|
Notice: This page contains information for the legacy Phidget21 Library. Phidget21 is out of support. Bugfixes may be considered on a case by case basis. Phidget21 does not support VINT Phidgets, or new USB Phidgets released after 2020. We maintain a selection of legacy devices for sale that are supported in Phidget21. We recommend that new projects be developed against the Phidget22 Library.
|
OS - iOS: Difference between revisions
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
===Checking=== | ===Checking=== | ||
When you run a Phidgets iOS example, you transfer and link the libraries and code all at the same time. This should 'just work' with our examples, but if problems arise this section gives more detail on pinpointing the source of the problem. We recommend starting with running the software examples right away - if the software works, you know the hardware works too. | |||
====Software==== | ====Software==== | ||
The easiest way to see whether your libraries are set up correctly within our examples or your own project is just to download them to the iOS device and run them. Detailed instructions for this (including choosing the right {{Code|HelloWorld}} project to run) are on the [[Language - iOS]] page. That page will be your next step - but if the examples do not run using the instructions, return here to debug your hardware. | |||
[[ | ====Hardware==== | ||
If you are having problems running the examples, you should check the [[#Remote Phidget|hardware of the host computer]]. | |||
=====Remote Phidget===== | |||
When using the [[#Webservice|Webservice]] to control a Phidget, the problem may be with the USB connection on the remote computer. Make sure both the server-side of (a) the webservice and (b) the USB connection are working by using the instructions on the [[Software Overview#Operating System Support|page specific to the operating system]] | |||
You need to access the logs from your debugging computer - e.g. the computer where you have installed Google's development plugins as described above. Plug a USB Phidget into your iOS device. Then, as soon as possible, from a command line on that computer, use the ADB (Android Debugging Bridge) program to access the program {{Code|dmesg}} on your Android device: | |||
<div class="source"> | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang=bash> | |||
adb shell dmesg | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
</div> | |||
This will print out the entirety of the kernel logs on your Android device. Even if you have been running your device for only a little while, this could be thousands of lines of output. If you plugged the Phidget in and then ran {{Code|dmesg}} right away, the kernel detection of the Phidget should be almost at the bottom of the logs. If you are on Linux or Mac OS, you can mitigate the length of this output using {{Code|tail -n 50}} or so. If you are on Windows, you may consider using a command redirection operator like {{Code|>}} to write to a file and then view the last 50 or so lines. | |||
Near the end of the output you will find something like this for a successful registration of a Phidget in the Android kernel: | |||
<div class="source"> | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang=text> | |||
<6>[ 3282.554249] usb 1-1.2: new full speed USB device using tegra-ehci and address 5 | |||
<6>[ 3282.612359] usb 1-1.2: New USB device found, idVendor=06c2, idProduct=0032 | |||
<6>[ 3282.612418] usb 1-1.2: New USB device strings: Mfr=1, Product=2, SerialNumber=3 | |||
<6>[ 3282.612466] usb 1-1.2: Product: PhidgetTemperatureSensor | |||
<6>[ 3282.612504] usb 1-1.2: Manufacturer: Phidgets Inc. | |||
<6>[ 3282.612540] usb 1-1.2: SerialNumber: 287638 | |||
<4>[ 3282.612576] device: '1-1.2': device_add | |||
<4>[ 3282.615639] device: '1-1.2:1.0': device_add | |||
<4>[ 3282.618632] device: '0003:06C2:0032.0003': device_add | |||
<3>[ 3282.631412] generic-usb 0003:06C2:0032.0003: claimed by neither input, hiddev nor hidraw | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
</div> | |||
If the kernel log Phidget attachment does '''not''' appear, make sure that other devices that are supposed to work with your tablet (USB data keys, keyboards, etc. - the list depending entirely on which tablet) do indeed work. Not having the Phidget appear in your kernel logs indicates there is a problem with your USB hardware on your Android device. | |||
Note that in order to consider a port on your tablet to be compatible with Phidgets it must be able to '''host''' USB devices. Simply finding and using a USB cable to connect the Phidget to the power charging port on your phone or tablet is not enough! A host USB port should either say so explicitly, or at least act like a 'normal' USB port such as ones you would find on your PC, and be able to use many common USB devices like memory sticks. | |||
If | If the kernel log attachment does appear, but your code doesn't run, the problem is probably with your code. Work through the [[Language - Android Java]] page to make sure you have all the libraries, jar files, and permissions set and linked properly to use your Phidget. | ||
