|
Notice: This page contains information for the legacy Phidget21 Library. Phidget21 is out of support. Bugfixes may be considered on a case by case basis. Phidget21 does not support VINT Phidgets, or new USB Phidgets released after 2020. We maintain a selection of legacy devices for sale that are supported in Phidget21. We recommend that new projects be developed against the Phidget22 Library.
|
Language - Adobe Director: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (51 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Language]] | [[Category:Language]] | ||
[[File:icon-Adobe_Director.png|64x64px|link=|alt= | {{OSLang|[[File:icon-Adobe_Director.png|64x64px|link=|alt=]]|Adobe Director, developed by [http://www.adobe.com Adobe Systems] is a tool used to build interactive and multimedia applications.}} | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
{{LanguageSupport|Adobe Director|the complete Phidget API, including events| | {{LanguageSupport|Adobe Director|the complete Phidget API, including events|the PhidgetInterfaceKit devices.|Windows.|}} | ||
}} | |||
==Quick Downloads== | ==Quick Downloads== | ||
{{QuickDownloads| | {{QuickDownloads|Adobe Director| | ||
{{APIQuickDownloads| | {{APIQuickDownloads|{{SERVER}}/documentation/COM_API_Manual.pdf}}| | ||
{{ExampleQuickDownloads| | {{ExampleQuickDownloads|{{SERVER}}/downloads/phidget21/examples/com/AdobeDirector.zip|}}| | ||
{{ExtraLibraryQuickDownloads| | {{ExtraLibraryQuickDownloads|{{SERVER}}/downloads/phidget21/libraries/windows/Phidget21-windevel.zip|COM|}} | ||
{{WindowsQuickDownloads}} | {{WindowsQuickDownloads}}}} | ||
}} | |||
==Getting started with Adobe Director== | ==Getting started with Adobe Director== | ||
| Line 25: | Line 20: | ||
{{ExampleCodeReasons}} | {{ExampleCodeReasons}} | ||
The only operating system we support with Adobe Director is [[#Windows (2000/XP/Vista/7)|Windows (2000/XP/Vista/7)]]. | |||
==Windows( | ==Windows (XP/Vista/7/8)== | ||
===Description of Library=== | ===Description of Library Files=== | ||
Adobe Director programs on Windows depend on the following: | |||
* <b>{{Code|phidget21.dll}}</b> contains the actual Phidget library, which is used at run-time. By default, it is placed in {{Code|C:\Windows\System32}}. | * <b>{{Code|phidget21.dll}}</b> contains the actual Phidget library, which is used at run-time. By default, it is placed in {{Code|C:\Windows\System32}}. The installers in the [[#Libraries and Drivers | Quick Downloads]] section put this file into your system. | ||
* <b>{{Code| | * <b>{{Code|Phidget21COM.dll}}</b> is the Component Object Model (COM) library and provides your project access to the Phidget ActiveX objects. This is part of our [{{SERVER}}/downloads/phidget21/libraries/windows/Phidget21-windevel.zip COM Library]. If you installed the Phidget drivers, it will have automatically registered the ActiveX objects into your system. If you are manually installing this file, you must register it through command line by running: {{Code|regsvr32 Phidget21COM.dll}}. | ||
If you do not want to use our installer, you can download | If you do not want to use our installer, you can download both [{{SERVER}}/downloads/phidget21/libraries/windows/Phidget21-windevel.zip files] and manually install them where you want; refer to our [[OS_-_Windows#Manual_File_Installation| Manual Installation Instructions]]. | ||
===Adobe Director 11.5=== | |||
====Use Our Examples==== | |||
=== | |||
1. Download the [{{SERVER}}/downloads/phidget21/examples/com/AdobeDirector.zip examples] and unpack them into a folder. These examples were written in Adobe Director 11.5. | |||
2. The easiest way to confirm that your environment is set up properly will be to run the HelloWorld Adobe Director example. In the Adobe Director environment, open up the file named {{Code|HelloWorld.dir}}. | |||
3. To run the example, click on Control → Play. | |||
[[File:AdobeDirector Play.PNG|link=|alt=Play]] | |||
4. This program will detect for devices that are attached/detached on the computer. Go ahead, and attach or detach your devices! Here is an example output: | |||
[[File:AdobeDirector HelloWorld Output.PNG|link=|alt=HelloWorld Output]] | |||
After confirming that the {{Code|HelloWorld}} example is working, you can proceed to run the example for your device. Currently, the only device we have example code for is the PhidgetInterfaceKit. | |||
Once you have the | Once you have the Adobe Director examples running, we have a teaching section below to help you follow them. | ||
====Write Your Own Code==== | ====Write Your Own Code==== | ||
