|
Notice: This page contains information for the legacy Phidget21 Library. Phidget21 is out of support. Bugfixes may be considered on a case by case basis. Phidget21 does not support VINT Phidgets, or new USB Phidgets released after 2020. We maintain a selection of legacy devices for sale that are supported in Phidget21. We recommend that new projects be developed against the Phidget22 Library.
|
Language - Flash AS3
| Flash, developed by Adobe Systems is used to build and deploy dynamic multimedia applications to the Internet. |
Introduction
If this is your first time working with a Phidget, we suggest starting with the Getting Started page for your specific device. This can be found in the user guide for your device. That page will walk you through installing drivers and libraries for your operating system, and will then bring you back here to use Flash ActionScript specifically.
Flash ActionScript is capable of using Phidgets only over the Phidget WebService, and it is unlike the majority of the other programming languages we support where the device can be used without the Phidget WebService. The complete Phidget API, including events are supported. We also provide example code in Flash ActionScript for all Phidget devices.
Flash ActionScript can be developed with Windows and OS X.
Only ActionScript 3 is supported. Interaction with Phidgets is made possible as the library uses web sockets to communicate with Phidgets over the PhidgetWebService.
You can compare Flash ActionScript with our other supported languages.
Quick Downloads
Just need the Flash ActionScript documentation, drivers, libraries, and examples? Here they are:
Documentation
Example Code
Libraries and Drivers
- ActionScript Libraries (same file as Examples above)
- 32-bit Windows Drivers Installer
- 64-bit Windows Drivers Installer
- Windows Driver and Library Files (Zipped)
- OS X Drivers Installer
Getting started with Flash ActionScript
If you are new to writing code for Phidgets, we recommend starting by running, then modifying existing examples. This will allow you to:
- Make sure your libraries are properly linked
- Go from source code to a test application as quickly as possible
- Ensure your Phidget is hooked up properly
Instructions are divided up by operating system. Choose:
Windows (2000/XP/Vista/7)
Description of Library Files
Flash ActionScript on Windows depend on the following files and folders. The installers in the Quick Downloads section put only the phidget21.dll and PhidgetWebservice21.exe into your system. You will need to manually put the com folder into your system.
phidget21.dllcontains the actual Phidget library, which is used at run-time. This needs to be installed on the computer that the Phidget is connected. By default, it is placed inC:\Windows\System32.PhidgetWebservice21.exeallows for controlling Phidgets remotely across the network. This needs to be installed on the computer that the Phidget is connected.comfolder is the Phidget ActionScript library. The computer that is used for Flash development will need this folder. It is to be manually placed in the same directory as your project root.
Unlike the majority of the programming languages we support (where applications can directly connect to the Phidgets), Flash can only connect to the Phidgets over the PhidgetWebService. There are potentially three roles that a computer can act as: host, developer, and an end user. It is possible for a single computer to act as more than one of these roles at the same time:
- Host: The computer that the Phidget is attached to, and can broadcast device information to any computer over the network. The
phidget21.dllandPhidgetWebservice21.exemust be installed on the host. The host must also have the PhidgetWebService started in order for it and other computers to connect to the Phidgets attached to the host. - Developer: The computer that is used to develop Flash applications. This computer needs the
comfolder in the root directory of your project. Thephidget21.dllandPhidgetWebservice21.exeare only needed if the Phidget is directly attached to the computer. - End user: The computer that is used to run the compiled flash application (i.e.,
.swf).Thephidget21.dllandPhidgetWebservice21.exeare only needed if the Phidget is directly connected to the computer. If the computer is used for developing Flash applications, then it will need thecomfolder in the root directory of your project.
Here is a table summarizing what files/folders are needed for each computer role:
| Computer Role | phidget21.dll
|
Phidget21WebService.dll
|
com folder
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Host | |||
| Developer | |||
| End User |
Please see the Phidget WebService page for a high-level introduction to our WebService.