====Troubleshooting==== | ====Troubleshooting==== | ||
If the examples '''do not''' work but USB '''does''' work (i.e. your computer can consistently see the device in the [[#Hardware|hardware]]), take a moment to check the basics: | If the examples '''do not''' work but USB '''does''' work (i.e. your remote computer or Android device can consistently see the device in the [[#Hardware|hardware]]), take a moment to check the basics: | ||
* No other programs, drivers, or processes are using the the Phidget on the host computer. | |||
* You have copied and linked the Phidget iOS libraries (as described on the [[Language - iOS]] page) | |||
* No other programs, drivers, or processes are using | |||
* The Phidget libraries are the latest version (visit the [[#Getting Started (Libraries and Drivers)| getting started section]] to download them) | * The Phidget libraries are the latest version (visit the [[#Getting Started (Libraries and Drivers)| getting started section]] to download them) | ||
* | * Ensure that the webservice drivers and the iOS libraries are both the latest version | ||
* Check the [[#Common Problems and Solutions|common problems]] section below, some specific combinations can cause problems | * Check the [[#Common Problems and Solutions|common problems]] section below, some specific combinations can cause problems | ||
If your problem doesn't seem to be fixed by these steps, make sure that the Phidget is seen '''consistently''' by USB (if it is erratic, try our [[General Troubleshooting|general troubleshooting guide]]). If you are still having problems after using the troubleshooting guide, please [[Contact Information|ask us]]! | If your problem doesn't seem to be fixed by these steps, make sure that the Phidget is seen '''consistently''' by USB in [[#Hardware|hardware]] (if it is erratic, try our [[General Troubleshooting|general troubleshooting guide]]). If you are still having problems after using the troubleshooting guide, please [[Contact Information|ask us]]! | ||
==Programming Languages== | ==Programming Languages== | ||
Revision as of 19:53, 10 April 2012
![]() iOS is a mobile OS used on iOS devices including the iPad, iPhone, and iPod touch.
iOS is a mobile OS used on iOS devices including the iPad, iPhone, and iPod touch.
Phidgets are designed to run on devices with an iOS version of 3.0 or later. It is strontly recommended that your device have the latest iOS version installed. As iOS devices do not have USB ports, the Phidgets will have to be connected on a computer with USB ports, and the iOS device will be able to interact with the Phidget over the Webservice. If you are looking for a compact and cheaper-than-a-tablet way to host Phidgets over a network, take a look at our Single Board Computer.
Getting Started (Libraries and Drivers)
If this is your first Phidget, we highly recommend working through the Getting Started guide for your specific Phidget device.
iOS code is developed on an external OS X machine, and so getting your Phidget to work locally on that platform first will help you distinguish any issues from network ones later.
If you are already a pro, and just want the drivers:
Installing
The 'installation' of the Phidget iOS libraries is simply linking and distributing the libraries with your code. As the most common platform to do this is through Xcode, we provide brief instructions on how to easily follow along with our already-linked examples later.
To install the libraries, follow these steps:
1. Download one of the Phidget installer for your system, depending on whether your system is 32 or 64-bit.
2. Unzip the file, and you will find three things:
- Libraries for the iOS device and iOS simulator
- Example code for the PhidgetInterfaceKit and PhidgetManager
- Skeleton project - contains the minimal project settings already filled in for Phidgets development.
Feel free to browse around within the folders to get a sense of what will be going on the iOS side. We describe how to link and use these library files later on the Write your own iOS code section of the iOS Cocoa Touch page. For now, having found them means you can copy and 'install' them to any project directory you want.
First, though, it will be useful to check to make sure Phidgets work with your iOS system.
Checking
When you run a Phidgets iOS example, you transfer and link the libraries and code all at the same time. This should 'just work' with our examples, but if problems arise this section gives more detail on pinpointing the source of the problem. We recommend starting with running the software examples right away - if the software works, you know the hardware works too.
Software
The easiest way to see whether your libraries are set up correctly within our examples or your own project is just to download them to the iOS device and run them. Detailed instructions for this (including choosing the right HelloWorld project to run) are on the Language - iOS page. That page will be your next step - but if the examples do not run using the instructions, return here to debug your hardware.
Hardware
If you are having problems running the examples, you should check the hardware of the host computer.