When you are building a project from scratch, or adding Phidget function calls to an existing project, you'll need to configure your environment to properly link the | When you are building a project from scratch, or adding Phidget function calls to an existing project, you'll need to configure your environment to properly link the Phidget ActiveX object. | ||
1. Create a new movie. | |||
2. Navigate to Insert → Control → ActiveX. | |||
[[File:AdobeDirector Add ActiveX 1.PNG |link=|alt=Add ActiveX Control]] | |||
3. Select the ActiveX control that corresponds to your device. Select {{Code|OK}}. | |||
[[File:AdobeDirector Add ActiveX 2.PNG |link=|alt=Add ActiveX Control]] | |||
4. A window will pop up listing the properties and methods of the ActiveX class. Select {{Code|OK}}. | |||
[[File:AdobeDirector Class ActiveX Properties.PNG |link=|alt=ActiveX Properties]] | |||
5. The ActiveX class will be added to your cast. Create an instance of it by dragging and dropping the cast member onto the stage. | |||
[[File:AdobeDirector ActiveX Cast.PNG |link=|alt=ActiveX Cast]] | |||
The project now has access to the Phidget function calls and you are ready to begin coding. | The project now has access to the Phidget function calls and you are ready to begin coding. | ||
| Line 140: | Line 77: | ||
The same [[#Follow the Examples|teaching ]] section which describes the examples also has further resources for programming your Phidget. | The same [[#Follow the Examples|teaching ]] section which describes the examples also has further resources for programming your Phidget. | ||
== | ==Follow the Examples== | ||
By following the instructions for your operating system and compiler above, you probably now have a working example and want to understand it better so you can change it to do what you want. This teaching section has resources for you to learn from the examples and write your own. | |||
Your main reference for writing Adobe Director code will be our Adobe Director API information, with syntax for all of our functions: | |||
{{UsingAPhidgetInCodeGeneral|both of which are available in Adobe Director|[{{SERVER}}/documentation/COM_API_Manual.pdf COM API]}} | |||
===Example Flow=== | |||
{{ExamplePseudocode|In Adobe Director, you catch these '''event''' functions using their specific names as shown below in the Code Snippets section. The specific syntax for different events and which Phidgets you can catch which events for can be found in the [{{SERVER}}/documentation/COM_API_Manual.pdf COM API] manual. Catching events by name hooks your event functions into the actual events when they occur. <br> | |||
In the example code, some event functions are common to all Phidgets. These are events such as '''OnAttach''' and '''OnDetach''', etc.<br><br> | |||
Some event functions will be specific to each device, like when a tag is read on an RFID board, or when a sensor value changes on an Interface Kit. | |||
|Creating a Phidget software object in Adobe Director is specific to the Phidget. For a Phidget Spatial, for example, this would involve creating a {{Code|Spatial}} ActiveX object, as shown in the [[#Write Your Own Code|Write Your Own Code]] section above. The examples show working instances of how to do this, and how to use other API functions.<br><br> | |||
The object provides device specific methods and properties which are available from the API for your specific Phidget.| | |||
[{{SERVER}}/documentation/COM_API_Manual.pdf COM API]}} | |||
===Code Snippets=== | |||
Specific calls in Adobe Director will differ in syntax from those on the [[General Phidget Programming]] page, but the concepts stay the same. | |||
[[ | It may help to have the [[General Phidget Programming]] page and this section open at the same time, because they parallel each other and you can refer to the Adobe Director syntax. However, many additional concepts are covered on the General Phidget Programming page on a high level, such as using multiple Phidgets, handling errors, and different styles of programming. | ||
For example, if we were using a [{{SERVER}}/products.php?product_id=1018 Phidget Interface Kit] as our device, the general calls would look like this: | |||
====Step One: Initialize and Open==== | |||
Your program can try to connect to the Phidget through a call to open. Open will continuously try to connect to a Phidget, based on the parameters given, even trying to reconnect if it gets disconnected. This means that simply calling open does not guarantee you can use the Phidget immediately. Because we then have to also attach the Phidget within software after opening, in Adobe Director the Open step and the next step - [[#Step Two: Wait for Attachment (plugging in) of the Phidget|Attach]] - are often combined within one event trigger. | |||
The different parameters and open calls can be used to open: | |||
* The first Phidget of a type it can find, | |||
* A Phidget based on a serial number, or even | |||