If you do not want to use our installer on Windows, you can download the phidget21.dll and manually install them where you want; refer to our Manual Installation Instructions.
Flash Professional
Adobe Flash professional allows you to develop in ActionScript and control Phidgets over the WebService. We support ActionScript 3.0.
Use Our Examples
This section will assume that the device is plugged into the host computer, and that the development computer has Flash Professional installed.
As the Flash ActionScript library only supports communication with Phidgets through the PhidgetWebService, begin by starting the WebService on the host computer with the default port (5001).
To run the examples on a development computer, download the Flash examples and unpack them into a folder. Here, you will find example programs for all devices. The source file will be named the same as the software object for your device. If you are not sure what the software object for your device is, find your Phidget on our webpage, and then check the API documentation for it.
When you have found your example, open that .fla file in the Adobe Professional Flash environment. The only thing left to do is to run the examples! Click on Control → Test Movie.
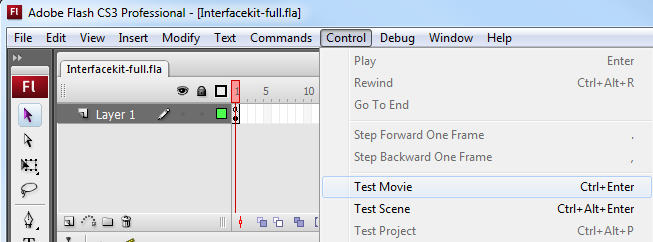
Once you have the Flash ActionScript examples running, we have a teaching section below to help you follow them.
You may also run the examples by navigating to Control → Test Scene. If you are running the examples with Debug → Debug Movie, you will have to change the Flash Global Security Settings in order for the example to run. More information will be provided about the Flash Global Security Settings in the Running Compiled Code section.
Write Your Own Code
When you are building a project from scratch, or adding Phidget function calls to an existing project, you'll need to configure your development environment to properly link the Phidget ActionScript library. To begin:
1. Place a copy of the com folder in the root directory of your Flash project.
2. Generate a new ActionScript 3 Flash file.
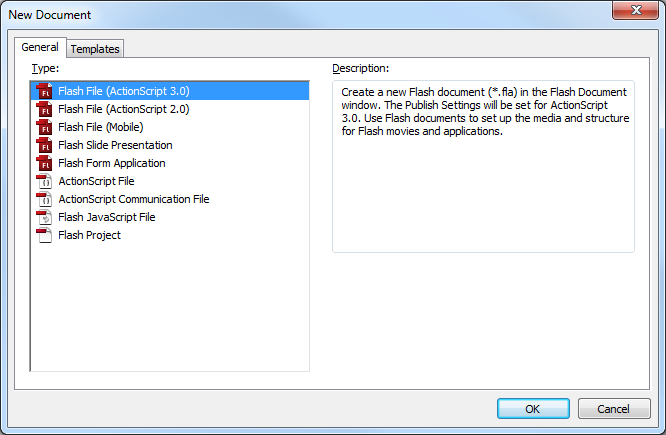
3. Then, in your code, you will need to include the Phidget ActionScript library. Navigate to Window → Actions to bring up the Actions window and enter in the following:
import com.phidgets.*;
import com.phidgets.events.*;
The project now has access to the Phidget function calls and you are ready to begin coding.
The same teaching section which describes the examples also has further resources for programming your Phidget.
Running Compiled Code
Running a compiled .swf application on an end user computer will prompt the Flash player to display a dialog box mentioning that the application will block all communications with the Internet.
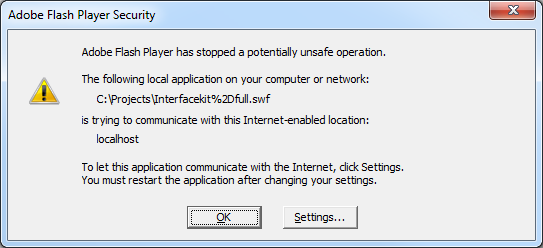
1. Click on the Settings button to bring up the Flash Global Security Settings Manager in your default web browser. Alternatively, you can access the manager with the following URL: http://www.macromedia.com/support/documentation/en/flashplayer/help/settings_manager04a.html.