Remote Phidget
When using the Webservice to control a Phidget, the problem may be with the USB connection on the remote computer. Make sure both the server-side of (a) the webservice and (b) the USB connection are working by using the instructions on the page specific to the operating system
You need to access the logs from your debugging computer - e.g. the computer where you have installed Google's development plugins as described above. Plug a USB Phidget into your iOS device. Then, as soon as possible, from a command line on that computer, use the ADB (Android Debugging Bridge) program to access the program dmesg on your Android device:
adb shell dmesg
This will print out the entirety of the kernel logs on your Android device. Even if you have been running your device for only a little while, this could be thousands of lines of output. If you plugged the Phidget in and then ran dmesg right away, the kernel detection of the Phidget should be almost at the bottom of the logs. If you are on Linux or Mac OS, you can mitigate the length of this output using tail -n 50 or so. If you are on Windows, you may consider using a command redirection operator like > to write to a file and then view the last 50 or so lines.
Near the end of the output you will find something like this for a successful registration of a Phidget in the Android kernel:
<6>[ 3282.554249] usb 1-1.2: new full speed USB device using tegra-ehci and address 5
<6>[ 3282.612359] usb 1-1.2: New USB device found, idVendor=06c2, idProduct=0032
<6>[ 3282.612418] usb 1-1.2: New USB device strings: Mfr=1, Product=2, SerialNumber=3
<6>[ 3282.612466] usb 1-1.2: Product: PhidgetTemperatureSensor
<6>[ 3282.612504] usb 1-1.2: Manufacturer: Phidgets Inc.
<6>[ 3282.612540] usb 1-1.2: SerialNumber: 287638
<4>[ 3282.612576] device: '1-1.2': device_add
<4>[ 3282.615639] device: '1-1.2:1.0': device_add
<4>[ 3282.618632] device: '0003:06C2:0032.0003': device_add
<3>[ 3282.631412] generic-usb 0003:06C2:0032.0003: claimed by neither input, hiddev nor hidraw
If the kernel log Phidget attachment does not appear, make sure that other devices that are supposed to work with your tablet (USB data keys, keyboards, etc. - the list depending entirely on which tablet) do indeed work. Not having the Phidget appear in your kernel logs indicates there is a problem with your USB hardware on your Android device.
Note that in order to consider a port on your tablet to be compatible with Phidgets it must be able to host USB devices. Simply finding and using a USB cable to connect the Phidget to the power charging port on your phone or tablet is not enough! A host USB port should either say so explicitly, or at least act like a 'normal' USB port such as ones you would find on your PC, and be able to use many common USB devices like memory sticks.
If the kernel log attachment does appear, but your code doesn't run, the problem is probably with your code. Work through the Language - Android Java page to make sure you have all the libraries, jar files, and permissions set and linked properly to use your Phidget.
Troubleshooting
If the examples do not work but USB does work (i.e. your remote computer or Android device can consistently see the device in the hardware), take a moment to check the basics:
- No other programs, drivers, or processes are using the the Phidget on the host computer.
- You have copied and linked the Phidget iOS libraries (as described on the Language - iOS page)
- The Phidget libraries are the latest version (visit the getting started section to download them)
- Ensure that the webservice drivers and the iOS libraries are both the latest version
- Check the common problems section below, some specific combinations can cause problems
If your problem doesn't seem to be fixed by these steps, make sure that the Phidget is seen consistently by USB in hardware (if it is erratic, try our general troubleshooting guide). If you are still having problems after using the troubleshooting guide, please ask us!
Programming Languages
After you have installed the drivers above, you should pick a programming language, install libraries, and run the examples for that specific language.
Phidgets’ philosophy is that you do not have to be an electrical engineer in order to do projects that use devices like sensors, motors, motor controllers, and interface boards. All you need to know is how to program.
On Windows, we recommend the following languages:
You can also use these languages, but they do not support event driven code, and must use logic code only:
The following languages are also supported, but to to a lack of demand, they full API is not implemented. Please refer to the specific language for more information on what features are unsupported.
Webservice
The Phidget Webservice allows you to remotely control a Phidget over a network.
Drivers for the Phidget Webservice on Windows are already included in the Drivers above. If you have a ![]() icon in your taskbar, you already have the Webservice drivers installed.
icon in your taskbar, you already have the Webservice drivers installed.
You can connect to a Phidget hosted on another computer if you know the IP address of the host computer. Phidgets optionally supports the use of mDNS, which allows Phidgets to be found and opened on the network by a server id instead of an IP address and port. When using a server id, both the client and server will need to be running an implementation of zero configuration networking. The Phidget Webservice takes advantage Bonjour software. It is a tool, developed by Apple to locate devices such as Phidgets, and printers. It allows you to connect to a Phidget over the Webservice while specifying the server id. Alternatively, an IP address and port can be supplied to connect to a Phidget over the Webservice. If you do not have Bonjour installed on your system, you will have to use the second method to connect to a Phidget.