* A Phidget across the network. | |||
The [{{SERVER}}/documentation/COM_API_Manual.pdf COM API] manual lists all of the available modes that open provides. One important thing to remember is that when working with Phidgets, a local connection will reserve the device until closed. This prevents any other instances from retrieving data from the Phidget, including other programs. The one connection per device limit does not apply when exclusively using the [[Phidget WebService]]. | |||
====Step Two: Wait for Attachment (plugging in) of the Phidget==== | |||
We can account for a connection by using event driven programming and tracking the AttachEvents and DetachEvents, or by calling WaitForAttachment as we show here. | |||
== | WaitForAttachment will block indefinitely until a connection is made to the Phidget, or an optional timeout is exceeded. Here, the Phidget is opened and then attached when on clicking the Open button inside a mouseUp event: | ||
<div class=source> | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang=text> | |||
on mouseUp me | |||
sprite(1).CallString("Open()") | |||
sprite(1).CallString("WaitForAttachment(3000)") | |||
end | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
</div> | |||
====Step Three: Do Things with the Phidget==== | |||
We recommend the use of event driven programming when working with Phidgets in Adobe Director. This allows the program to execute other tasks until the Phidget fires a new event. In Adobe Director, you can hook an event handler inside a script for the Phidget object by catching the event by name with the following code: | |||
<div class= | <div class=source> | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang= | <syntaxhighlight lang=text> | ||
on OnSensorChange(Index, SensorValue) me | |||
member("OutputField").text = string(Index) & ": " & string(SensorValue) | |||
end | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
With this method, the code inside OnSensorChange will get executed every time the InterfaceKit reports a change on one of its analog inputs. Please refer to the [{{SERVER}}/documentation/COM_API_Manual.pdf COM API] manual for a full list of events and their usage. | |||
Some values can be directly read and set on the Phidget, and inside polling loops used as an alternative to event driven programming. Simply use the CallString method for obtaining data such as SensorValue(Index) or OutputState(Index, OutputState) for Interface Kits. For example: | |||
<div class= | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang= | <div class=source> | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang=text> | |||
sprite(1).CallString("OutputState(0,1)") | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Other events for different Phidgets can be found in the device's [[:Category:UserGuide|user guide]], and in the [{{SERVER}}/documentation/COM_API_Manual.pdf COM API] manual. | |||
====Step Four: Close and Delete==== | |||
You can use {{Code|CallString("Close")}} at any time outside of the Phidget's own event handlers to close the connection. | |||
====Multiple Phidgets==== | |||
Multiple Phidgets of the same type can easily be run inside the same Adobe Director program. This requires another PhidgetInterfaceKit ActiveX object to be created and placed. The new object can then be set up, opened and used in the same process as the previous one. If the application needs to distinguish between the devices, open can be called with the serial number of a specific Phidget. | |||
The complete set of functions you have available for all Phidgets can be found in the [{{SERVER}}/documentation/COM_API_Manual.pdf COM API]. | |||
==Common Problems and Solutions/Workarounds== | ==Common Problems and Solutions/Workarounds== | ||
=== | ===Windows users in The Netherlands=== | ||
A number of users in the Netherlands have reported issues with running our example code. It is possible this is an issue related to the Dutch language pack used for Windows however, we do not currently really know why. As we aren't able to run a Dutch version of Windows here, it is difficult to debug. If you would like to help us work through the example code that we provide and help us figure out why, please [[Contact Us]]. | |||
Latest revision as of 18:54, 6 June 2017
| Adobe Director, developed by Adobe Systems is a tool used to build interactive and multimedia applications. |
Introduction
If this is your first time working with a Phidget, we suggest starting with the Getting Started page for your specific device. This can be found in the user guide for your device. That page will walk you through installing drivers and libraries for your operating system, and will then bring you back here to use Adobe Director specifically.
