Voltage Output Guide
Introduction
An analog output is simply an interface that takes digital data and outputs it in the form of an analog signal. Since this type of output is meant to generate signals, it is usually low current (20mA or less) and is not meant to be used for supplying high-power devices. The current can't be controlled, so this output is only suitable for interfacing with devices that accept voltage signals.
Analog outputs are commonly used for generating simple waveforms for test purposes, employing dimmer control on low-current electronics, or controlling devices such as proportional control relays.
Technical Explanation
How it works
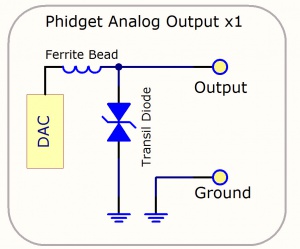
When the user selects an output value in software, the digital-to-analog converter (DAC) on the board converts this digital value into an analog voltage signal. The resulting signal is filtered through a ferrite bead, and reaches the output on the terminal block. The transil diode protects the analog outputs from electrostatic discharge.
Basic Use
To use an analog output, simply connect the output terminals to the device you want to supply an analog signal to. Make sure that the device is specified to draw less current than the maximum current per channel of the analog output. If you exceed the maximum current of a Phidget Analog Output, an over-current error will be thrown, because passing the current limit will cause the output voltage to vary depending on the resistance of the load and thus lose accuracy. For example, the 1002 - PhidgetAnalog 4-Output is most accurate when supplying 5 mA or less. The actual limit may vary from channel to channel, so it's a good idea to stay as far from the current limit as your application will allow.
If you need to generate an analog signal with a higher current limit, you can build a simple amplifier circuit in between the analog output and the load.
Avoiding Startup Transients
When an analog output board is first powered up, the voltage level on the output will be unpredictable for a few milliseconds. If this behaviour is causing problems for your system, you may want to put a relay on the output and write your program to switch the relay on after an appropriate amount of time has elapsed after startup. For output boards that support multiple range settings, this method could also be used to avoid transient behaviour when switching the range setting.