This section helps you install, check, and use the Webservice on Windows, but we also have an overview of the Phidget Webservice in general.
Turning the Webservice On and Off
There are two methods that can be used to turn the Webservice on and off. The first method is through the Phidget Control Panel. In the Webservice tab, you can start, restart or stop the Webservice. You can also choose to have the Webservice start up automatically upon Windows boot up by selecting Automatic as the Startup Type. By leaving the Startup Type as Manual, you will have to manually turn the Webservice on everytime you wish to use it.
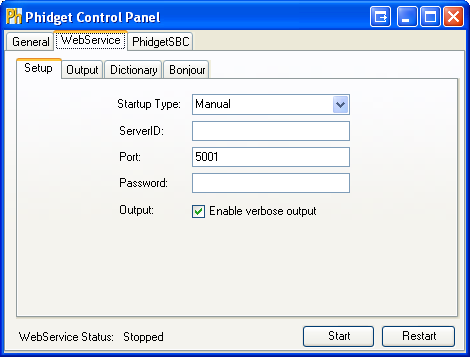
The second method of turning the Webservice on and off is through command line. If you used our installer, the Webservice utility is automatically installed in C:\Program Files\Phidgets\PhidgetWebservice21.exe.
You can get command line help with PhidgetWebservice21.exe using the -h option:
PhidgetWebservice21 -h
'phidgetwebservice21' is a Phidget and Dictionary server from Phidgets Inc. See www.phidgets.com for more information.
Usage: phidgetwebservice21 [OPTION]
All parameters are optional. The default parameters are: port=5001, ServerName=(Computer Name) and no password
Options:
-p Port
-n Server Name
-P Password
-v Debug mode
-h Display this help
To find the defaults used by phidget21webservice, the command line is the fastest way to learn the default server name and IP address of your computer:
- For the default server name, type
hostnamein the command line. - For your IP address, type
ipconfig -allin the command line.- A line in the return text, will say something like
192.168.2.198, which is your IP.
- A line in the return text, will say something like
Here are some example usage. The Windows command line is used. Traverse to the Phidget installation directory(By default, it is located in C:\Program Files\Phidgets).
To start the Webservice with default parameters:
PhidgetWebservice21.exe
To start the Webservice with a server name of myServer:
PhidgetWebservice21.exe -n myServer
To stop the Webservice, simply close the command line window or press Ctrl and c at the same time in the command line window.
Using the Webservice
To use a Phidget over the Webservice, you'll want to:
- Have two different computers connected to the same network. We will call the computer that has the Phidget directly connected to the USB port the host. The client will be the computer that runs a Phidget application to connect to the Phidget attached to the host. Please note that If you only have a single computer, you can also connect to the Phidget over the Webservice. The computer will simply act as both a host and client.
- Start the Webservice on the computer that directly connects to the Phidget
- Run your program on the remote computer that will control the Phidget over the network
The easiest way to test these steps on Windows is download and install Bonjour onto both the host and client. Next, we will set up the Webservice and run the Phidget program on the client. Please follow these steps:
1. On the host, open up the Phidget Control Panel and traverse to the Setup tab of the WebService section.

2. Leave all fields the way it is, and click on Start to run the Webservice.
3. You can determine that the Webservice is running by looking at the WebService status at the bottom of the window.
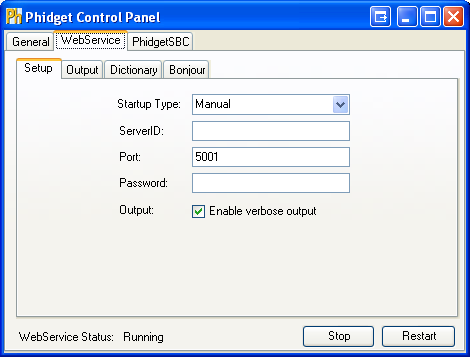
4. Ensure that the Phidget is plugged in to the host.
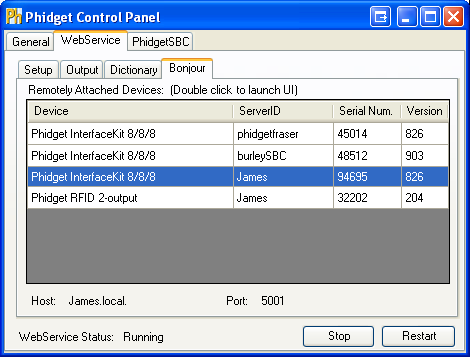
5. On the client's Phidget Control Panel, open up the Bonjour tab in the Webservice section. You will see the Phidget that is plugged into the host as one of the entries listed. Double click it to open the example application.