Adobe Director is capable of using the complete Phidget API, including events. We also provide example code in Adobe Director for the PhidgetInterfaceKit devices.
Adobe Director can be developed with Windows..
You can compare Adobe Director with our other supported languages.
Quick Downloads
Just need the Adobe Director documentation, drivers, libraries, and examples? Here they are:
Documentation
Example Code
Libraries and Drivers
- COM Libraries
- 32-bit Windows Drivers Installer
- 64-bit Windows Drivers Installer
- Windows Driver and Library Files (Zipped)
Getting started with Adobe Director
If you are new to writing code for Phidgets, we recommend starting by running, then modifying existing examples. This will allow you to:
- Make sure your libraries are properly linked
- Go from source code to a test application as quickly as possible
- Ensure your Phidget is hooked up properly
The only operating system we support with Adobe Director is Windows (2000/XP/Vista/7).
Windows (XP/Vista/7/8)
Description of Library Files
Adobe Director programs on Windows depend on the following:
phidget21.dllcontains the actual Phidget library, which is used at run-time. By default, it is placed inC:\Windows\System32. The installers in the Quick Downloads section put this file into your system.Phidget21COM.dllis the Component Object Model (COM) library and provides your project access to the Phidget ActiveX objects. This is part of our COM Library. If you installed the Phidget drivers, it will have automatically registered the ActiveX objects into your system. If you are manually installing this file, you must register it through command line by running:regsvr32 Phidget21COM.dll.
If you do not want to use our installer, you can download both files and manually install them where you want; refer to our Manual Installation Instructions.
Adobe Director 11.5
Use Our Examples
1. Download the examples and unpack them into a folder. These examples were written in Adobe Director 11.5.
2. The easiest way to confirm that your environment is set up properly will be to run the HelloWorld Adobe Director example. In the Adobe Director environment, open up the file named HelloWorld.dir.
3. To run the example, click on Control → Play.
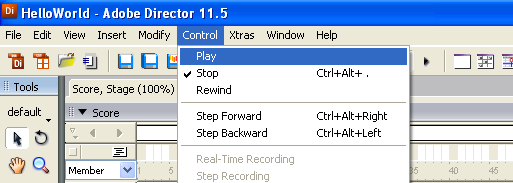
4. This program will detect for devices that are attached/detached on the computer. Go ahead, and attach or detach your devices! Here is an example output:
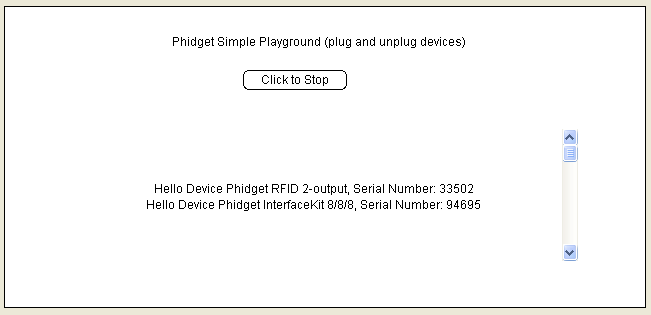
After confirming that the HelloWorld example is working, you can proceed to run the example for your device. Currently, the only device we have example code for is the PhidgetInterfaceKit.
Once you have the Adobe Director examples running, we have a teaching section below to help you follow them.
Write Your Own Code
When you are building a project from scratch, or adding Phidget function calls to an existing project, you'll need to configure your environment to properly link the Phidget ActiveX object.
