|
Notice: This page contains information for the legacy Phidget21 Library. Phidget21 is out of support. Bugfixes may be considered on a case by case basis. Phidget21 does not support VINT Phidgets, or new USB Phidgets released after 2020. We maintain a selection of legacy devices for sale that are supported in Phidget21. We recommend that new projects be developed against the Phidget22 Library.
|
Language - Max/MSP: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:icon-MaxMSP.png|64x64px]] Max/MSP, developed by [http://cycling74.com Cycling74] is a visual programming language for creating music and media applications. | [[File:icon-MaxMSP.png|64x64px]] Max/MSP, developed by [http://cycling74.com Cycling74] is a visual programming language for creating music and media applications. | ||
__TOC__ | |||
==Introduction== | |||
{{LanguageSupport|Max/MSP|the complete Phidget API, including events|all Phidget devices.| Windows and Mac OS X.}} | |||
== | ==Quick Downloads== | ||
Just need the Max/MSP drivers, libraries, and examples? Here they are: | |||
API Documentation: | |||
Should we include the next 2 links? | |||
*[[General API]] (more help on functions common to all Phidgets) | |||
*[[Device List | Device Specific APIs]] (more help on functions specific to your Phidget) | |||
Max/MSP Library and Example Code: | |||
*[http://www.phidgets.com/downloads/examples/WinMaxMSP_2.1.8.20120123.zip Windows] | |||
*[http://www.phidgets.com/downloads/examples/WinMaxMSP_2.1.8.20120123.zip Mac OS X] | |||
Libraries and Drivers: | |||
*[http://www.phidgets.com/downloads/libraries/Phidget-x86_2.1.8.20111220.exe 32 bit Windows (drivers, with libraries)] | |||
*[http://www.phidgets.com/downloads/libraries/Phidget-x64_2.1.8.20111220.exe 64 bit Windows (drivers, with libraries)] | |||
*[http://www.phidgets.com/downloads/libraries/libphidget_2.1.8.20111028.tar.gz General Linux Libraries] ([[OS - Linux | Linux Library Setup Instructions]]) | |||
*[http://www.phidgets.com/downloads/libraries/Phidget_2.1.8.20111103.dmg General Mac OSX Libraries] ([[OS - Mac OS X | Mac OS X Library Setup Instructions]]) | |||
==Getting started with Max/MSP== | |||
If you are new to writing code for Phidgets, we recommend starting by running, then modifying existing examples. This will allow you to: | |||
{{ExampleCodeReasons}} | |||
Instructions are divided up by operating system. Choose: | |||
*[[#Windows(2000/XP/Vista/7)|Windows 2000 / XP / Vista / 7]] | |||
*[[#Mac OS X |Mac OS X]] | |||
==Windows(2000/XP/Vista/7)== | |||
===Libraries=== | |||
*[http://www.phidgets.com/downloads/examples/WinMaxMSP_2.1.8.20120123.zip Windows Library and Examples] | |||
*[http://www.phidgets.com/downloads/examples/WinMaxMSP_2.1.8.20120123.zip Mac OS X Library and Examples] | |||
===Description=== | |||
Max/MSP programs on Windows depend on the following files, which the installers above put onto your system: | |||
* <b><code>phidget21.dll</code></b> contains the actual Phidgets library, which is used at run-time. If you used our installer, it's already correctly placed in <code>C:\Windows\System32</code>. It can be manually installed - check our [[Manual Installation instructions]]. | |||
You will also need one of the following two files, depending on the .NET framework version you are targeting: | |||
* <b><code>Phidget<Device Name>.mxe</code></b> is the Phidgets library for Max/MSP 4.5 or higher. It is to be placed in the same directory as your <code>.help</code> file | |||
===Use Our Examples=== | |||