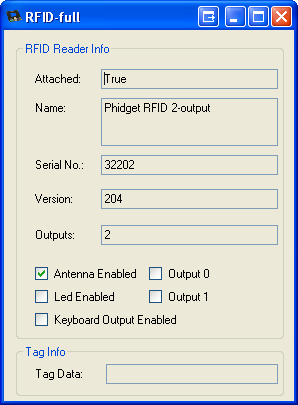
6. The example application will open up, and you will be able to interact with the Phidget over the Webservice.
7. You can confirm that the Webservice was indeed behind this exchange by killing the Webservice process while still allowing the remote program to run. On the host's Phidget Control Panel, traverse to the Setup tab of the Webservice section. Hit Stop to terminate the Webservice.

8. Take a look at the example application on the client. Since the application can no longer connect to the Webservice, the attached state of the Phidget is false.
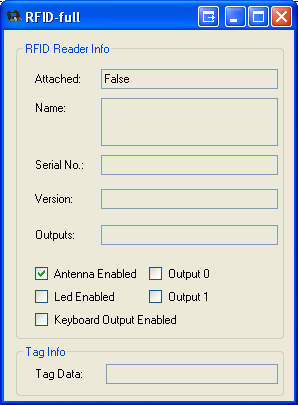
Debugging the Webservice
In addition to enabling logging in your Phidget code, you can get additional debugging information from the Webservice itself. This additional debugging can be enabled from the Enable verbose output checkbox in the Phidget Control Panel.

The debugging information is shown in the Output tab.
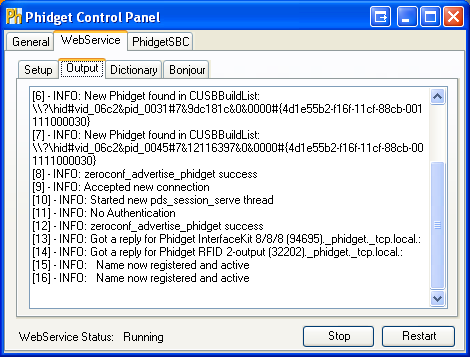
If you are using the command line approach to start the Webservice, debug information is enabled by specifying the -v option:
PhidgetWebservice21.exe -v -n "myServer"
The debugging information is shown command line output.
Advanced Uses
Manual File Installation
The Phidget installer installs the most commonly used files onto your system. However, there may be special cases where you want to install the Phidget libraries without the installers. This section will describe the purpose of each individual file and cover how to manually install and distribute the libraries with your code.
Description of Library files
phidget21.dllcontains the actual Phidget library, which is used at run-time. It is also placed inC:\Windows\System32.PhidgetWebService21.exeis used to control Phidgets remotely across a network using the PhidgetWebservce.PhidgetWindowsService21.exeis a Windows service that controlsPhidgetWebService21.exe.phidget21.libis used by your compiler to link to the dll. Your compiler has to know where this file is, by default our installer putsphidget21.libintoC:\Program Files\Phidgets, so you can either point your compiler to that location, or copy and link to it in a directory for your project workspace.phidget21.libis written to be compatible with most compilers - but your specific compiler may need a different format. Check our documentation for your specific compiler for details. Please note that we provide versions of thephidget21.libthat are specifically optimized for 32-bit or 64-bit systems. If you are using a 64 bit versions of Windows, thephidget21.libis placed inC:\Program Files\Phidgets; The 32 bit version ofphidget21.libis placed inC:\Program Files\Phidgets\x86.phidget21.hlists all the Phidget API function calls available to your code. Your compiler also has to know where this file is. By default, our installer putsphidget21.hintoC:\Program Files\Phidgetsso you can either point your compiler to that location, or copy and link to it in a directory for your project workspace.phidget21.jaris an archive containing the Phidgets library, used by the Java programming language.Phidget21.NET.dllis the Phidgets library for .NET framework 2.0 or greater. Any .NET language can be used, including C# , and Visual Basic .NET.Phidget21.NET1.1.dllis the Phidgets library for .NET framework 1.1. Any .NET language can be used, including C# , and Visual Basic .NET.Phidget21.NET.XMLprovides the IntelliSense in-line documentation for the .NET library in Visual Studio.Phidget21COM.dllis the Component Object Model(COM) library and provides your project access to the Phidget ActiveX objects. This libraries is used by the AdobeDirector, AutoIT, Delphi, Visual Basic 6.0, Visual Basic for Applications, Visual Basic Script.Phidget21Manager.exeis a tool to quickly determine whether your system is able to control Phidgets, and also act as a debugging tool.Examplesfolder contain example applications that allows you to quickly see if your Phidget is properly configured.x86 folderfolder contain the 32 bit versions ofphidget21.dll,phidget21.lib,Phidget21COM.dll. These folder will only appear on 64 bit installations and is useful if you want to code against the 32 bit libraries.