1. Create a new movie.
2. Navigate to Insert → Control → ActiveX.
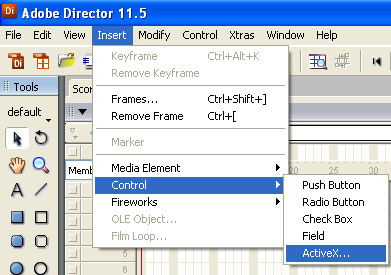
3. Select the ActiveX control that corresponds to your device. Select OK.
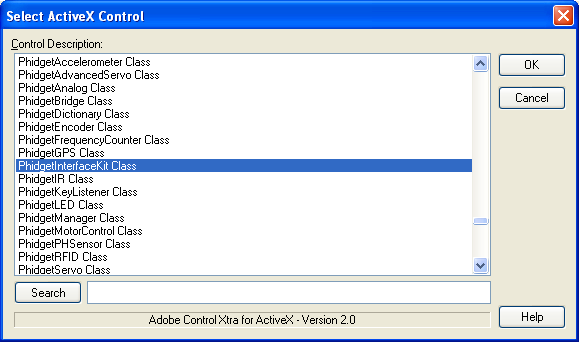
4. A window will pop up listing the properties and methods of the ActiveX class. Select OK.
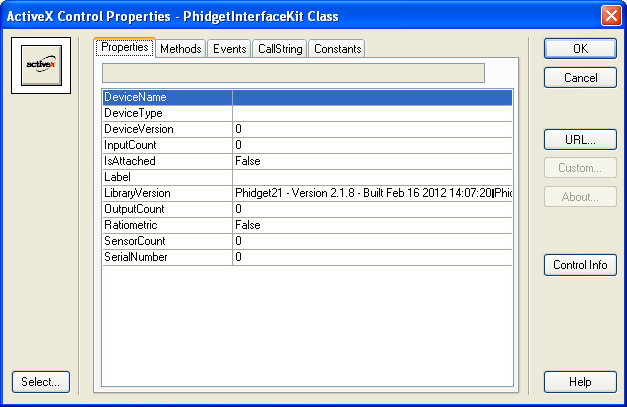
5. The ActiveX class will be added to your cast. Create an instance of it by dragging and dropping the cast member onto the stage.
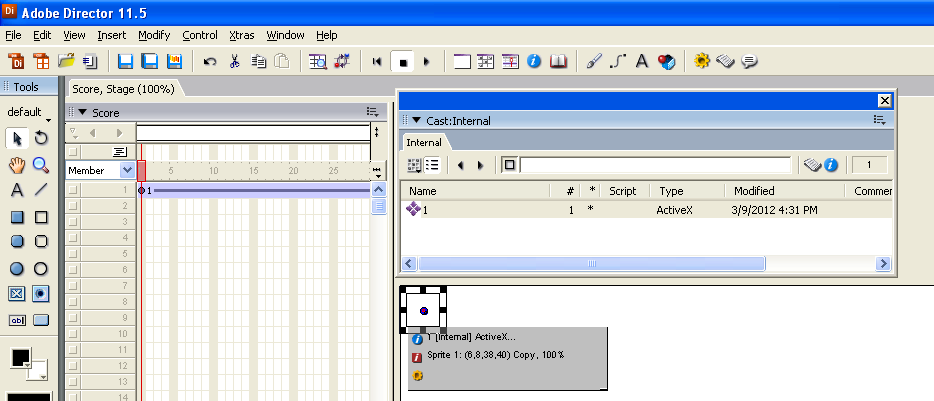
The project now has access to the Phidget function calls and you are ready to begin coding.
The same teaching section which describes the examples also has further resources for programming your Phidget.
Follow the Examples
By following the instructions for your operating system and compiler above, you probably now have a working example and want to understand it better so you can change it to do what you want. This teaching section has resources for you to learn from the examples and write your own.
Your main reference for writing Adobe Director code will be our Adobe Director API information, with syntax for all of our functions:
- COM API (This is the complete set of functions you have available for all Phidgets)
- Device Specific APIs - The one for your Phidget can be found in its user guide.
To learn the details behind opening, configuring, using, and closing your Phidget, try the General Phidget Programming page. That page also describes using the Phidget in an event-driven manner and in a traditional manner, both of which are available in Adobe Director.