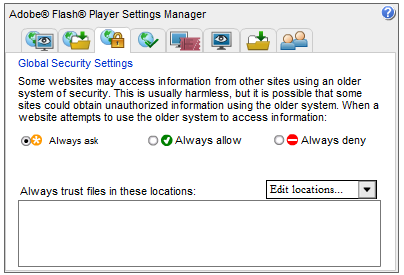
2. In the Global Security Settings tab, navigate to Edit locations ... → Add locations.
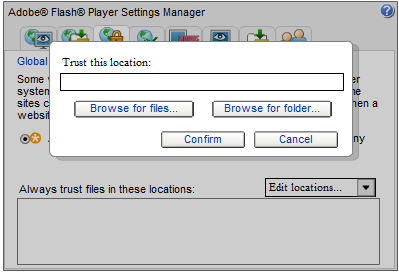
3. Then, browse and add the application or the folder containing the application.
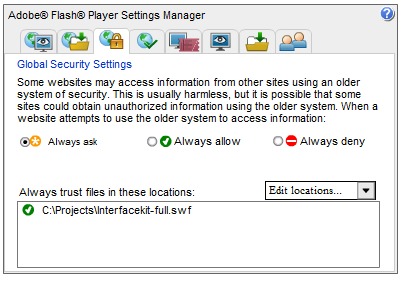
This will allow the Flash Player to allow the application to accept any communication with the Internet.
OS X
Flash ActionScript has excellent support on OS X over the PhidgetWebService.
The first step in using Flash ActionScript on Mac is to install...
Flash Professional
Use Our Examples
Write Your Own Code
Follow the Examples
By following the instructions for your operating system and compiler above, you probably now have a working example and want to understand it better so you can change it to do what you want. This teaching section has resources for you to learn from the examples and write your own.
Your main reference for writing ActionScript code will be our ActionScript API information, with syntax for all of our functions:
- ActionScript API (This is the complete set of functions you have available for all Phidgets)
- Device Specific APIs - The one for your Phidget can be found in its user guide.
To learn the details behind opening, configuring, using, and closing your Phidget, try the General Phidget Programming page. That page also describes using the Phidget in an event-driven manner and in a traditional manner, both of which are available in C/C++.
Code Snippets
Specific calls in ActionScript will differ in syntax from those on the General Phidget Programming page, but the concepts stay the same.
It may help to have the General Phidget Programming page and this section open at the same time, because they parallel each other and you can refer to the ActionScript syntax. However, many additional concepts are covered on the General Phidget Programming page on a high level, such as using multiple Phidgets, handling errors, and different styles of programming. Remember that Actionscript cannot open Phidgets directly - rather, it must use a form of remote open to use the WebService.
Step One: Initialize and Open
The WebService allows a single Phidget to be opened by multiple applications - this is something that cannot be done with the regular, direct interface.
Coding For Your Phidget Before you can use the Phidget, you must include a reference to the library in the action frame (Window | Actions). In Actionscript 3.0:
import com.phidgets.PhidgetInterfaceKit;
import com.phidgets.events.*;
Getting_Started_Flash created: 11/10/10
Page 1
Afterwards, the Phidget object will need to be declared and then initialized. For example, we can
declare a PhidgetInterfaceKit with:
public var phid:com.phidgets.PhidgetInterfaceKit;
phid = new PhidgetInterfaceKit();
The object name for any type of Phidget is listed in the API manual. Every type of Phidget also inherits functionality from the Phidget base class. Connecting to the Phidget The program can try to connect to the Phidget through an open call. Open will continuously try to connect to a Phidget, based on the parameters given, even trying to reconnect if it gets disconnected. This means that simply calling open does not guarantee you can use the Phidget immediately. We can handle this by using event driven programming and tracking the AttachEvents and DetachEvents, or checking the isAttached property.
phid.open("localhost", 5001); The API manual lists all of the available modes that open provides. In Flash, the parameters can be used to open the first Phidget of a type it can find or based on its serial number. One important thing to remember is that when working with Phidgets, a local connection will reserve the device until closed. This means other programs that open the Phidget may end up preventing other instances from retrieving data. The one connection per device limit does not apply when exclusively using the Phidget WebService, and the Actionscript libraries by extension.