Special Cases of Library Install
Regardless of what language you will be using to program Phidgets, you will need the phidget21.dll placed in the C:\WINDOWS\system32 directory. Additional files are needed for the language that you choose. Please refer to the documentation provided by your language to determine what files are needed and the steps needed to install them onto your system.
You can find the phidget21.dll in the link below:
- Phidget21 Libraries (32-Bit and 64-Bit development files without an installer)
PhidgetWebService21.exe is also provided in the link above.
Windows in a Virtual Machine
Phidgets can also be used inside a virtual machine. Instructions for VMWare and VirtualBox are provided. Virtual PC is not supported as USB Phidgets requires a virtual platform that supports HID USB Devices. Since Virtual PC does not support HID USB devices, Phidgets may not be used.
As always, please ensure that you have the latest Phidget drivers installed on the virtual machine and that you are using the latest version of your virtual software.
VMWare:
To enable USB Phidgets, select Virtual Machine -> Removable Devices -> and select the Phidget Input Device -> Connect.
VirtualBox
To enable USB Phidgets, VirtualBox Guest Additions(Devices -> Install Guest Additions) may need to be installed. Afterwards, click on Devices -> USB Devices and select the Phidget device to enable. The state should go from Busy to Captured. VirtualBox may bring up a new hardware wizard in the host operating system, which has to be installed. Please note that Phidgets with USB hubs(i.e, 1019), are undetectable; Fortunately, Phidgets that are attached to such Phidgets are detectable.
Common Problems and Solutions
Issue: A corrupt installation fails on uninstall or repair
Affected Operating Systems: Windows
Solution: If the normal uninstall fails, or for whatever reason, you can choose to remove the Phidgets framework manually. Please perform the following:
- Shut down any programs using the Phidget libraries, including the webservice and the Phidget Control Panel.
- Delete C:\Program Files\Phidgets\
- Remove the Phidgets key from the Registry [-HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services PhidgetWebservice21].
In most cases this is enough to get the installer working again. If you need to remove all traces of the Phidgets libraries manually, perform the following additional steps:
- Unregister the COM library: regsvr32 /u “C:\Program Files\Phidgets\Phidget21COM.dll”
- Remove Phidget21.NET and Policy.2.1.Phidget21.NET from C:\Windows\Assembly\
- Delete ‘C:\Documents and Settings\All Users\Application Data\Phidgets’ (WindowsXP) or ‘C:\Users\All Users\Phidgets’ (Vista).
- Delete C:\Windows\system32\phidget21.dll
- Delete Phidgets from the start menu
- Search for and remove keys mentioning Phidgets from the registry in the following locations:
- [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\]
- [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Classes\Installer\Products\]
- [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\.NETFramework\AssemblyFolders\Phidgets Inc]
- [HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run\Phidget21Manager]
- [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Classes\Installer\Assemblies\Global\]
- 9. Reboot
NOTE: You can go through the registry and purge any other keys mentioning Phidgets if you still have problems, but at this point you should be able to reinstall under most cases. There will also be keys relating to the installer, the .NET library and the COM library, but they should not interfere with anything.
Issue: Event data is sporadic/slow/clumped over the webservice
Affected Operating Systems: Windows
Windows implements 200ms delayed ACKs for network traffic. When traffic is one-way only - as it is with event data, the data will all arrive in clumps every 200ms because of delayed ACKs.
This can be a great drawback for application which rely on low latency event data over the network. (source: http://support.microsoft.com/kb/214397)
This delayed ACK behavior can be disabled in windows to decrease event latency as documented here: http://support.microsoft.com/kb/328890
In the future, the Phidgets library may implement this differently, but so far we have been unable to match the performance achieved by disabling delayed ACK. Template:CreativeCommons