Please start by downloading the Max/MSP Examples. These examples were written in Visual Studio 2005 and 2008, but Visual Studio 2010 will easily upgrade them. | |||
*[http://www.phidgets.com/downloads/examples/WinMaxMSP_2.1.8.20120123.zip Max/MSP Examples] | |||
To run the examples, you first download them [[#Quick Downloads|from above]] and unpack them into a folder. To load all projects in Visual Studio, go to File | Open | Project, and open <code>AllExamples/AllExamples.sln</code> or <code>AllExamples/AllExamples_vs2008.sln</code> for Visual Studio 2005 and 2008, respectively. | |||
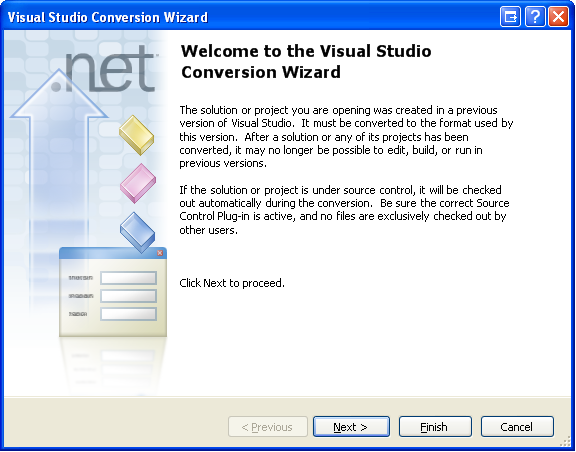
If you are opening the Phidget examples in Visual Studio 2010, you will need to go through the Visual Studio Conversion Wizard to convert the 2005 or 2008 project. | |||
<br/><br/>[[File:VS2005 Conversion Wizard.PNG]]<br/><br/> | |||
This will load all of the examples available for C#, and then you can set your main project to be the one that matches your device. If you aren't sure what the software example for your device is called, check the software object listed in the [[Device List | Getting Started guide for your device]]. | |||
This | |||
The only thing left to do is to run the examples! Click on Debug -> Start Debugging. Please note that the projects, by default try to find the <code>Phidget21.NET.dll</code> in the <code>C:\Program Files\Phidgets</code>. If you have it installed in another location, please change the path accordingly. If you are receiving an error message regarding that the namespace Phidgets cannot be found, please re-add the reference to <code>Phidget21.NET.dll</code>. Please see the [[#Write Your Own Code | next section]] for details. | |||
<br/><br/> | |||
[[File:CSharp VS2005 Run.PNG ]] | |||
<br/><br/> | |||
Once you have the C# examples running, we have a [[#Follow The Examples|teaching section]] below to help you follow them. | |||
=====Write Your Own Code===== | |||
When you are building a project from scratch, or adding Phidget function calls to an existing project, you'll need to configure your compiler / development environment to properly link the Phidget C# libraries. To begin: | |||
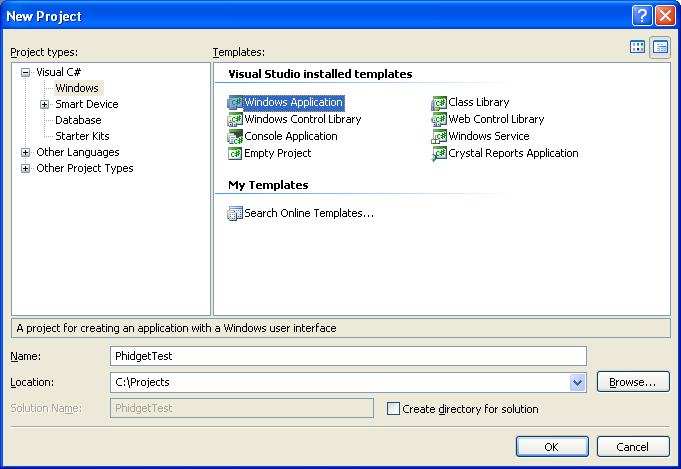
* Generate a new Visual C# Windows Applications project with a descriptive name such as PhidgetTest. | |||
<br/>[[File:CSharp VS2005 New Project.PNG ]] | |||
<br/> | |||
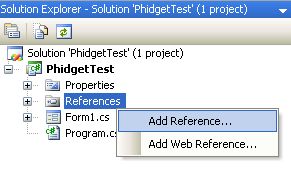
[[ | * Add a reference to the .NET Phidgets library. | ||
<br/>[[File:CSharp VS2005 Add Reference.PNG ]]<br/> | |||
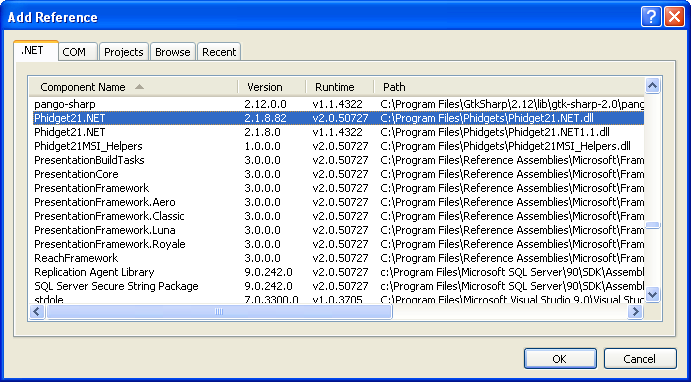
* Under the .NET tab, select <code>Phidget21.NET.dll</code>. | |||
If you used our installer, these files are installed in <code>C:\Program Files\Phidgets</code>, by default. If it does not appear in this list, then you can browse to the Phidget Framework installation directory and add the file. | |||
<br/>[[File:CSharp VS2005 Add Reference 2.PNG ]]<br/><br/> | |||
Then, in your code, you will need to include the Phidget library: | |||
<div style="background-color: #f3f3f3; border-color: #1c9edb; border-width:1px; border-style: dashed;"> | |||
<font size="3"> | <font size="3"> | ||
<source lang=cpp> | |||
using Phidgets; | |||
using Phidgets.Events; | |||
</source> | |||
</font> | </font> | ||
</div> | |||
The project now has access to the Phidget21 function calls and you are ready to begin coding. | |||
</ | |||
The same [[#Follow The Examples|teaching section]] which describes the examples also has further resources for programming your Phidget. | |||