Step Two: Wait for Attachment (plugging in) of the Phidget
Step Three: Do Things with the Phidget
Event Driven Programming We recommend the use of event driven programming when working with Phidgets. In Actionscript 3.0, we hook an event handler with the following code:
phid.addEventListener(PhidgetDataEvent.SENSOR_CHANGE, onSensorChange);
function onSensorChange(evt:PhidgetDataEvent):void{
trace (evt.Data); //Echo
}
//Insert your code here
With this method, the code inside onSensorChange will get executed every time the PhidgetInterfaceKit reports a change on one of its analog inputs. The values from the report can be accessed from the PhidgetDataEvent object properties. Some events such as Attach and Detach belong to the base Phidget object and thus are common to all types of Phidgets. Please refer to the API manual for a full list of events and their usage. Getting_Started_Flash created: 11/10/10 Page 2 Working directly with the Phidget Some values can be directly read and set on the Phidget and used as an alternative to event driven programming. Simply use the instance properties or call member functions such as getSensorValue(index: int) or setOutputState(index: int, val: Boolean) for PhidgetInterfaceKits.
Step Four: Close and Delete
More How-To's
The General Phidget Programming page gives more information about:
- Using Multiple Phidgets (or a Phidget other than the Interface Kit)
- Catching exceptions and errors and using logging
- Event catching versus direct polling
- And more....
Working with multiple Phidgets
Multiple Phidgets of the same type can easily be run inside the same program. In our case, it requires
another PhidgetInterfaceKit instance to be defined and initialized. The new instance can then be set
up, opened and used in the same process as the previous one.
If the application needs to distinguish between the devices, open can be called with the serial
number of a specific Phidget.
Flash Security Settings
During debugging or after publishing the project, you may encounter some difficulties with Flash
network security settings either inside or outside of the development environment with Phidgets.
Permissions for your project folder can be added through the settings manager at http://www.
macromedia.com/support/documentation/en/flashplayer/help/settings_manager04a.html, under
“Always trust files in these locations” | “Edit locations...” | “Add location...”.
Other Phidgets
The design given in this document can also be followed for almost all Phidgets. For example, if you
were using a PhidgetRFID instead of an PhidgetInterfacekit, you would declare a RFID object instead
of a InterfaceKit object. The methods and events available would change but they can be accessed in
a similar manner.
Common Problems and Solutions/Workarounds
Problem: My compiled application is experiencing the following security error upon launching: "SecurityError: Error #2010: Local-with-filesystem SWF files are not permitted to use sockets".
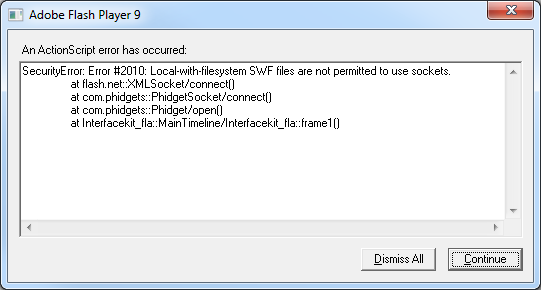
Solution: The symptom of this problem is similar to the one that is discussed in steps 1 - 3 of the Running Compiled Code section. Please see that section for a remedy. To access the Flash Global Security Settings Manager, go to http://www.macromedia.com/support/documentation/en/flashplayer/help/settings_manager04a.html.
