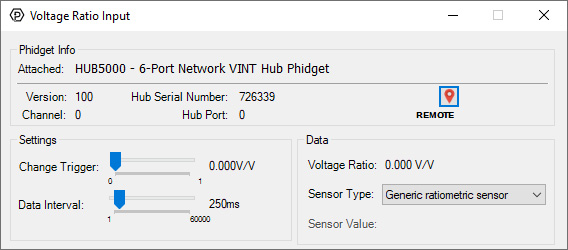 General information about the selected object will be displayed at the top of the window. You can also experiment with the following functionality:
For more information about Voltage Ratio Inputs, check out the Voltage Ratio Input Primer. |
Finding The Addressing Information
Before you can access the device in your own code, and from our examples, you'll need to take note of the addressing parameters for your Phidget. These will indicate how the Phidget is physically connected to your application. For simplicity, these parameters can be found by clicking the button at the top of the Control Panel example for that Phidget.
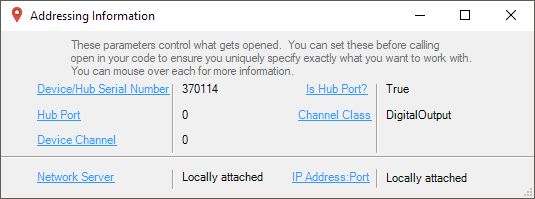
In the Addressing Information window, the section above the line displays information you will need to connect to your Phidget from any application. In particular, note the Channel Class field as this will be the API you will need to use with your Phidget, and the type of example you should use to get started with it. The section below the line provides information about the network the Phidget is connected on if it is attached remotely. Keep track of these parameters moving forward, as you will need them once you start running our examples or your own code.
Using Your Own Program
You are now ready to start writing your own code for the device. The best way to do that is to start from our Code Samples.
Select your programming language of choice from the drop-down list to get an example for your device. You can use the options provided to further customize the example to best suit your needs.
Once you have your example, you will need to follow the instructions on the page for your programming language to get it running. To find these instructions, select your programming language from the Programming Languages page.
Technical Details
Upgrading the Firmware
You can download the most recent HUB5000 firmware binary here:
To upgrade the firmware, go into the web configuration page as outlined in the getting started section of this page. From there, click on "System", and upload this file by click on "select file" under the "Upgrade Firmware" section. After that, click on "Upgrade and Restart". You'll be instructed to wait a few minutes before logging back in to the web interface. When you do, you can confirm that the new version has successfully installed by checking to see if the firmware version listed in the "Status" section matches the first three numbers in the firmware file name that you downloaded. You can also check the version in the "Network Phidgets" tab on the Phidget Control Panel.
CE Compliance
In order for the HUB5000 to be completely CE compliant, you must put a ferrite bead on the ethernet cable (if using the ethernet connection). This is only necessary when building the HUB5000 into a larger system that needs to be CE compliant and happens to use the HUB5000 wired with ethernet. You can find clamp-on ferrite beads at electronic parts stores such as digikey.
VINT Ports
For more information on the capabilities of the ports on the VINT Hub, see the VINT Primer.
Configuration Page
Configuration using the Phidget Control Panel
To get to the HUB5000's configuration page, open the Phidget Control Panel and find it under the "Network Phidgets" tab as outlined in the getting started section of this page.
Configuration using Phone
If the HUB5000 is in access point mode, you can access the configuration page through your phone: Connect to the HUB5000 Wi-Fi signal and enter the password on the sticker. Once you're connected, go to your internet app and go to address 192.168.100.1. This will take you to the configuration login page.
Settings
- Status: This section lists the hardware and firmware version of the HUB5000, along with the network addresses.
- Network: This section allows you to change the network connection settings and switch between Access Point mode and Client mode.
- Phidgets: This section has controls for the Phidget Server (including the ability to change the log level and view the log file), and has controls for the Web Server.
- System: This section allows you to change the password and has other advanced settings including firmware upgrade and system/kernel logs.
Factory Reset (Reset Passwords)

Pressing the reset button will reboot the HUB5000.
Holding it down for 10 seconds and releasing will perform a factory reset, which will clear all settings including the web configuration page password and reset the Wi-Fi password to the one on the HUB5000's label.
Holding the button down before plugging in power, and keeping pressed for 15 seconds before releasing, will restore the original factory firmware. This should be a last resort for when a regular reset isn't working, or if something went wrong with a firmware upgrade.
Setting the Device Label
When opening channels with Phidgets, you can set a number of properties to make sure you match the precise channel you want. The HUB5000 has a unique serial number which can be used to find its ports or any VINT devices connected to them. If you want something more customizable and human-readable, you can use the device label instead. You can customize the device label by using writeDeviceLabel on the Hub object after it's been opened.
Once a device label has been written, you can use it to address any of the VINT Hub's channels, or the channels of any VINT device connected to the hub.
What to do Next
- Programming Languages - Find your preferred programming language here and learn how to write your own code with Phidgets!
- Phidget Programming Basics - Once you have set up Phidgets to work with your programming environment, we recommend you read our page on to learn the fundamentals of programming with Phidgets.