==Mac OS X== | |||
Max/MSP has excellent support on Mac OS X. | |||
[[ | The first step in using C# on Mac is to install the Phidget libraries. Compile and install them as explained on the [[Device List|getting started guide for your device]]. Then, the [[OS - Mac OS X]] page also describes the different Phidget files, their installed locations, and their roles.... | ||
==Follow The Examples== | |||
The | |||
By following the instructions for your operating system and compiler above, you probably now have a working example and want to understand it better so you can change it to do what you want. This teaching section has resources for you to learn from the examples and write your own. | |||
Next, comes our API information. These resources outline the Max/MSP Phidget functions: | |||
{{UsingAPhidgetInCodeGeneral|both of which are available in Max/MSP|[http://www.phidgets.com/documentation/Phidget21.NET.zip C# API]}} | |||
=== | ===Example Flow=== | ||
{{ExamplePseudocode|In C#, you can name these '''event''' functions whatever you like. You will then pass them as function pointers to the Phidget library below in the Main Code section. This hooks them into the actual events when they occur. <br> | |||
For example, | In the example code, the event functions common to all Phidgets are called things like '''AttachHandler()''' and '''DetachHandler()''', etc.<br><br> | ||
The | Some event functions will be specific to each device, like when a tag is read on an RFID board, or when a sensor value changes on an Interface Kit. | ||
Other functions are given in the examples to show you more detail on using your Phidget. For example, '''DeviceInitialize()''' will show what needs to be set up for your Phidget before using it. | |||
|Creating a Phidget software object in C# is specific to the Phidget. For a Phidget Spatial, for example, this would involve creating a <code>Spatial</code> object. The examples show how to do this and other API functions.<br><br> | |||
The object provides device specific methods and properties which are available from the API for your specific Phidget.| | |||
[http://www.phidgets.com/documentation/Phidget21.NET.zip C# API]}} | |||
== | ==Code Snippets== | ||
==Common Problems and Solutions/Workarounds== | ==Common Problems and Solutions/Workarounds== | ||
Here you can put various frequent problems and our recommended solutions. | Here you can put various frequent problems and our recommended solutions. | ||
Revision as of 20:40, 24 January 2012
![]() Max/MSP, developed by Cycling74 is a visual programming language for creating music and media applications.
Max/MSP, developed by Cycling74 is a visual programming language for creating music and media applications.
Introduction
If this is your first time working with a Phidget, we suggest starting with the Getting Started page for your specific device. This can be found in the user guide for your device. That page will walk you through installing drivers and libraries for your operating system, and will then bring you back here to use Max/MSP specifically.
Max/MSP is capable of using the complete Phidget API, including events. We also provide example code in Max/MSP for all Phidget devices.
Max/MSP can be developed with Windows and Mac OS X..{{{5}}}
You can compare Max/MSP with our other supported languages.
Quick Downloads
Just need the Max/MSP drivers, libraries, and examples? Here they are:
API Documentation: Should we include the next 2 links?