Example Flow
The Hello World example has this general structure so you can follow along. We also have an in-depth general introduction to writing Phidget code (like open, read data, etc), as well as the COM API for specific syntax:
|
// ----- Event and Other Functions ----- Create any Language-Specific Functions (exception handling) Create General Attach, Detach, and Error Handling Functions:
|
In Adobe Director, you catch these event functions using their specific names as shown below in the Code Snippets section. The specific syntax for different events and which Phidgets you can catch which events for can be found in the COM API manual. Catching events by name hooks your event functions into the actual events when they occur. | |
|
// ----- Main Code -----
Close Device Delete Device
|
Creating a Phidget software object in Adobe Director is specific to the Phidget. For a Phidget Spatial, for example, this would involve creating a |
Code Snippets
Specific calls in Adobe Director will differ in syntax from those on the General Phidget Programming page, but the concepts stay the same.
It may help to have the General Phidget Programming page and this section open at the same time, because they parallel each other and you can refer to the Adobe Director syntax. However, many additional concepts are covered on the General Phidget Programming page on a high level, such as using multiple Phidgets, handling errors, and different styles of programming.
For example, if we were using a Phidget Interface Kit as our device, the general calls would look like this:
Step One: Initialize and Open
Your program can try to connect to the Phidget through a call to open. Open will continuously try to connect to a Phidget, based on the parameters given, even trying to reconnect if it gets disconnected. This means that simply calling open does not guarantee you can use the Phidget immediately. Because we then have to also attach the Phidget within software after opening, in Adobe Director the Open step and the next step - Attach - are often combined within one event trigger.
The different parameters and open calls can be used to open:
- The first Phidget of a type it can find,
- A Phidget based on a serial number, or even
- A Phidget across the network.
The COM API manual lists all of the available modes that open provides. One important thing to remember is that when working with Phidgets, a local connection will reserve the device until closed. This prevents any other instances from retrieving data from the Phidget, including other programs. The one connection per device limit does not apply when exclusively using the Phidget WebService.
Step Two: Wait for Attachment (plugging in) of the Phidget
We can account for a connection by using event driven programming and tracking the AttachEvents and DetachEvents, or by calling WaitForAttachment as we show here.
WaitForAttachment will block indefinitely until a connection is made to the Phidget, or an optional timeout is exceeded. Here, the Phidget is opened and then attached when on clicking the Open button inside a mouseUp event:
on mouseUp me
sprite(1).CallString("Open()")
sprite(1).CallString("WaitForAttachment(3000)")
end
Step Three: Do Things with the Phidget
We recommend the use of event driven programming when working with Phidgets in Adobe Director. This allows the program to execute other tasks until the Phidget fires a new event. In Adobe Director, you can hook an event handler inside a script for the Phidget object by catching the event by name with the following code:
on OnSensorChange(Index, SensorValue) me
member("OutputField").text = string(Index) & ": " & string(SensorValue)
end
With this method, the code inside OnSensorChange will get executed every time the InterfaceKit reports a change on one of its analog inputs. Please refer to the COM API manual for a full list of events and their usage.
Some values can be directly read and set on the Phidget, and inside polling loops used as an alternative to event driven programming. Simply use the CallString method for obtaining data such as SensorValue(Index) or OutputState(Index, OutputState) for Interface Kits. For example:
sprite(1).CallString("OutputState(0,1)")
Other events for different Phidgets can be found in the device's user guide, and in the COM API manual.
Step Four: Close and Delete
You can use CallString("Close") at any time outside of the Phidget's own event handlers to close the connection.
Multiple Phidgets
Multiple Phidgets of the same type can easily be run inside the same Adobe Director program. This requires another PhidgetInterfaceKit ActiveX object to be created and placed. The new object can then be set up, opened and used in the same process as the previous one. If the application needs to distinguish between the devices, open can be called with the serial number of a specific Phidget.
The complete set of functions you have available for all Phidgets can be found in the COM API.
Common Problems and Solutions/Workarounds
Windows users in The Netherlands
A number of users in the Netherlands have reported issues with running our example code. It is possible this is an issue related to the Dutch language pack used for Windows however, we do not currently really know why. As we aren't able to run a Dutch version of Windows here, it is difficult to debug. If you would like to help us work through the example code that we provide and help us figure out why, please Contact Us.
