|
Notice: This page contains information for the legacy Phidget21 Library. Phidget21 is out of support. Bugfixes may be considered on a case by case basis. Phidget21 does not support VINT Phidgets, or new USB Phidgets released after 2020. We maintain a selection of legacy devices for sale that are supported in Phidget21. We recommend that new projects be developed against the Phidget22 Library.
|
Use Phidgets Wirelessly with the SBC
The project described here is a basic network control program for an LED plugged in to an SBC.
Practical concepts covered are (click on links to see other projects on that topic):
|

|
As with any of our described projects, Phidgets takes care of the electrical component design. This project demonstrates what the SBC already does naturally from the time it ships. If you want something more powerful and flexible to control Phidgets over a network, you may be interested in these other Application Guides:
- Web Page on the SBC - Controlling Phidgets over the web using CGI
- Web Server on the SBC - Controlling Phidgets over the web using a full self-contained webserver embedded in C code
Time: About an hour
Special Needed Tools: A Phidget SBC, Ethernet and power cords (or Wireless), an LED, and your computer.
You should have already worked through the 1072 - Getting Started page to have set up the network on your SBC and obtained its IP or local link address.
Introduction
When the SBC is powered on and connected to a network, it automatically handles any network requests for the Phidgets attached to it. All sensor and other Phidget data is broadcast over the local network as it changes, and all incoming Phidget control requests to the SBC over the local network are directed to the appropriate Phidgets.
This Webservice system looks something like this:
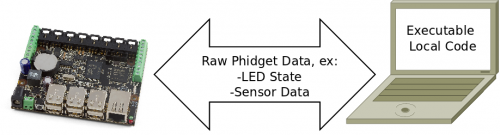
To create these requests to control the attached Phidgets, or to receive incoming sensor data, we write code on the controlling and receiving computer. This application guide simply blinks an LED plugged in to the SBC, and does so over the network.
Phidgets
For this, you will need:
- A 1072 0 - PhidgetSBC2, set up as per the 1072 - Getting Started guide
- This is the SBC that this guide used; others will probably work fine as well
- An LED, such as one of the ones from Phidgets (many part numbers starting at 3600), attached to digital output port 0 (long wire) and ground (short wire)
Code
On your external computer, you can use this code to control the Interface Kit (which is attached to the SBC) over the network:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "phidget21.h"
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
int result;
int outputState;
int i;
CPhidgetInterfaceKitHandle interfaceKit = 0;
CPhidgetInterfaceKit_create(&interfaceKit);
CPhidget_openRemoteIP((CPhidgetHandle)interfaceKit, -1, "phidgetsbc.local", 5001, NULL);
result = CPhidget_waitForAttachment((CPhidgetHandle)interfaceKit, 10000);
if (result) {
printf("No Device!\n");
return 0;
}
outputState = 1;
CPhidgetInterfaceKit_setOutputState(interfaceKit, 0, outputState);
for (i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
if (outputState) { outputState = 0; }
else { outputState = 1; }
CPhidgetInterfaceKit_setOutputState(interfaceKit, 0, outputState);
}
CPhidgetInterfaceKit_setOutputState(interfaceKit, 0, 0);
CPhidget_close((CPhidgetHandle)interfaceKit);
CPhidget_delete((CPhidgetHandle)interfaceKit);
return 0;
}
Some highlights:
- Line 14 is the line that actually opens the Interface Kit over the network.
- Notice that there is no mention of the SBC, or any SBC object.
- The SBC will simply act as a transparent pipe between the Phidget and your computer.