- General API (more help on functions common to all Phidgets)
- Device Specific APIs (more help on functions specific to your Phidget)
Max/MSP Library and Example Code:
Libraries and Drivers:
- 32 bit Windows (drivers, with libraries)
- 64 bit Windows (drivers, with libraries)
- General Linux Libraries ( Linux Library Setup Instructions)
- General Mac OSX Libraries ( Mac OS X Library Setup Instructions)
Getting started with Max/MSP
If you are new to writing code for Phidgets, we recommend starting by running, then modifying existing examples. This will allow you to:
- Make sure your libraries are properly linked
- Go from source code to a test application as quickly as possible
- Ensure your Phidget is hooked up properly
Instructions are divided up by operating system. Choose:
Windows(2000/XP/Vista/7)
Libraries
Description
Max/MSP programs on Windows depend on the following files, which the installers above put onto your system:
phidget21.dllcontains the actual Phidgets library, which is used at run-time. If you used our installer, it's already correctly placed inC:\Windows\System32. It can be manually installed - check our Manual Installation instructions.
You will also need one of the following two files, depending on the .NET framework version you are targeting:
Phidget<Device Name>.mxeis the Phidgets library for Max/MSP 4.5 or higher. It is to be placed in the same directory as your.helpfile
Use Our Examples
Please start by downloading the Max/MSP Examples. These examples were written in Visual Studio 2005 and 2008, but Visual Studio 2010 will easily upgrade them.
To run the examples, you first download them from above and unpack them into a folder. To load all projects in Visual Studio, go to File | Open | Project, and open AllExamples/AllExamples.sln or AllExamples/AllExamples_vs2008.sln for Visual Studio 2005 and 2008, respectively.
If you are opening the Phidget examples in Visual Studio 2010, you will need to go through the Visual Studio Conversion Wizard to convert the 2005 or 2008 project.
This will load all of the examples available for C#, and then you can set your main project to be the one that matches your device. If you aren't sure what the software example for your device is called, check the software object listed in the Getting Started guide for your device.
The only thing left to do is to run the examples! Click on Debug -> Start Debugging. Please note that the projects, by default try to find the Phidget21.NET.dll in the C:\Program Files\Phidgets. If you have it installed in another location, please change the path accordingly. If you are receiving an error message regarding that the namespace Phidgets cannot be found, please re-add the reference to Phidget21.NET.dll. Please see the next section for details.
Once you have the C# examples running, we have a teaching section below to help you follow them.
Write Your Own Code
When you are building a project from scratch, or adding Phidget function calls to an existing project, you'll need to configure your compiler / development environment to properly link the Phidget C# libraries. To begin:
- Generate a new Visual C# Windows Applications project with a descriptive name such as PhidgetTest.
- Add a reference to the .NET Phidgets library.
- Under the .NET tab, select
Phidget21.NET.dll.
If you used our installer, these files are installed in C:\Program Files\Phidgets, by default. If it does not appear in this list, then you can browse to the Phidget Framework installation directory and add the file.
Then, in your code, you will need to include the Phidget library:
using Phidgets;
using Phidgets.Events;
The project now has access to the Phidget21 function calls and you are ready to begin coding.
The same teaching section which describes the examples also has further resources for programming your Phidget.
Mac OS X
Max/MSP has excellent support on Mac OS X.
The first step in using C# on Mac is to install the Phidget libraries. Compile and install them as explained on the getting started guide for your device. Then, the OS - Mac OS X page also describes the different Phidget files, their installed locations, and their roles....
Follow The Examples
By following the instructions for your operating system and compiler above, you probably now have a working example and want to understand it better so you can change it to do what you want. This teaching section has resources for you to learn from the examples and write your own.
Next, comes our API information. These resources outline the Max/MSP Phidget functions:
- C# API (This is the complete set of functions you have available for all Phidgets)
- Device Specific APIs - The one for your Phidget can be found in its user guide.
To learn the details behind opening, configuring, using, and closing your Phidget, try the General Phidget Programming page. That page also describes using the Phidget in an event-driven manner and in a traditional manner, both of which are available in Max/MSP.
Example Flow
The Hello World example has this general structure so you can follow along. We also have an in-depth general introduction to writing Phidget code (like open, read data, etc), as well as the C# API for specific syntax:
|
// ----- Event and Other Functions ----- Create any Language-Specific Functions (exception handling) Create General Attach, Detach, and Error Handling Functions:
|
In C#, you can name these event functions whatever you like. You will then pass them as function pointers to the Phidget library below in the Main Code section. This hooks them into the actual events when they occur. | |
|
// ----- Main Code -----
Close Device Delete Device
|
Creating a Phidget software object in C# is specific to the Phidget. For a Phidget Spatial, for example, this would involve creating a |
Code Snippets
Common Problems and Solutions/Workarounds
Here you can put various frequent problems and our recommended solutions.